Cyclo (-RGDfK)Inhibitor of αvβ3 integrin CAS# 161552-03-0 |
- MNS
Catalog No.:BCC3943
CAS No.:1485-00-3
- BIO 1211
Catalog No.:BCC3945
CAS No.:187735-94-0
- Cilengitide
Catalog No.:BCC3942
CAS No.:188968-51-6
- A 205804
Catalog No.:BCC3944
CAS No.:251992-66-2
- Firategrast
Catalog No.:BCC1575
CAS No.:402567-16-2
- Zaurategrast
Catalog No.:BCC2070
CAS No.:455264-31-0
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 161552-03-0 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 10196873 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C27H41N9O7 | M.Wt | 603.7 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | DMSO : 125 mg/mL (207.07 mM; Need ultrasonic) H2O : 50 mg/mL (82.83 mM; Need ultrasonic) | ||
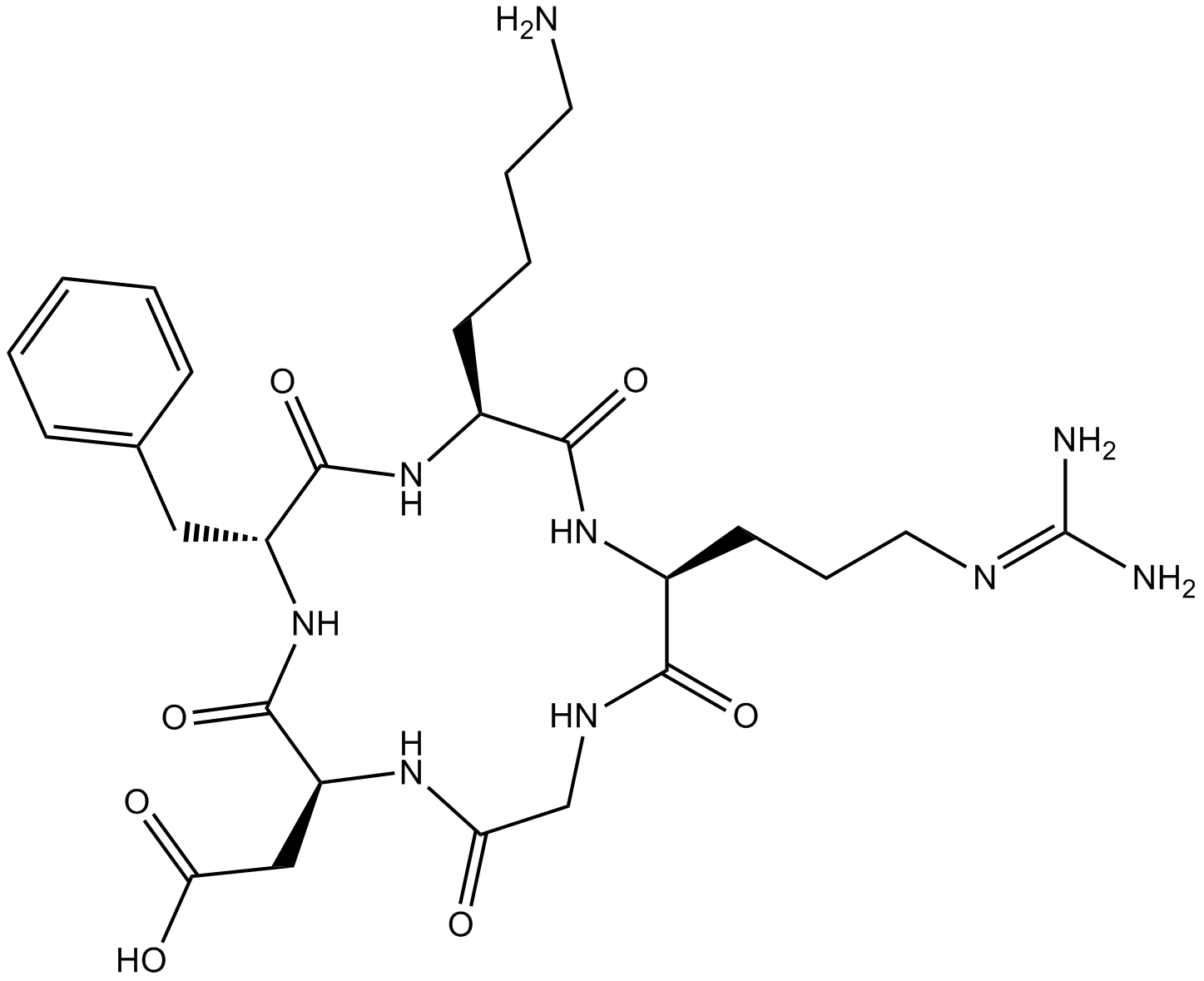
| Sequence | Cyclo(-Arg-Gly-Asp-D-Phe-Lys) | ||
| Chemical Name | 2-[(2S,5R,8S,11S)-8-(4-aminobutyl)-5-benzyl-11-[3-(diaminomethylideneamino)propyl]-3,6,9,12,15-pentaoxo-1,4,7,10,13-pentazacyclopentadec-2-yl]acetic acid | ||
| SMILES | C1C(=O)NC(C(=O)NC(C(=O)NC(C(=O)NC(C(=O)N1)CCCN=C(N)N)CCCCN)CC2=CC=CC=C2)CC(=O)O | ||
| Standard InChIKey | NVHPXYIRNJFKTE-HAGHYFMRSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C27H41N9O7/c28-11-5-4-9-18-24(41)34-17(10-6-12-31-27(29)30)23(40)32-15-21(37)33-20(14-22(38)39)26(43)36-19(25(42)35-18)13-16-7-2-1-3-8-16/h1-3,7-8,17-20H,4-6,9-15,28H2,(H,32,40)(H,33,37)(H,34,41)(H,35,42)(H,36,43)(H,38,39)(H4,29,30,31)/t17-,18-,19+,20-/m0/s1 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Cyclo (-RGDfK) is a potent and selective inhibitor of the αvβ3 integrin. | |||||
| Targets | Integrin | |||||

Cyclo (-RGDfK) Dilution Calculator

Cyclo (-RGDfK) Molarity Calculator

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
In one study where this peptide was labeled with 125I, it was found to bind specifically and with high affinity to αvβ3 receptors on neovascular blood vessel sections of different major human cancers. The integrin alpha(IIb)beta(3)-specific cyclic hexapeptide contains an Arg-Gly-Asp (RGD) sequence.
- Fmoc-Alaninol
Catalog No.:BCC2729
CAS No.:161529-13-1
- Simiarenol
Catalog No.:BCN1714
CAS No.:1615-94-7
- 4-Chlorocinnamic acid
Catalog No.:BCN5032
CAS No.:1615-02-7
- 7-NINA
Catalog No.:BCC5674
CAS No.:161467-34-1
- SIN-1 chloride
Catalog No.:BCC5670
CAS No.:16142-27-1
- ABT
Catalog No.:BCC7998
CAS No.:1614-12-6
- HTH-01-015
Catalog No.:BCC4010
CAS No.:1613724-42-7
- SGC-CBP30
Catalog No.:BCC2419
CAS No.:1613695-14-9
- Fmoc-Chg-OH
Catalog No.:BCC3164
CAS No.:161321-36-4
- 1-O-Acetyl-6-O-isobutyrylbritannilactone
Catalog No.:BCN7795
CAS No.:1613152-34-3
- SR-9243
Catalog No.:BCC3983
CAS No.:1613028-81-1
- H-Orn(Z)-OtBu.HCl
Catalog No.:BCC2677
CAS No.:161234-80-6
- Ro 48-8071
Catalog No.:BCC5545
CAS No.:161582-11-2
- (S)-N-Glycidylphthalimide
Catalog No.:BCN3815
CAS No.:161596-47-0
- 2'',3''-Di-O-acetyl-5''-deoxy-5-fuluro-D-cytidine
Catalog No.:BCN1545
CAS No.:161599-46-8
- beta-Amyrin acetate
Catalog No.:BCN1715
CAS No.:1616-93-9
- ZK 200775
Catalog No.:BCC7339
CAS No.:161605-73-8
- Epimedonin B
Catalog No.:BCN7889
CAS No.:1616061-69-8
- Hispidanin B
Catalog No.:BCN7394
CAS No.:1616080-84-2
- VRT-1353385
Catalog No.:BCC6433
CAS No.:1616113-45-1
- EPZ015666
Catalog No.:BCC5653
CAS No.:1616391-65-1
- Erythrinin D
Catalog No.:BCN6858
CAS No.:1616592-59-6
- 1,5-difluoro-3-methyl-2-nitrobenzene
Catalog No.:BCN6404
CAS No.:1616526-80-7
- Erythrinin G
Catalog No.:BCN6857
CAS No.:1616592-61-0
(18)F-Fluoroglucosylation of peptides, exemplified on cyclo(RGDfK).[Pubmed:19350236]
Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2009 Sep;36(9):1469-74.
PURPOSE: Oxime formation between an aminooxy-functionalized peptide and an (18)F-labelled aldehyde has recently been introduced as a powerful method for the rapid one-step chemoselective synthesis of radiofluorinated peptides. MATERIALS AND METHODS: Here, the potential of using routinely produced and thus readily available [(18)F]fluorodeoxyglucose ([(18)F]FDG) as the aldehydic prosthetic group was investigated using an aminooxyacetyl-conjugated cyclic RGD peptide (cyclo(RGDfK(Aoa-(Boc)) as a model peptide. RESULTS: The use of [(18)F]FDG from routine production ([(18)F]FDGTUM) containing an excess of D: -glucose did not allow the radiosynthesis of [(18)F]FDG-RGD in activities >37 MBq in reasonable yield, rendering the direct use of clinical grade [(18)F]FDG for the routine clinical synthesis of (18)F-labelled peptides impossible. Using no-carrier-added (n.c.a.) [(18)F]FDG obtained via HPLC separation of [(18)F]FDGTUM from excess glucose, however, afforded [(18)F]FDG-RGD in yields of 56-93% (decay corrected) and activities up to 37 MBq. Suitable reaction conditions were 20 min at 120 degrees C and pH 2.5, and a peptide concentration of 5 mM. In a preliminary in vivo biodistribution study in M21 melanoma-bearing nude mice, [(18)F]FDG-RGD showed increased tumour accumulation compared to the "gold standard" [(18)F]galacto-RGD (2.18 vs 1.49 %iD/g, respectively, at 120 min after injection), but also slightly increased uptake in non-target organs, leading to comparable tumour/organ ratios for both compounds. CONCLUSION: These data demonstrate that chemoselective (18)F-labelling of aminooxy-functionalized peptides using n.c.a. [(18)F]FDG represents a radiofluorination/glycosylation strategy that allows preparation of (18)F-labelled peptides in high yield with suitable pharmacokinetics. As soon as the necessary n.c.a. preparation of [(18)F]FDG prior to reaction with the Aoa-peptide can be implemented in a fully automated [(18)F]FDG-synthesis, [(18)F]fluoroglucosylation of peptides may represent a promising alternative to currently used chemoselective one-step (18)F-labelling protocols.
Molecular targeting radiotherapy with cyclo-RGDFK(C) peptides conjugated to 177Lu-labeled gold nanoparticles in tumor-bearing mice.[Pubmed:24730235]
J Biomed Nanotechnol. 2014 Mar;10(3):393-404.
Peptides based on the cyclic Arg-Gly-Asp (RGD) sequence have been designed to antagonize the function of alpha(v)beta(3) integrin, thereby inhibiting angiogenesis. The conjugation of RGD peptides to radiolabeled gold nanoparticles (AuNP) produces biocompatible and stable multimeric systems with target-specific molecular recognition. The aim of this research was to evaluate the therapeutic response of 177Lu-AuNP-RGD in athymic mice bearing alpha(v)beta(3)-integrin-positive C6 gliomas and compare it with that of 177Lu-AuNP or 177Lu-RGD. The radiation absorbed dose, metabolic activity (SUV, [18F]fluor-deoxy-glucose-microPET/CT), histological characteristics and VEGF gene expression (by real-time polymerase chain reaction) in tumor tissues following treatment with 177Lu-AuNP-RGD, 177Lu-AuNP or 177Lu-RGD were assessed. Of the radiopharmaceuticals evaluated, 1177Lu-AuNP-RGD delivered the highest tumor radiation absorbed dose (63.8 +/- 7.9 Gy). These results correlated with the observed therapeutic response, in which 177Lu-AuNP-RGD significantly (p < 0.05) induced less tumor progression, less tumor metabolic activity, fewer intratumoral vessels and less VEGF gene expression than the other radiopharmaceuticals, a consequence of high tumor retention and a combination of molecular targeting therapy (multimeric RGD system) and radiotherapy (177Lu). There was a low uptake in non-target organs and no induction of renal toxicity. 177Lu-labeled gold nanoparticles conjugated to cyclo-RGDfK(C) demonstrate properties suitable for use as an agent for molecular targeting radiotherapy.


