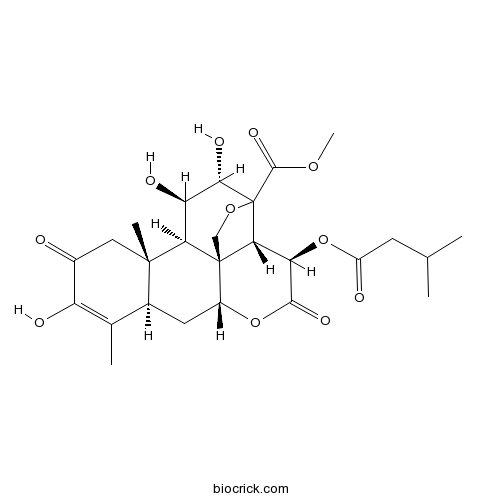
Bruceine Aantibabesial activity CAS# 25514-31-2 |
- RVX-208
Catalog No.:BCC4475
CAS No.:1044870-39-4
- Bromodomain Inhibitor, (+)-JQ1
Catalog No.:BCC1132
CAS No.:1268524-70-4
- CPI-203
Catalog No.:BCC4099
CAS No.:1446144-04-2
- BET-BAY 002
Catalog No.:BCC5510
CAS No.:1588521-78-1
- SGC-CBP30
Catalog No.:BCC2419
CAS No.:1613695-14-9
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 25514-31-2 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 329238 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C26H34O11 | M.Wt | 522.54 |
| Type of Compound | Diterpenoids | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | Soluble in DMSO | ||
| SMILES | CC1=C(C(=O)CC2(C1CC3C45C2C(C(C(C4C(C(=O)O3)OC(=O)CC(C)C)(OC5)C(=O)OC)O)O)C)O | ||
| Standard InChIKey | LPZSTPCYWWRQFU-AEECFKQJSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C26H34O11/c1-10(2)6-15(28)37-18-20-25-9-35-26(20,23(33)34-5)21(31)17(30)19(25)24(4)8-13(27)16(29)11(3)12(24)7-14(25)36-22(18)32/h10,12,14,17-21,29-31H,6-9H2,1-5H3/t12-,14+,17+,18+,19+,20+,21-,24-,25+,26?/m0/s1 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | 1. Bruceine A and bruceine B show strong antitrypanosomal activities with IC(50) values in the range of 2.9-17.8nM. 2. Bruceine A has anthelmintic activity, it exhibits significant activity against Dactylogyrus intermedius with EC(50) values of 0.49 mg/L. 3. Bruceine A exhibits NF-κB p65 inhibition, and cytotoxic potential against HT-29, HeLa, and HL-60 cells . 4. Bruceine A has antibabesial activity, it can inhibit the in vitro growth of Babesia gibsoni in canine erythrocytes at lower concentration and kill the parasites within 24 hr at a concentration of 25 nM. |
| Targets | Antifection | p65 | NF-kB | ROS |

Bruceine A Dilution Calculator

Bruceine A Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 1.9137 mL | 9.5686 mL | 19.1373 mL | 38.2746 mL | 47.8432 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.3827 mL | 1.9137 mL | 3.8275 mL | 7.6549 mL | 9.5686 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.1914 mL | 0.9569 mL | 1.9137 mL | 3.8275 mL | 4.7843 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0383 mL | 0.1914 mL | 0.3827 mL | 0.7655 mL | 0.9569 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0191 mL | 0.0957 mL | 0.1914 mL | 0.3827 mL | 0.4784 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
IC50: 7.7 nM against the parasites
Canine babesiosis is a tick-borne disease caused by the intraerythrocytic apicomplexan parasites, Babesia gibsoni and B. canis. Clinical signs of B. gibsoni infection are anemia, fever, thrombocytopenia, splenomegaly, lymphadenopathy, and lethargy. Bruceine A, a natural quassinoid compound extracted from the Brucea javanica (L.) Merr. dried fruits, was reported to have antibabesial activity.
In vitro: Bruceine A inhibited the in-vitro Babesia gibsoni growth in canine erythrocytes at lower concentration compared with the antibabesial drug diminazene aceturate and killed the parasites within 24 hr at a concentration of 25 nM [1].
In vivo: Oral administration of bruceine A at a dosage of 6.4 mg/kg/day for 5 days resulted in no clinical findings in a dog. An untreated dog developed typical acute babesiosis symptoms including high fever, severe anemia, and complete loss of appetite and movement. However, the two bruceine A-treated dogs maintained their healthy conditions throughout the experimental period of 4 weeks [1].
Clinical trials: Currenlty there is no clinical data available.
Reference:
[1] Nakao R, Mizukami C, Kawamura Y, Subeki, Bawm S, Yamasaki M, Maede Y, Matsuura H, Nabeta K, Nonaka N, Oku Y, Katakura K. Evaluation of efficacy of bruceine A, a natural quassinoid compound extracted from a medicinal plant, Brucea javanica, for canine babesiosis. J Vet Med Sci. 2009 Jan;71(1):33-41.
- Bruceine C
Catalog No.:BCN8000
CAS No.:25514-30-1
- Bruceine B
Catalog No.:BCN7615
CAS No.:25514-29-8
- 1-Acetyl-4-piperidinecarboxylic acid
Catalog No.:BCC8447
CAS No.:25503-90-6
- 4-Phenylbutan-2-one
Catalog No.:BCN3808
CAS No.:2550-26-7
- 3-Epioleanolic acid
Catalog No.:BCN3050
CAS No.:25499-90-5
- Tasquinimod
Catalog No.:BCC1987
CAS No.:254964-60-8
- 4-Allyloxy-2-hydroxybenzophenone
Catalog No.:BCC8675
CAS No.:2549-87-3
- Kushenol X
Catalog No.:BCN3350
CAS No.:254886-77-6
- Kushenol W
Catalog No.:BCN3307
CAS No.:254886-76-5
- 2,3-Bis(3,4-dimethoxybenzyl)butyrolactone
Catalog No.:BCN1473
CAS No.:25488-59-9
- Curryangine
Catalog No.:BCN7907
CAS No.:25488-37-3
- Talsupram hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC7924
CAS No.:25487-28-9
- Ibotenic acid
Catalog No.:BCC6591
CAS No.:2552-55-8
- Isoferulic acid
Catalog No.:BCN5122
CAS No.:25522-33-2
- Z-Ile-Glu-Pro-Phe-Ome
Catalog No.:BCC5526
CAS No.:255257-97-4
- Mayumbine
Catalog No.:BCN5123
CAS No.:25532-45-0
- Propidium iodide
Catalog No.:BCC8015
CAS No.:25535-16-4
- 1-(4-Hydroxybenzoyl)glucose
Catalog No.:BCN6900
CAS No.:25545-07-7
- 7-Methoxy-4-methylcoumarin
Catalog No.:BCN6540
CAS No.:2555-28-4
- Efetaal
Catalog No.:BCN8494
CAS No.:2556-10-7
- 1,6,7-Trihydroxyxanthone
Catalog No.:BCN5124
CAS No.:25577-04-2
- Delta-Tocotrienol
Catalog No.:BCN6696
CAS No.:25612-59-3
- 7beta-Acetoxytaxuspine C
Catalog No.:BCN7219
CAS No.:256347-91-8
- BAY 41-2272
Catalog No.:BCC7932
CAS No.:256376-24-6
Bioactivity-guided isolation of cytotoxic constituents of Brucea javanica collected in Vietnam.[Pubmed:19026551]
Bioorg Med Chem. 2009 Mar 15;17(6):2219-24.
Five new triterpenoids (1-5), together with two known quassinoids, bruceantin (6) and Bruceine A (7), and a known flavonolignan, (-)-hydnocarpin (8), were isolated from the chloroform-soluble subfraction of a methanol extract of the combined twigs, leaves, and inflorescence of Brucea javanica collected in Vietnam. The structures of the new compounds 1-5 were established on the basis of spectroscopic methods. All isolates were evaluated for cytotoxicity against a small panel of human cancer cell lines. Quassinoids 6 and 7 were found to be highly active against these cell lines. (-)-Hydnocarpin (8) showed a potentiating effect when combined with both 6 and 7, during cytotoxicity testing using the MCF-7 human breast cancer cell line.
NF-kappaB inhibitors from Brucea javanica exhibiting intracellular effects on reactive oxygen species.[Pubmed:20944100]
Anticancer Res. 2010 Sep;30(9):3295-300.
AIM: Brucea javanica was studied to identify nuclear factor kappaB (NF-kappaB) inhibitors exhibiting reactive oxygen species (ROS) intracellular amplification. MATERIAL AND METHODS: Eight compounds were evaluated for selective cytotoxicity using HT-29, HeLa, and HL-60 cells, and in a NF-kappaB assay. Active compounds were then tested using ROS and mitochondria transmembrane potential (MTP) assays. NF-kappaB and nuclear factor activated T-cell (NFAT) translocation were also assessed using their respective whole cell assays. RESULTS: Bruceajavanone B, bruceantin, Bruceine A, (-)-hydnocarpin, and chrysoeriol exhibited cytotoxic potential and NF-kappaB p65 inhibition. Chrysoeriol exhibited selective cytotoxicity against leukemia cells with greater potency and also showed an ability to up-regulate NFAT transcriptional pathways through the amplification of intracellular ROS, in the presence of H2O2, to a greater degree than bruceantin and bruceine. CONCLUSION: Chrysoeriol selectively kills leukemic cells and potentiates the amplification of ROS levels. Therefore, chrysoeriol could serve as a potential chemotherapeutic modifier for leukemia chemotherapy since leukemia cells have a higher susceptibility to elevated ROS levels.
Evaluation of efficacy of bruceine A, a natural quassinoid compound extracted from a medicinal plant, Brucea javanica, for canine babesiosis.[Pubmed:19194074]
J Vet Med Sci. 2009 Jan;71(1):33-41.
Bruceine A, a natural quassinoid compound extracted from the dried fruits of Brucea javanica (L.) Merr., was evaluated for its antibabesial activity in vitro and in vivo. Bruceine A inhibited the in vitro growth of Babesia gibsoni in canine erythrocytes at lower concentration compared with the standard antibabesial drug diminazene aceturate and killed the parasites within 24 hr at a concentration of 25 nM. Oral administration of Bruceine A at a dosage of 6.4 mg/kg/day for 5 days resulted in no clinical findings in a dog with normal ranges of hematological and biochemical values in the blood. Three dogs were infected with B. gibsoni and two of them were treated with Bruceine A at a dosage of 6.4 mg/kg/day for 6 days from day 5 post-infection. An untreated dog developed typical acute babesiosis symptoms including severe anemia, high fever, and complete loss of appetite and movement. However, the two Bruceine A-treated dogs maintained their healthy conditions throughout the experimental period of 4 weeks although complete elimination of parasites from the peripheral blood was not achieved and decreases in the packed cell volume and the erythrocyte and platelet counts were observed. Since natural quassinoid compounds have been used as traditional medicines for the treatment of various ailments including cancer and malaria, the present results suggest that Bruceine A or other related compounds are potential candidates for the treatment of canine babesiosis.
In vivo anthelmintic activity of bruceine A and bruceine D from Brucea javanica against Dactylogyrus intermedius (Monogenea) in goldfish (Carassius auratus).[Pubmed:21196080]
Vet Parasitol. 2011 Apr 19;177(1-2):127-33.
The present study was designated to ascertain the anthelmintic activity of the dried fruits of Brucea javanica and to isolate and characterise the active constituents. The methanol extract from the fruits of B. javanica showed significant anthelmintic activity against Dactylogyrus intermedius (EC(50) (median effective concentration) value=49.96 mg l(-1)). Based on this finding, the methanol extract was fractionated on silica gel column chromatography in a bioassay-guided fractionation affording two known quassinoids showing potent activity, Bruceine A and bruceine D. Both Bruceine A and D exhibited significant activity against D. intermedius with EC(50) values of 0.49 mg l(-1) and 0.57 mg l(-1), respectively, which were more effective than the positive control, mebendazole (EC(50) value=1.25 mg l(-1)). In addition, the 48-h median lethal concentration (LC(50)) for Bruceine A and D against the host (Carassius auratus) was 10.6-fold and 9.7-fold higher than the EC(50) for D. intermedius. These results provide evidence that the isolated compounds might be potential sources of new anti-parasitic drugs for the control of Dactylogyrus. This is the first report on an in vivo anthelmintic investigation for B. javanica against D. intermedius.
In vitro antitrypanosomal activities of quassinoid compounds from the fruits of a medicinal plant, Brucea javanica.[Pubmed:18986767]
Vet Parasitol. 2008 Dec 20;158(4):288-94.
The medicinal plant Brucea javanica (L.) Merr. (Simaroubaceae) is widely distributed throughout Asia where its bitter fruits have been used in traditional medicine for various ailments. Fifteen C-20 quassinoids were isolated from the fruits of B. javanica and examined for their in vitro antitrypanosomal activities against trypomastigotes of Trypanosoma evansi. Bruceine A, bruceantinol, bruceine C, brusatol, and bruceine B showed strong antitrypanosomal activities with IC(50) values in the range of 2.9-17.8nM, which compared well with the standard trypanocidal drugs diminazene aceturate (IC(50)=8.8nM) and suramin (IC(50)=43.2nM). However, dehydroBruceine A, dehydrobruceine B, and dehydrobrusatol were about 2100, 900, and 1200 times less active, respectively, than Bruceine A, bruceine B, and brusatol. The relationship of the structure and antitrypanosomal activity of these quassinoid compounds suggested that the presence of a diosphenol moiety in ring A and the nature of the C-15 side chain are important for their activities against T. evansi. This is the first report on the antitrypanosomal activity of isolated quassinoids.


