BIO 5192α4β1 inhibitor CAS# 327613-57-0 |
- Cyclo (-RGDfK)
Catalog No.:BCC3590
CAS No.:161552-03-0
- Cilengitide
Catalog No.:BCC3942
CAS No.:188968-51-6
- TR-14035
Catalog No.:BCC4266
CAS No.:232271-19-1
- BIO 5192
Catalog No.:BCC8002
CAS No.:327613-57-0
- Firategrast
Catalog No.:BCC1575
CAS No.:402567-16-2
- Zaurategrast
Catalog No.:BCC2070
CAS No.:455264-31-0
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 327613-57-0 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 10350459 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C38H46Cl2N6O8S | M.Wt | 817.78 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | Soluble to 100 mM in DMSO and to 50 mM in 1eq. NaOH | ||
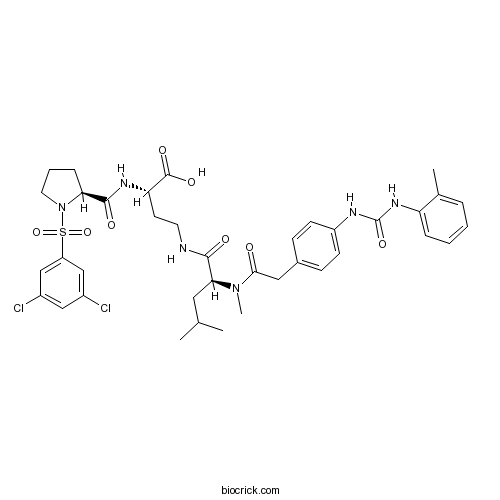
| Chemical Name | (2S)-2-[[(2S)-1-(3,5-dichlorophenyl)sulfonylpyrrolidine-2-carbonyl]amino]-4-[[(2S)-4-methyl-2-[methyl-[2-[4-[(2-methylphenyl)carbamoylamino]phenyl]acetyl]amino]pentanoyl]amino]butanoic acid | ||
| SMILES | CC1=CC=CC=C1NC(=O)NC2=CC=C(C=C2)CC(=O)N(C)C(CC(C)C)C(=O)NCCC(C(=O)O)NC(=O)C3CCCN3S(=O)(=O)C4=CC(=CC(=C4)Cl)Cl | ||
| Standard InChIKey | MNQBPRHHZPXCKZ-ZDCRTTOTSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C38H46Cl2N6O8S/c1-23(2)18-33(45(4)34(47)19-25-11-13-28(14-12-25)42-38(52)44-30-9-6-5-8-24(30)3)35(48)41-16-15-31(37(50)51)43-36(49)32-10-7-17-46(32)55(53,54)29-21-26(39)20-27(40)22-29/h5-6,8-9,11-14,20-23,31-33H,7,10,15-19H2,1-4H3,(H,41,48)(H,43,49)(H,50,51)(H2,42,44,52)/t31-,32-,33-/m0/s1 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Highly selective and potent inhibitor of integrin α4β1 (Very Late Antigen-4; VLA-4) (Kd < 10 pM). Selectively binds α4β1 over a range of other integrins (IC50 values are 1.8, 138, 1053, > 500 and > 10,000 nM for α4β1, α9β1, α2β1, α4β7 and αIIbβ3, respectively). Induces a 30-fold increase in mobilization of murine hematopoietic stem and progenitor cells; displays a 3-fold additive effect with AMD 3100. |

BIO 5192 Dilution Calculator

BIO 5192 Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 1.2228 mL | 6.1141 mL | 12.2282 mL | 24.4565 mL | 30.5706 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.2446 mL | 1.2228 mL | 2.4456 mL | 4.8913 mL | 6.1141 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.1223 mL | 0.6114 mL | 1.2228 mL | 2.4456 mL | 3.0571 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0245 mL | 0.1223 mL | 0.2446 mL | 0.4891 mL | 0.6114 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0122 mL | 0.0611 mL | 0.1223 mL | 0.2446 mL | 0.3057 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
BIO5192 is a small molecule inhibitor of integrin α4β1 with an IC50 value of 1.8 ± 0.7 nM [1].
Integrin α4β1 is important in inflammatory processes. In the inflammatory processes, α4β1 regulates the migration of lymphocytes into inflamed tissues [1].
In assays using cells expressing α4β7, α9β1, α2β1, and αIIbβ3, BIO5192 showed high selectivity for α4β1. The affinity of BIO5192 for α4β1 was 250- to 1000-fold higher than for α4β7 that shared many ligands the same as α4β1. BIO5192 bound even less tightly to α2β1 and αIIbβ3. A significant but low level (KD=140 nM) of binding was seen on α9β1 in buffer containing 1 mM Mn2+ [1].
After 24 h of BIO5192 treatment, the lymphocyte count rose about 1.5-fold. Half as many cells as when TA-2 was given were released into the circulation following the treatment with BIO5192. Data showed that BIO5192 remained bound to 100% of the α4β1 receptors for 24 h and 50% for 48 h. Rats treated with BIO5192 at 30 mg/kg, s.c. showed a 1- to 2-day shift when dosed q.d. and a 3-day delay in the onset of disease EAE when dosed b.i.d. compared with the control groups. The delay in the onset of EAE in the BIO5192-treated group was consistent with the finding that bound BIO5192 would occupy α4β1 long beyond the point at which the BIO5192 was no longer detected in blood [1].
Reference:
[1]. Leone DR, Giza K, Gill A, et al. An assessment of the mechanistic differences between two integrin α4β1 inhibitors, the monoclonal antibody TA-2 and the small molecule BIO5192, in rat experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis[J]. Journal of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics, 2003, 305(3): 1150-1162.
- Macrocarpal L
Catalog No.:BCN5248
CAS No.:327601-97-8
- Phorbol 13-acetate
Catalog No.:BCN7231
CAS No.:32752-29-7
- Heliosupine
Catalog No.:BCN1980
CAS No.:32728-78-2
- tcY-NH2
Catalog No.:BCC5770
CAS No.:327177-34-4
- Cyclohexanecarboxylic acid
Catalog No.:BCN3443
CAS No.:98-89-5
- VU 0285683
Catalog No.:BCC6154
CAS No.:327056-22-4
- TDZD-8
Catalog No.:BCC4258
CAS No.:327036-89-5
- TCS-PIM-1-4a
Catalog No.:BCC5461
CAS No.:327033-36-3
- Chlorogenic acid
Catalog No.:BCN5906
CAS No.:327-97-9
- H-Nle-OH
Catalog No.:BCC3295
CAS No.:327-57-1
- MHY1485
Catalog No.:BCC6404
CAS No.:326914-06-1
- Shz 1
Catalog No.:BCC6334
CAS No.:326886-05-9
- Macrocarpal O
Catalog No.:BCN7371
CAS No.:327622-65-1
- Protopanaxatriol
Catalog No.:BCC9245
CAS No.:32773-56-1
- Labetalol HCl
Catalog No.:BCC5489
CAS No.:32780-64-6
- Panaxatriol
Catalog No.:BCN1081
CAS No.:32791-84-7
- Nomifensine
Catalog No.:BCC7226
CAS No.:32795-47-4
- H-D-Leu-OH
Catalog No.:BCC2975
CAS No.:328-38-1
- Ceranib 1
Catalog No.:BCC6186
CAS No.:328076-61-5
- Phortress
Catalog No.:BCC3901
CAS No.:328087-38-3
- Coniferyl alcohol
Catalog No.:BCN4651
CAS No.:32811-40-8
- (H-Cys-OMe)2.2HCl
Catalog No.:BCC2916
CAS No.:32854-09-4
- Lannaconitine
Catalog No.:BCN2504
CAS No.:32854-75-4
- GlyH-101
Catalog No.:BCC4104
CAS No.:328541-79-3
Differential effects of treatment with a small-molecule VLA-4 antagonist before and after onset of relapsing EAE.[Pubmed:12933585]
Blood. 2003 Dec 15;102(13):4464-71.
Interaction of very late antigen-4 (VLA-4) with its ligand vascular cell adhesion molecule-1 (VCAM-1) is required for central nervous system (CNS) migration of encephalitogenic T cells in relapsing experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis (R-EAE). Anti-VLA-4 monoclonal antibody (mAb) treatment prior to EAE onset inhibits disease induction; however, treatment initiated after the appearance of clinical symptoms increases relapse rates, augments Th1 responses, and enhances epitope spreading perhaps due to the activation of costimulatory signals. To negate the potential costimulatory activity of intact anti-VLA-4, we examined the ability of BIO 5192, a small-molecule VLA-4 antagonist, to regulate active proteolipid protein 139-151 (PLP139-151)-induced R-EAE. BIO 5192 administered one week after peptide priming (ie, before clinical disease onset) delayed the clinical disease onset but led to severe disease exacerbation upon treatment removal. BIO 5192 treatment initiated during disease remission moderately enhanced clinical disease while mice were on treatment and also resulted in posttreatment exacerbation. Interestingly, BIO 5192 treatment begun at the peak of acute disease accelerated entrance into disease remission and inhibited relapses, but treatment removal again exacerbated disease. Enhanced disease was caused by the release of encephalitogenic cells from the periphery and the rapid accumulation of T cells in the CNS. Collectively, these results further demonstrate the complexity of VLA-4/VCAM interactions, particularly in a relapsing-remitting autoimmune disease.
BIO5192, a small molecule inhibitor of VLA-4, mobilizes hematopoietic stem and progenitor cells.[Pubmed:19571319]
Blood. 2009 Aug 13;114(7):1340-3.
Here we show that interruption of the VCAM-1/VLA-4 axis with a small molecule inhibitor of VLA-4, BIO5192, results in a 30-fold increase in mobilization of murine hematopoietic stem and progenitors (HSPCs) over basal levels. An additive affect on HSPC mobilization (3-fold) was observed when plerixafor (AMD3100), a small molecule inhibitor of the CXCR-4/SDF-1 axis, was combined with BIO5192. Furthermore, the combination of granulocyte colony-stimulating factor (G-CSF), BIO5192, and plerixafor enhanced mobilization by 17-fold compared with G-CSF alone. HSPCs mobilized by BIO5192 or the combination of BIO5192 and plerixafor mobilized long-term repopulating cells, which successfully engraft and expand in a multilineage fashion in secondary transplantation recipients. Splenectomy resulted in a dramatic enhancement of G-CSF-induced mobilization while decreasing both plerixafor- and BIO5192-induced mobilization of HSPCs. These data provide evidence for the utility of small molecule inhibitors of VLA-4 either alone or in combination with G-CSF or AMD3100 for mobilization of hematopoietic stem and progenitor cells.
A chemical approach to stem-cell biology and regenerative medicine.[Pubmed:18480815]
Nature. 2008 May 15;453(7193):338-44.
An improved understanding of stem-cell and regenerative biology, as well as a better control of stem-cell fate, is likely to produce treatments for many devastating diseases and injuries. Chemical approaches are starting to have an increasingly important role in this young field. Attention has focused on chemical approaches that allow the precise manipulation of cells in vitro to obtain homogeneous cell types for cell-based therapies. Another promising approach is the development of conventional chemical and biological therapeutics to stimulate endogenous cells to regenerate. Such therapeutics can act on target cells or their niches in vivo to promote cell survival, proliferation, differentiation, reprogramming and homing.
An assessment of the mechanistic differences between two integrin alpha 4 beta 1 inhibitors, the monoclonal antibody TA-2 and the small molecule BIO5192, in rat experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis.[Pubmed:12626659]
J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2003 Jun;305(3):1150-62.
Integrin alpha 4 beta 1 plays an important role in inflammatory processes by regulating the migration of lymphocytes into inflamed tissues. Here we evaluated the biochemical, pharmacological, and pharmacodynamic properties and efficacy in experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis (EAE), a model of multiple sclerosis, of two types of alpha 4 beta 1 inhibitors, the anti-rat alpha 4 monoclonal antibody TA-2 and the small molecule inhibitor BIO5192 [2(S)-[[1-(3,5-dichloro-benzenesulfonyl)-pyrrolidine-2(S)-carbonyl]-amino]-4-[4-m ethyl-2(S)-(methyl-[2-[4-(3-o-tolyl-ureido)-phenyl]-acetyl]-amino)-pentanoylamino ]-butyric acid]. TA-2 has been extensively studied in rats and provides a benchmark for assessing function. BIO5192 is a highly selective and potent (KD of <10 pM) inhibitor of alpha 4 beta 1. Dosing regimens were identified for both inhibitors, which provided full receptor occupancy during the duration of the study. Both inhibitors induced leukocytosis, an effect that was used as a pharmacodynamic marker of activity, and both were efficacious in the EAE model. Treatment with TA-2 caused a decrease in alpha 4 integrin expression on the cell surface, which resulted from internalization of alpha 4 integrin/TA-2 complexes. In contrast, BIO5192 did not modulate cell surface alpha 4 beta 1. Our results with BIO5192 indicate that alpha 4 beta 7 does not play a role in this model and that blockade of alpha 4 beta 1/ligand interactions without down-modulation is sufficient for efficacy in rat EAE. BIO5192 is highly selective and binds with high affinity to alpha 4 beta 1 from four of four species tested. These studies demonstrate that BIO5192, a novel, potent, and selective inhibitor of alpha 4 beta 1 integrin, will be a valuable reagent for assessing alpha 4 beta 1 biology and may provide a new therapeutic for treatment of human inflammatory diseases.


