CDK9 inhibitorCDK9 inhibitor CAS# 1415559-43-1 |
- LDC000067
Catalog No.:BCC5452
CAS No.:1073485-20-7
- CDK9 inhibitor 2
Catalog No.:BCC1466
CAS No.:1263369-28-3
- LY2857785
Catalog No.:BCC8050
CAS No.:1619903-54-6
- PHA-793887
Catalog No.:BCC2521
CAS No.:718630-59-2
- Dinaciclib (SCH727965)
Catalog No.:BCC3765
CAS No.:779353-01-4
- P276-00
Catalog No.:BCC4415
CAS No.:920113-03-7
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 1415559-43-1 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 66577006 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C26H21N5O4S | M.Wt | 499.54 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | DMSO : 25 mg/mL (50.05 mM; Need ultrasonic) H2O : < 0.1 mg/mL (insoluble) | ||
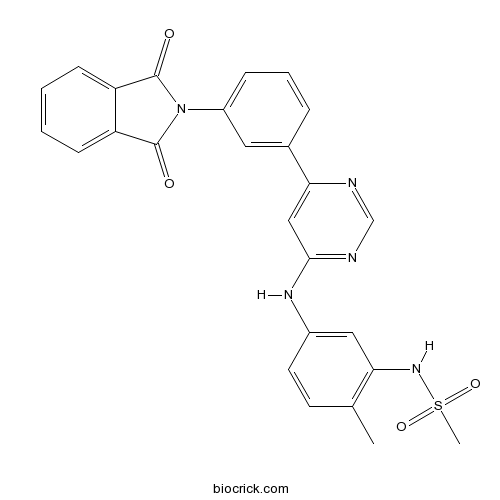
| Chemical Name | N-[5-[[6-[3-(1,3-dioxoisoindol-2-yl)phenyl]pyrimidin-4-yl]amino]-2-methylphenyl]methanesulfonamide | ||
| SMILES | CC1=C(C=C(C=C1)NC2=NC=NC(=C2)C3=CC(=CC=C3)N4C(=O)C5=CC=CC=C5C4=O)NS(=O)(=O)C | ||
| Standard InChIKey | CKUFOBCNTCLXJP-UHFFFAOYSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C26H21N5O4S/c1-16-10-11-18(13-22(16)30-36(2,34)35)29-24-14-23(27-15-28-24)17-6-5-7-19(12-17)31-25(32)20-8-3-4-9-21(20)26(31)33/h3-15,30H,1-2H3,(H,27,28,29) | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | CDK9-IN-1 is a novel, selective CDK9 inhibitor for the treatment of HIV infection, with an IC50 of 39 nM for CDK9/CycT1, extracted from reference, compound 87.In Vitro:CDK9-IN-1 is a potent CDK9 inhibitor that shows high activity against HIV-1 replication[1]. References: | |||||

CDK9 inhibitor Dilution Calculator

CDK9 inhibitor Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.0018 mL | 10.0092 mL | 20.0184 mL | 40.0368 mL | 50.046 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.4004 mL | 2.0018 mL | 4.0037 mL | 8.0074 mL | 10.0092 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.2002 mL | 1.0009 mL | 2.0018 mL | 4.0037 mL | 5.0046 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.04 mL | 0.2002 mL | 0.4004 mL | 0.8007 mL | 1.0009 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.02 mL | 0.1001 mL | 0.2002 mL | 0.4004 mL | 0.5005 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
CDK9 inhibitor is a small-molecule selective inhibitor of CDK9 (cyclin dependent kinase 9) with IC50 value of 39 nM [1].
CDKs are a group of serine/threonine kinases and are widely spread in all known eukaryotes. CDKs are activated through binding to cyclins and forming heterodimers. In the dimer, CDK acts as a catalytic subunit and phosphorylates the down-stream proteins such as nuclear lamina protein, nucleolin and histone H1. Through this way, CDKs take participate in the cell cycle regulation. CDK9 is a special member of the CDK family. It can affect the elongation phase of transcription through phosphorylating RNA polymerase II. The partner of it is positive elongation factor b (P-TEFb). It is reported that CDK9 is necessary for the infection of many kinds of viruses such as HIV-1 and HSV1 [1].
CDK9 inhibitor is a 4-aminophenyl derivative based on the (6-phenyl-pyrimidin-4-yl)-phenylamine structure. It showed elevated selectivity against CDK9 than the previous found inhibitors. The IC50 values of CDK9 inhibitor for CDK1/CycB, CDK2/CycE, CDK3/CycE, CDK4/CycD1, CDK5/p35, CDK6/CycD1 and CDK7/CycH are all higher than 1 μM. CDK9 inhibitor has no cytotoxicity. The treatment of CDK9 inhibitor at concentrations of 1 μM and 2 μM resulted in the cell viabilities of 101% and 115%, respectively. It also showed no significant toxicity in H9 cells. In the p24 assay, CDK9 inhibitor exerted its potency in inhibiting HIV-1 propagation with about 10% reduction of p24 production [1].
References:
1.Németh G, Varga Z, Greff Z, et al. Novel, selective CDK9 inhibitors for the treatment of HIV infection. Curr Med Chem, 2011;18(3):342-58.
- MK-8245 Trifluoroacetate
Catalog No.:BCC1769
CAS No.:1415559-41-9
- LY 231617
Catalog No.:BCC7005
CAS No.:141545-89-3
- Pelandjauic acid
Catalog No.:BCN3752
CAS No.:141545-69-9
- 5S rRNA modificator
Catalog No.:BCC5442
CAS No.:1415238-77-5
- Levosimendan
Catalog No.:BCC4793
CAS No.:141505-33-1
- Aloin A
Catalog No.:BCN1042
CAS No.:1415-73-2
- Rauvoyunine B
Catalog No.:BCN6995
CAS No.:1414883-82-1
- Rauvoyunine A
Catalog No.:BCN7002
CAS No.:1414883-81-0
- Guajadial B
Catalog No.:BCN3972
CAS No.:1414455-03-0
- Diosgenin glucoside
Catalog No.:BCN1250
CAS No.:14144-06-0
- ABT-751 (E7010)
Catalog No.:BCC1085
CAS No.:141430-65-1
- MRS 2219
Catalog No.:BCC6966
CAS No.:14141-47-0
- GSK256066 2,2,2-trifluoroacetic acid
Catalog No.:BCC1605
CAS No.:1415560-64-3
- Crizotinib hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC5306
CAS No.:1415560-69-8
- PF-543
Catalog No.:BCC1854
CAS No.:1415562-82-1
- PF-543 Citrate
Catalog No.:BCC1855
CAS No.:1415562-83-2
- ST-836 hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC1969
CAS No.:1415564-68-9
- Angustin A
Catalog No.:BCN7651
CAS No.:1415795-50-4
- Angustin B
Catalog No.:BCN7652
CAS No.:1415795-51-5
- UNC1215
Catalog No.:BCC2023
CAS No.:1415800-43-9
- JW 642
Catalog No.:BCC6324
CAS No.:1416133-89-5
- Beta-D-glucopyranosyl oleanolate
Catalog No.:BCN6530
CAS No.:14162-53-9
- Dronedarone HCl
Catalog No.:BCC4777
CAS No.:141625-93-6
- (±)-BI-D
Catalog No.:BCC5537
CAS No.:1416258-16-6
Inhibitory effect of CDK9 inhibitor FIT-039 on hepatitis B virus propagation.[Pubmed:27515132]
Antiviral Res. 2016 Sep;133:156-64.
Current therapies for hepatitis B virus (HBV) cannot completely eliminate the HBV genome because of the stable population of covalently closed circular DNA (cccDNA) and so on. FIT-039, which is a cyclin-dependent kinase (CDK) 9 inhibitor, is known to suppress the replication of several DNA viruses including HSV, HPV and human adenovirus. In this study, we investigated the antiviral effect of FIT-039 on HBV infection. HepG2 cells expressing human sodium taurocholate cotransporting polypeptide (HepG2/NTCP cells) were infected with HBV in the presence of FIT-039. FIT-039 dose-dependently reduced intracellular viral RNA, nucleocapsid-associated viral DNA, and supernatant viral antigens without cytotoxicity in the infected cells (IC50 = 0.33 muM, CC50 > 50 muM). The antiviral activity of FIT-039 was prominent at an early phase of viral infection, although the compound did not inhibit preS1-binding to HepG2/NTCP cells. FIT-039 reduced cccDNA in HBV-replicating or HBV-infected cells. Furthermore, the antiviral activity of entecavir was significantly enhanced by the combination with FIT-039 in the chimeric mice having human hepatocytes infected with HBV. None of the mice had significant drug-related body weight or serum human-albumin concentration changes. These data suggest that CDK9 inhibitor FIT-039 is a promising antiviral candidate for HBV infection.
Multiple CDK inhibitor dinaciclib suppresses neuroblastoma growth via inhibiting CDK2 and CDK9 activity.[Pubmed:27378523]
Sci Rep. 2016 Jul 5;6:29090.
Neuroblastoma (NB), the most common extracranial solid tumor of childhood, is responsible for approximately 15% of cancer-related mortality in children. Aberrant activation of cyclin-dependent kinases (CDKs) has been shown to contribute to tumor cell progression in many cancers including NB. Therefore, small molecule inhibitors of CDKs comprise a strategic option in cancer therapy. Here we show that a novel multiple-CDK inhibitor, dinaciclib (SCH727965, MK-7965), exhibits potent anti-proliferative effects on a panel of NB cell lines by blocking the activity of CDK2 and CDK9. Dinaciclib also significantly sensitized NB cell lines to the treatment of chemotherapeutic agents such as doxorubicin (Dox) and etoposide (VP-16). Furthermore, dinaciclib revealed in vivo antitumor efficacy in an orthotopic xenograft mouse model of two NB cell lines and blocked tumor development in the TH-MYCN transgenic NB mouse model. Taken together, this study suggests that CDK2 and CDK9 are potential therapeutic targets in NB and that abrogating CDK2 and CDK9 activity by small molecules like dinaciclib is a promising strategy and a treatment option for NB patients.
The CDK9 Inhibitor Dinaciclib Exerts Potent Apoptotic and Antitumor Effects in Preclinical Models of MLL-Rearranged Acute Myeloid Leukemia.[Pubmed:26627013]
Cancer Res. 2016 Mar 1;76(5):1158-69.
Translocations of the mixed lineage leukemia (MLL) gene occur in 60% to 80% of all infant acute leukemias and are markers of poor prognosis. MLL-AF9 and other MLL fusion proteins aberrantly recruit epigenetic regulatory proteins, including histone deacetylases (HDAC), histone methyltransferases, bromodomain-containing proteins, and transcription elongation factors to mediate chromatin remodeling and regulate tumorigenic gene expression programs. We conducted a small-molecule inhibitor screen to test the ability of candidate pharmacologic agents targeting epigenetic and transcriptional regulatory proteins to induce apoptosis in leukemic cells derived from genetically engineered mouse models of MLL-AF9-driven acute myeloid leukemia (AML). We found that the CDK inhibitor dinaciclib and HDAC inhibitor panobinostat were the most potent inducers of apoptosis in short-term in vitro assays. Treatment of MLL-rearranged leukemic cells with dinaciclib resulted in rapidly decreased expression of the prosurvival protein Mcl-1, and accordingly, overexpression of Mcl-1 protected AML cells from dinaciclib-induced apoptosis. Administration of dinaciclib to mice bearing MLL-AF9-driven human and mouse leukemias elicited potent antitumor responses and significantly prolonged survival. Collectively, these studies highlight a new therapeutic approach to potentially overcome the resistance of MLL-rearranged AML to conventional chemotherapies and prompt further clinical evaluation of CDK inhibitors in AML patients harboring MLL fusion proteins.
Conformational Adaption May Explain the Slow Dissociation Kinetics of Roniciclib (BAY 1000394), a Type I CDK Inhibitor with Kinetic Selectivity for CDK2 and CDK9.[Pubmed:27090615]
ACS Chem Biol. 2016 Jun 17;11(6):1710-9.
Roniciclib (BAY 1000394) is a type I pan-CDK (cyclin-dependent kinase) inhibitor which has revealed potent efficacy in xenograft cancer models. Here, we show that roniciclib displays prolonged residence times on CDK2 and CDK9, whereas residence times on other CDKs are transient, thus giving rise to a kinetic selectivity of roniciclib. Surprisingly, variation of the substituent at the 5-position of the pyrimidine scaffold results in changes of up to 3 orders of magnitude of the drug-target residence time. CDK2 X-ray cocrystal structures have revealed a DFG-loop adaption for the 5-(trifluoromethyl) substituent, while for hydrogen and bromo substituents the DFG loop remains in its characteristic type I inhibitor position. In tumor cells, the prolonged residence times of roniciclib on CDK2 and CDK9 are reflected in a sustained inhibitory effect on retinoblastoma protein (RB) phosphorylation, indicating that the target residence time on CDK2 may contribute to sustained target engagement and antitumor efficacy.


