Bay 11-7821(BAY 11-7082)IKK/NF-κB/TNFα inhibitor CAS# 19542-67-7 |
- QNZ (EVP4593)
Catalog No.:BCC2249
CAS No.:545380-34-5
- Andrographolide
Catalog No.:BCN5735
CAS No.:5508-58-7
- Tanshinone IIA
Catalog No.:BCN5763
CAS No.:568-72-9
- JSH-23
Catalog No.:BCC4610
CAS No.:749886-87-1
- SC75741
Catalog No.:BCC5448
CAS No.:913822-46-5
- IMD 0354
Catalog No.:BCC4556
CAS No.:978-62-1
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 19542-67-7 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 5353431 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C10H9NO2S | M.Wt | 207.25 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Synonyms | Bay 11-7082 | ||
| Solubility | DMSO : ≥ 100 mg/mL (482.51 mM) *"≥" means soluble, but saturation unknown. | ||
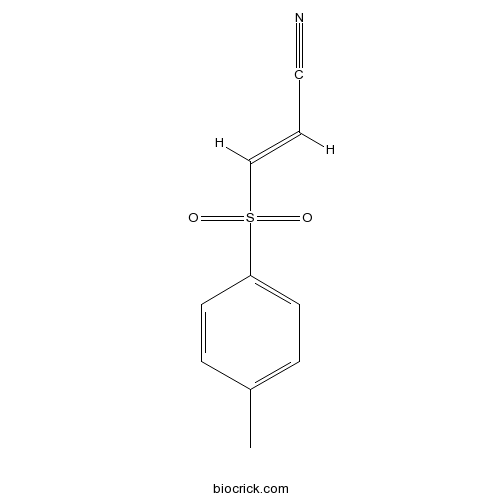
| Chemical Name | (E)-3-(4-methylphenyl)sulfonylprop-2-enenitrile | ||
| SMILES | CC1=CC=C(C=C1)S(=O)(=O)C=CC#N | ||
| Standard InChIKey | DOEWDSDBFRHVAP-KRXBUXKQSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C10H9NO2S/c1-9-3-5-10(6-4-9)14(12,13)8-2-7-11/h2-6,8H,1H3/b8-2+ | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | E2 ubiquitin (Ub) conjugating enzyme inhibitor. Inhibits the conjugation of Ub to a range of E2 enzymes. Inhibits E2 enzyme mediated IκBα phosphorylation and indirectly decreases NF-κb activity. Also reversibly activates MAPK signaling. Induces apoptosis of leukemic T cell and B-cell lymphoma cell lines. |

Bay 11-7821(BAY 11-7082) Dilution Calculator

Bay 11-7821(BAY 11-7082) Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 4.8251 mL | 24.1255 mL | 48.2509 mL | 96.5018 mL | 120.6273 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.965 mL | 4.8251 mL | 9.6502 mL | 19.3004 mL | 24.1255 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.4825 mL | 2.4125 mL | 4.8251 mL | 9.6502 mL | 12.0627 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0965 mL | 0.4825 mL | 0.965 mL | 1.93 mL | 2.4125 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0483 mL | 0.2413 mL | 0.4825 mL | 0.965 mL | 1.2063 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
Bay 11-7821(Bay 11-7082) is an inhibitor of IKK with IC50 value of 10μM [1].
Bay 11-7821 inhibits the TNFα-induced phosphorylation of IκB-α, results in an inhibition of NF-κB. This subsequently causes the inhibition of the TNFα-induced surface expression of E-selectin, VCAM-1, and ICAM-1. It is reported that, Bay 11-7821 does not inhibit entire TNFα-induced phosphorylation but selectively inhibits phosphorylation of IκB-α [1].
Experiments show that Bay 11-7821 is highly toxic at concentrations of effective IKK inhibition. It can induce cell necrosis in MM cells. Additionally, Bay 11-7821 is proved to have an anti-inflammatory ability via inducing death of B-cell lymphoma and leukaemic T-cell. It is also reported to inhibit the NALP3 inflammasome in macrophages [2, 3].
References:
[1] Pierce JW, Schoenleber R, Jesmok G, Best J, Moore SA, Collins T, Gerritsen ME. Novel inhibitors of cytokine-induced IkappaBalpha phosphorylation and endothelial cell adhesion molecule expression show anti-inflammatory effects in vivo. J Biol Chem. 1997 Aug 22;272(34):21096-103.
[2] Rauert-Wunderlich H1, Siegmund D, Maier E, Giner T, Bargou RC, Wajant H, Stühmer T. The IKK inhibitor Bay 11-7082 induces cell death independent from inhibition of activation of NFκB transcription factors. PLoS One. 2013;8(3):e59292.
[3] Strickson S1, Campbell DG, Emmerich CH, Knebel A, Plater L, Ritorto MS, Shpiro N, Cohen P. The anti-inflammatory drug BAY 11-7082 suppresses the MyD88-dependent signalling network by targeting the ubiquitin system. Biochem J. 2013 May 1;451(3):427-37.
- JAK2 Inhibitor V, Z3
Catalog No.:BCC1667
CAS No.:195371-52-9
- Alphitolic acid
Catalog No.:BCN1189
CAS No.:19533-92-7
- Galantamine hydrobromide
Catalog No.:BCN2869
CAS No.:1953-04-4
- Tiopronin (Thiola)
Catalog No.:BCC3870
CAS No.:1953-02-2
- GLP-2 (rat)
Catalog No.:BCC5892
CAS No.:195262-56-7
- N-(3-Methoxybenzyl)oleamide
Catalog No.:BCC6942
CAS No.:883715-21-7
- 4-DAMP
Catalog No.:BCC6661
CAS No.:1952-15-4
- Dihydrosenkyunolide C
Catalog No.:BCC8942
CAS No.:195142-72-4
- 4-Hydroxycinnamamide
Catalog No.:BCN1188
CAS No.:194940-15-3
- Daphnetin 7-methyl ether
Catalog No.:BCN2734
CAS No.:19492-03-6
- ACPT-I
Catalog No.:BCC5702
CAS No.:194918-76-8
- Ginsenoside Rs3
Catalog No.:BCN3716
CAS No.:194861-70-6
- Wortmannin
Catalog No.:BCC3874
CAS No.:19545-26-7
- Chiirirhamnin
Catalog No.:BCN3179
CAS No.:195450-50-1
- AP1903
Catalog No.:BCC5361
CAS No.:195514-63-7
- Piromidic Acid
Catalog No.:BCC3840
CAS No.:19562-30-2
- Methyl 4-O-feruloylquinate
Catalog No.:BCC9041
CAS No.:195723-10-5
- 2,16,19-Kauranetriol 2-O-beta-D-allopyranoside
Catalog No.:BCN1510
CAS No.:195723-38-7
- (+-)-Byakangelicin
Catalog No.:BCN5000
CAS No.:19573-01-4
- Atrasentan hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC1380
CAS No.:195733-43-8
- 2,6,16-Kauranetriol 2-O-beta-D-allopyranoside
Catalog No.:BCN1509
CAS No.:195735-16-1
- HTMT dimaleate
Catalog No.:BCC6736
CAS No.:195867-54-0
- (R)-Nepicastat HCl
Catalog No.:BCC4315
CAS No.:195881-94-8
- 25S-Inokosterone
Catalog No.:BCN3873
CAS No.:19595-18-7
BAY 11-7082 ameliorates diabetic nephropathy by attenuating hyperglycemia-mediated oxidative stress and renal inflammation via NF-kappaB pathway.[Pubmed:25704036]
Environ Toxicol Pharmacol. 2015 Mar;39(2):690-9.
Diabetic nephropathy is a serious microvascular complication for patients associated with diabetes mellitus. Recent studies have suggested that NF-kappaB is the main transcription factor for the inflammatory response mediated progression of diabetic nephropathy. Hence, the present study is hypothesized to explore the renoprotective nature of BAY 11-7082 an IkappaB phosphorylation inhibitor on Streptozotocin (STZ) induced diabetic nephropathy in Sprague-Dawley (SD) rats. Male SD rats were divided into five groups, group I sham control, group II drug control, group III diabetic control (STZ 50mg/kg), group IV and V are test drug groups to which a single dose of STZ 50mg/kg was injected initially and later received BAY 11-7082 1mg/kg and 3mg/kg, respectively from 5th to 8th week. Eight weeks after STZ injection, diabetic rats exhibited significant renal dysfunction, as evidenced by reduced creatinine clearance, increased blood glucose, urea nitrogen and creatinine, which were reversed to near normal by BAY 11-7082. BAY 11-7082 treated rats showed significant improvement in the decreased enzymatic antioxidant SOD, non-enzymatic antioxidant GSH levels, and elevated lipid peroxidation and nitric oxide levels as observed in the diabetic rats. BAY 11-7082 treatment was found to significantly recover kidney histological architecture in the diabetic rats. Altered levels of inflammatory cytokines like TNF-alpha, IL-1beta, IL-6 and nuclear transcriptional factor subunit NF-kappaB p65 were reverted to the normal level upon treatment with BAY 11-7082. Our results suggest that by limiting the activation of NF-kappaB, thereby reducing the expression of inflammatory cytokines and by inhibiting the oxidative damage BAY 11-7082 protect the rats against diabetic nephropathy.
Nuclear factor kappaB inhibitor BAY 11-7082 suppresses oxidative stress induced by endothelin-1 (ET-1) in rat kidney.[Pubmed:27259223]
Postepy Hig Med Dosw (Online). 2015 Dec 31;69:1512-8.
AIM: The aim of the study was to evaluate the effect of BAY 11-7082, an NF-kappaB inhibitor, on basal and ET-1-induced production of reactive oxygen species (ROS), TNF-alpha and p65 protein in rat kidney. MATERIAL/METHODS: The experimental animals were divided into five groups (n=7) receiving: 1) saline (control); 2 and 3) ET-1 in a dose of 3 mug/kg body weight (b.w.) or 12.5 mug/kg b.w.; 4) BAY 11-7082 (10 mg/kg b.w.); 5) BAY 11-7082 (10 mg/kg b.w.) and ET-1 (12.5 mug/kg b.w.), respectively. In kidney homogenates the concentration of thiobarbituric acid reactive substances (TBARS), H2O2, TNF-alpha, p65 protein and GSH/GSSG ratio were determined. RESULTS: ET-1 resulted in a dose-dependent increase in TBARS and hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) levels, and a decrease in GSH/GSSG ratio when compared to the controls. BAY 11-7082 administered 1 h before ET-1 administration at a dose of 12.5 mug/kg resulted in a decrease (P<0.001) in TBARS and H2O2 levels and an increase (P<0.001) in GSH/GSSG ratio compared to the ET-1 groups. The level of TNF-alpha was increased (P<0.001) in the presence of ET-1, while BAY 11-7082 reduced the TNF-alpha level (P<0.001). The rats receiving BAY 11-7082 showed a decrease in NF-kappaB p65 protein level in the nuclear fraction and an increase in the cytoplasmic fraction. CONCLUSIONS: The results suggest that BAY 11-7082 plays a protective role against ET-1 induced oxidative stress in kidney tissue. These actions of BAY 11-7082 may result from reduced activity of NF-kappaB signaling pathways. Inhibition of the NF-kappaB pathway may be a promising strategy for preventing the progression of kidney damage.
Pharmacological targeting of glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase in human erythrocytes by Bay 11-7082, parthenolide and dimethyl fumarate.[Pubmed:27353740]
Sci Rep. 2016 Jun 29;6:28754.
In mature erythrocytes, glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase (G6PDH) and 6-phosphogluconate dehydrogenase (6PGDH) yield NADPH, a crucial cofactor of the enzyme glutathione reductase (GR) converting glutathione disulfide (GSSG) into its reduced state (GSH). GSH is essential for detoxification processes in and survival of erythrocytes. We explored whether the anti-inflammatory compounds Bay 11-7082, parthenolide and dimethyl fumarate (DMF) were able to completely deplete a common target (GSH), and to impair the function of upstream enzymes of GSH recycling and replenishment. Treatment of erythrocytes with Bay 11-7082, parthenolide or DMF led to concentration-dependent eryptosis resulting from complete depletion of GSH. GSH depletion was due to strong inhibition of G6PDH activity. Bay 11-7082 and DMF, but not parthenolide, were able to inhibit the GR activity. This approach "Inhibitors, Detection of their common target that is completely depleted or inactivated when pharmacologically relevant concentrations of each single inhibitor are applied, Subsequent functional analysis of upstream enzymes for this target" (IDS), can be applied to a broad range of inhibitors and cell types according to the selected target. The specific G6PDH inhibitory effect of these compounds may be exploited for the treatment of human diseases with high NADPH and GSH consumption rates, including malaria, trypanosomiasis, cancer or obesity.
BAY 11-7082 inhibits the NF-kappaB and NLRP3 inflammasome pathways and protects against IMQ-induced psoriasis.[Pubmed:28096316]
Clin Sci (Lond). 2017 Mar 1;131(6):487-498.
BAY 11-7082 antagonizes I-kappaB kinase-beta preventing nuclear translocation of nuclear factor-kappaB (NF-kappaB); it also inhibits NOD-like receptor family, pyrin domain containing 3 (NLRP3) inflammasome activation. NF-kappaB is involved in psoriasis, whereas the role of NLRP3 is controversial. We investigated BAY 11-7082 effects in an experimental model of psoriasis-like dermatitis. Psoriasis-like lesions were induced by a topical application of imiquimod (IMQ) cream (62.5 mg/day) on the shaved back skin of C57BL/6 and NLRP3 knockout (KO) mice for 7 consecutive days. Sham psoriasis animals were challenged with Vaseline cream. Sham and IMQ animals were randomized to receive BAY 11-7082 (20 mg/kg/i.p.) or its vehicle (100 mul/i.p of 0.9% NaCl). Skin of IMQ animals developed erythema, scales, thickening and epidermal acanthosis. IMQ skin samples showed increased expression of pNF-kappaB and NLRP3 activation. BAY 11-7082 blunted epidermal thickness, acanthosis and inflammatory infiltrate. BAY 11-7082 reduced pNF-kappaB, NLRP3, tumour necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-alpha), interleukin (IL)-6 and IL-1beta expression, blunted the phosphorylation of signal transducer and activators of transcription 3 (STAT3) and decreased IL-23 levels. In addition, BAY 11-7082 reawakened the apoptotic machinery. NLRP3 KO animals showed a reduced total histological score but persistent mild acanthosis, dermal thickness and expression of pNF-kappaB and pSTAT3, following IMQ application. Our data suggest that BAY 11-7082 might represent an interesting approach for the management of psoriasis-like dermatitis depending on the dual inhibition of NF-kappaB and NLRP3.
The anti-inflammatory drug BAY 11-7082 suppresses the MyD88-dependent signalling network by targeting the ubiquitin system.[Pubmed:23441730]
Biochem J. 2013 May 1;451(3):427-37.
The compound BAY 11-7082 inhibits IkappaBalpha [inhibitor of NF-kappaB (nuclear factor kappaB)alpha] phosphorylation in cells and has been used to implicate the canonical IKKs (IkappaB kinases) and NF-kappaB in >350 publications. In the present study we report that BAY 11-7082 does not inhibit the IKKs, but suppresses their activation in LPS (lipopolysaccharide)-stimulated RAW macrophages and IL (interleukin)-1-stimulated IL-1R (IL-1 receptor) HEK (human embryonic kidney)-293 cells. BAY 11-7082 exerts these effects by inactivating the E2-conjugating enzymes Ubc (ubiquitin conjugating) 13 and UbcH7 and the E3 ligase LUBAC (linear ubiquitin assembly complex), thereby preventing the formation of Lys63-linked and linear polyubiquitin chains. BAY 11-7082 prevents ubiquitin conjugation to Ubc13 and UbcH7 by forming a covalent adduct with their reactive cysteine residues via Michael addition at the C3 atom of BAY 11-7082, followed by the release of 4-methylbenzene-sulfinic acid. BAY 11-7082 stimulated Lys48-linked polyubiquitin chain formation in cells and protected HIF1alpha (hypoxia-inducible factor 1alpha) from proteasomal degradation, suggesting that it inhibits the proteasome. The results of the present study indicate that the anti-inflammatory effects of BAY 11-7082, its ability to induce B-cell lymphoma and leukaemic T-cell death and to prevent the recruitment of proteins to sites of DNA damage are exerted via inhibition of components of the ubiquitin system and not by inhibiting NF-kappaB.
Bay 11-7082 inhibits transcription factor NF-kappaB and induces apoptosis of HTLV-I-infected T-cell lines and primary adult T-cell leukemia cells.[Pubmed:12176906]
Blood. 2002 Sep 1;100(5):1828-34.
Human T-cell leukemia virus type I (HTLV-I) is the causative agent of an aggressive form of leukemia designated adult T-cell leukemia (ATL). We have previously demonstrated that all T-cell lines infected with HTLV-I and primary leukemic cells from ATL patients display constitutively high activity of transcription factor NF-kappaB. In this study we showed that Bay 11-7082, an inhibitor of NF-kappaB, induced apoptosis of HTLV-I-infected T-cell lines but only negligible apoptosis of HTLV-I-negative T cells. Bay 11-7082 rapidly and efficiently reduced the DNA binding of NF-kappaB in HTLV-I-infected T-cell lines and down-regulated the expression of the antiapoptotic gene, Bcl-x(L), regulated by NF-kappaB, whereas it had little effect on the DNA binding of another transcription factor, AP-1. Although the viral protein Tax is an activator of NF-kappaB, Bay 11-7082-induced apoptosis of HTLV-I-infected cells was not associated with reduced expression of Tax. Furthermore, Bay 11-7082- induced apoptosis of primary ATL cells was more prominent than that of normal peripheral blood mononuclear cells, and apoptosis of these cells was also associated with down-regulation of NF-kappaB activity. Our results indicate that NF-kappaB plays a crucial role in the pathogenesis and survival of HTLV-I-infected leukemic cells and that it is a suitable target for the prevention and treatment of ATL.
Novel inhibitors of cytokine-induced IkappaBalpha phosphorylation and endothelial cell adhesion molecule expression show anti-inflammatory effects in vivo.[Pubmed:9261113]
J Biol Chem. 1997 Aug 22;272(34):21096-103.
We have identified two compounds that inhibit the expression of endothelial-leukocyte adhesion molecules intercellular adhesion molecule-1, vascular cell adhesion molecule-1, and E-selectin. These compounds act by inhibiting tumor necrosis factor-alpha-induced phosphorylation of IkappaB-alpha, resulting in decreased nuclear factor-kappaB and decreased expression of adhesion molecules. The effects on both IkappaB-alpha phosphorylation and surface expression of E-selectin were irreversible and occurred at an IC50 of approximately 10 microM. These agents selectively and irreversibly inhibited the tumor necrosis factor-alpha-inducible phosphorylation of IkappaB-alpha without affecting the constitutive IkappaB-alpha phosphorylation. Although these compounds exhibited other activities, including stimulation of the stress-activated protein kinases, p38 and JNK-1, and activation of tyrosine phosphorylation of a 130-140-kDa protein, these effects are probably distinct from the effects on adhesion molecule expression since they were reversible. One compound was evaluated in vivo and shown to be a potent anti-inflammatory drug in two animal models of inflammation. The compound reduced edema formation in a dose-dependent manner in the rat carrageenan paw edema assay and reduced paw swelling in a rat adjuvant arthritis model. These studies suggest that inhibitors of cytokine-inducible IkappaBalpha phosphorylation exert anti-inflammatory activity in vivo.


