BufalinCAS# 465-21-4 |
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 465-21-4 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 10061 | Appearance | White powder |
| Formula | C24H34O4 | M.Wt | 386.52 |
| Type of Compound | Steroids | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | DMSO : 100 mg/mL (258.72 mM; Need ultrasonic) | ||
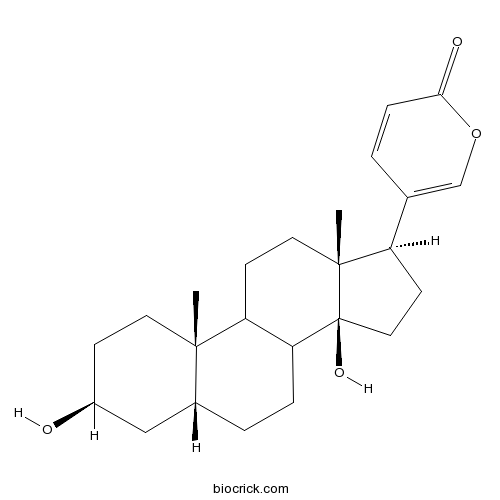
| Chemical Name | 5-[(3S,5R,10S,13R,14S,17R)-3,14-dihydroxy-10,13-dimethyl-1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,11,12,15,16,17-tetradecahydrocyclopenta[a]phenanthren-17-yl]pyran-2-one | ||
| SMILES | CC12CCC(CC1CCC3C2CCC4(C3(CCC4C5=COC(=O)C=C5)O)C)O | ||
| Standard InChIKey | QEEBRPGZBVVINN-ZXRSHIDQSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C24H34O4/c1-22-10-7-17(25)13-16(22)4-5-20-19(22)8-11-23(2)18(9-12-24(20,23)27)15-3-6-21(26)28-14-15/h3,6,14,16-20,25,27H,4-5,7-13H2,1-2H3/t16-,17+,18-,19?,20?,22+,23-,24+/m1/s1 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Bufalin a major digoxin-like immunoreactive component of the Chinese medicine Chan Su; has been shown to exert a potential for anticancer activity against various human cancer cell lines in vitro. Bufalin is a potent small-molecule inhibitor of the steroid receptor coactivators steroid receptor coactivator (SRC)-3 and SRC-1, it also as a potentially broad-spectrum small-molecule inhibitor for cancer. Bufalin can partly reverse the MDR of K562/VCR cells, with a possible mechanism of down-regulating MRP1 expression and activating apoptosis pathway by altering Bcl-xL/Bax ratio. |
| Targets | PKA | cAMP | p38MAPK | Bcl-2/Bax | P-gp | Src | Akt |
| In vitro | Reversal effect of bufalin on multidrug resistance in K562/VCR vincristine-resistant leukemia cell line.[Pubmed: 25618972]J Tradit Chin Med. 2014 Dec;34(6):678-83. To probe insights into the reversal effect of Bufalin on vincristine-acquired multidrug resistance (MDR) in human leukemia cell line K562/VCR. The cooperative interaction of two different signaling pathways in response to bufalin induces apoptosis in human leukemia U937 cells.[Pubmed: 8662906]J Biol Chem. 1996 Jun 14;271(24):14067-72.Bufalin, an active principle of Chinese medicine, chan'su, induced typical apoptosis in human leukemia U937 cells. |
| Kinase Assay | Bufalin is a potent small-molecule inhibitor of the steroid receptor coactivators SRC-3 and SRC-1.[Pubmed: 24390736 ]Secreted protein acidic and rich in cysteine antagonizes bufalin‑induced apoptosis in gastric cancer cells.[Pubmed: 25936899]Mol Med Rep. 2015 Aug;12(2):2926-32.Bufalin is an active compound in the traditional Chinese medicine Chan Su, which has been shown to induce apoptosis in a range of cancer cell types. However, certain gastric cancer cells are known to be resistant to Bufalin. Intracellular secreted protein acidic and rich in cysteine (SPARC) regulates proliferation and apoptosis. This study aimed to evaluate the role of SPARC in Bufalin-induced apoptosis in SGC7901 and MGC803 gastric cancer cells. Cancer Res. 2014 Mar 1;74(5):1506-1517.Virtually all transcription factors partner with coactivators that recruit chromatin remodeling factors and interact with the basal transcription machinery. Coactivators have been implicated in cancer cell proliferation, invasion, and metastasis, including the p160 steroid receptor coactivator (SRC) family composed of SRC-1 (NCOA1), SRC-2 (TIF2/GRIP1/NCOA2), and SRC-3 (AIB1/ACTR/NCOA3). Given their broad involvement in many cancers, they represent candidate molecular targets for new chemotherapeutics. Here, we report on the results of a high-throughput screening effort that identified the cardiac glycoside Bufalin as a potent small-molecule inhibitor for SRC-3 and SRC-1. Bufalin strongly promoted SRC-3 protein degradation and was able to block cancer cell growth at nanomolar concentrations. When incorporated into a nanoparticle delivery system, Bufalin was able to reduce tumor growth in a mouse xenograft model of breast cancer. Our work identifies Bufalin as a potentially broad-spectrum small-molecule inhibitor for cancer. |
| Cell Research | Effects of bufalin and cinobufagin on the proliferation of androgen dependent and independent prostate cancer cells.[Pubmed: 12497584 ]Prostate. 2003 Feb 1;54(2):112-24.Cardiac glycosides may induce oncolytic effects in cancers. This study was to evaluate Bufalin and cinobufagin effects on the proliferation of prostate cancer cell lines named LNCaP, DU145, and PC3.
|

Bufalin Dilution Calculator

Bufalin Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.5872 mL | 12.9359 mL | 25.8719 mL | 51.7438 mL | 64.6797 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.5174 mL | 2.5872 mL | 5.1744 mL | 10.3488 mL | 12.9359 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.2587 mL | 1.2936 mL | 2.5872 mL | 5.1744 mL | 6.468 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0517 mL | 0.2587 mL | 0.5174 mL | 1.0349 mL | 1.2936 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0259 mL | 0.1294 mL | 0.2587 mL | 0.5174 mL | 0.6468 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
Bufalin a major digoxin-like immunoreactive component of the Chinese medicine Chan Su; has been shown to exert a potential for anticancer activity against various human cancer cell lines in vitro. IC50 value: Target: Anticaner natural compound in vitro: bufalin remarkably inhibited growth in human gallbladder cancer cells by decreasing cell proliferation, inducing cell cycle arrest and apoptosis in a dose-dependent manner. Bufalin also disrupted the mitochondrial membrane potential (ΔΨm) and regulated the expression of cell cycle and apoptosis regulatory molecules. Activation of caspase-9 and the subsequent activation of caspase-3 indicated that bufalin may be inducing mitochondria apoptosis pathways [1]. bufalin suppressed the protein levels associated with DNA damage and repair, such as a DNA dependent serine/threonine protein kinase (DNA-PK), DNA repair proteins breast cancer 1, early onset (BRCA1), 14-3-3 σ (an important checkpoint keeper of DDR), mediator of DNA damage checkpoint 1 (MDC1), O6-ethylguanine-DNA methyltransferase (MGMT) and p53 (tumor suppressor protein) [2]. TNF-α significantly increased p65 translocation into nucleus (P < 0.01) and enhanced NF-κB DNA-binding activity, which were dose-dependently inhibited by bufalin. Furthermore, bufalin attenuated the TNF-α-induced interleukin-1beta (IL-1β), IL-6, and IL-8 production in RAFLSs in a concentration-dependent manner [3]. bufalin enhanced TRAIL-induced apoptosis in MCF-7 and MDA-MB-231 breast cancer cells by activating the extrinsic apoptotic pathway. Bufalin also promoted the clustering of death receptor 4 (DR4) and DR5 in aggregated lipid rafts [4]. in vivo: bufalin (0.3 and 0.6 mg/kg, i.p.) potently decreased carrageenan-induced paw edema. Bufalin down regulated the expression levels of nitric oxide synthase (iNOS), cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2), interleukin-1β (IL-1β), interleukin-6 (IL-6), and tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α) during these treatments [5].
References:
[1]. Jiang L, et al. Bufalin induces cell cycle arrest and apoptosis in gallbladder carcinoma cells. Tumour Biol. 2014 Nov;35(11):10931-41.
[2]. Wu SH, et al. Bufalin induces cell death in human lung cancer cells through disruption of DNA damage response pathways. Am J Chin Med. 2014;42(3):729-42.
[3]. Rong X, et al. Bufalin, a bioactive component of the chinese medicine chansu, inhibits inflammation and invasion of human rheumatoid arthritis fibroblast-like synoviocytes. Inflammation. 2014 Aug;37(4):1050-8.
[4]. Yan S, et al. Bufalin enhances TRAIL-induced apoptosis by redistributing death receptors in lipid rafts in breast cancer cells. Anticancer Drugs. 2014 Jul;25(6):683-9.
[5]. Wen L, et al. Anti-inflammatory and antinociceptive activities of bufalin in rodents. Mediators Inflamm. 2014;2014:171839.
- Polyporenic acid C
Catalog No.:BCN3645
CAS No.:465-18-9
- Oleandrin
Catalog No.:BCN5511
CAS No.:465-16-7
- Neritaloside
Catalog No.:BCN5509
CAS No.:465-13-4
- Gamabufotalin
Catalog No.:BCN2358
CAS No.:465-11-2
- Germanicol
Catalog No.:BCN7507
CAS No.:465-02-1
- Arjunolic acid
Catalog No.:BCN5508
CAS No.:465-00-9
- Pseudotaraxasterol
Catalog No.:BCN5507
CAS No.:464-98-2
- Asiatic acid
Catalog No.:BCN5506
CAS No.:464-92-6
- Conquinamine
Catalog No.:BCN6622
CAS No.:464-86-8
- Quinamine
Catalog No.:BCN6590
CAS No.:464-85-7
- Arenobufagin
Catalog No.:BCN5401
CAS No.:464-74-4
- Benzopinacol
Catalog No.:BCC8860
CAS No.:464-72-2
- Resibufogenin
Catalog No.:BCN5366
CAS No.:465-39-4
- Quinovic acid
Catalog No.:BCN5512
CAS No.:465-74-7
- Marrubiin
Catalog No.:BCC8208
CAS No.:465-92-9
- Hederagenin
Catalog No.:BCN5513
CAS No.:465-99-6
- alpha-Spinasterol acetate
Catalog No.:BCN5510
CAS No.:4651-46-1
- Cycloartanol
Catalog No.:BCN4860
CAS No.:4657-58-3
- Hederagonic acid
Catalog No.:BCN5514
CAS No.:466-01-3
- Hedragonic acid
Catalog No.:BCN6911
CAS No.:466-02-4
- Proscillaridin A
Catalog No.:BCC8239
CAS No.:466-06-8
- Uzarigenin
Catalog No.:BCN5515
CAS No.:466-09-1
- Benzoylaconine
Catalog No.:BCN5400
CAS No.:466-24-0
- Bullatine B
Catalog No.:BCN2375
CAS No.:466-26-2
Effects of bufalin and cinobufagin on the proliferation of androgen dependent and independent prostate cancer cells.[Pubmed:12497584]
Prostate. 2003 Feb 1;54(2):112-24.
BACKGROUND: Cardiac glycosides may induce oncolytic effects in cancers. This study was to evaluate Bufalin and cinobufagin effects on the proliferation of prostate cancer cell lines named LNCaP, DU145, and PC3. METHODS: Cell proliferation was measured by MTT assay. The cytotoxic effects were determined by lactate dehydrogenase measurements. The intracellular calcium concentration ([Ca(2+)](i)) was measured by a dual-wavelength spectrometer system. TUNEL assay and flow cytometry were performed to measure percentage of apoptotic cells. A colorimetric assay was to measure caspases activities. RESULTS: Bufalin and cinobufagin inhibited proliferation of cancer cells at doses of 0.1, 1, or 10 microM after 2-4 days of culture. Cytotoxicity of Bufalin and cinobufagin on the DU145 and LNCaP cells was dose-dependent. Bufalin or cinobufagin increased [Ca(2+)](i) and apoptosis in cancer cells after a 24-hr culture as well as caspase 3 activities in DU145 and PC3 cells and caspase 9 activities in LNCaP cells. CONCLUSIONS: Bufalin and cinobufagin may inhibit the proliferation of prostate cancer cell lines associated with sustained elevation of the [Ca(2+)](i) and that of apoptosis.
Reversal effect of bufalin on multidrug resistance in K562/VCR vincristine-resistant leukemia cell line.[Pubmed:25618972]
J Tradit Chin Med. 2014 Dec;34(6):678-83.
OBJECTIVE: To probe insights into the reversal effect of Bufalin on vincristine-acquired multidrug resistance (MDR) in human leukemia cell line K562/VCR. METHODS: Proliferative inhibition rate and the reversal index (RI) of Bufalin were determined by Methyl thiazolyl tetrazolium assay. The uptake of Adriamycin (ADM) in K562/VCR cells, cell cycle and apoptosis rate were determined by flow cytometry (FCM). Cell morphologic changes were observed with Wright-Giemsa staining. The expression of P-glycoprotein (P-gp), multidrug-associated protein-1 (MRP1), Bcl-xL and Bax protein were measured by immunocytochemistry. RESULTS: The human leukemia multidrug resistant K562/VCR cells showed no cross-resistance to Bufalin. The RIs of Bufalin at concentrations of 0.0002, 0.001 and 0.005 mumol/L were 4.85, 6.94 and 14.77, respectively. Preincubation of 0.001 mumol/L Bufalin for 2 h could increase intracellular ADM fluorescence intensity to 28.07% (P < 0.05) and down-regulate MRP1 expression simultaneously, but no remarkable effect was found on P-gp protein. Cell cycle analysis indicated increased apoptosis rate and apparent decreased G2/M phase proportion after treatment with Bufalin. When exposed to 0.01 mumol/L Bufalin, typical morphological changes of apoptosis could be observed. Down-regulation of Bcl-xL and up-regulation of Bax expression in K562/VCR cells could be detected by immunocytochemistry. CONCLUSION: Bufalin could partly reverse the MDR of K562/VCR cells, with a possible mechanism of down-regulating MRP1 expression and activating apoptosis pathway by altering Bcl-xL/Bax ratio.
The cooperative interaction of two different signaling pathways in response to bufalin induces apoptosis in human leukemia U937 cells.[Pubmed:8662906]
J Biol Chem. 1996 Jun 14;271(24):14067-72.
Bufalin, an active principle of Chinese medicine, chan'su, induced typical apoptosis in human leukemia U937 cells. When U937 cells were treated with 10(-8) M Bufalin in the absence of serum, mitogen-activated protein (MAP) kinase activity was markedly increased 6 h after the start of treatment and elevated so for 12 h. Prior to the activation of MAP kinase, increased activities of Ras, Raf-1, and MAP kinase kinase were found, but these enzymes were transiently activated by the treatment with Bufalin. These results suggest that the signal was transmitted sequentially from Ras, Raf-1, and MAP kinase kinase to MAP kinase. In association with this signal transduction, the concentration of cAMP in the cells decreased markedly, suggesting that Raf-1 was also activated by a decrease in the extent of phosphorylation by protein kinase A. In fact, pretreatment of U937 cells with forskolin and 3-isobutyl-1-methylxanthine, which are known to increase the concentration of cAMP in the cells, and subsequent treatment with Bufalin resulted in a decrease in both Raf-1 activity and DNA fragmentation. To confirm the participation of MAP kinase in the apoptotic process, antisense cDNA for MAP kinase kinase 1 was expressed in U937 cells. The transformants were significantly resistant to both DNA fragmentation and cell death in response to Bufalin. Our findings suggest that a pathway with the persistent activation of MAP kinase in U937 cells in response to Bufalin is at least one of the signal transduction pathways involved in the induction of apoptosis.


