CoriatinCAS# 91653-75-7 |
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 91653-75-7 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 73813185 | Appearance | Powder |
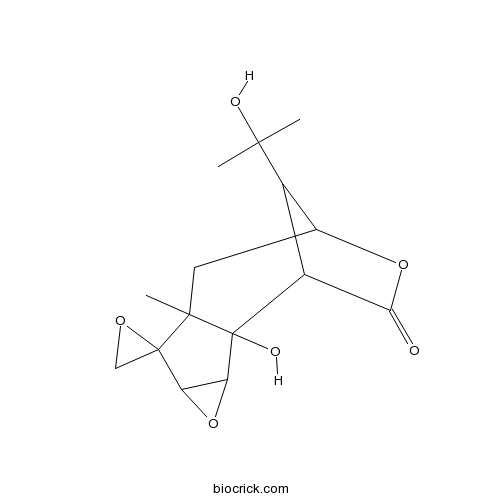
| Formula | C15H20O6 | M.Wt | 296.3 |
| Type of Compound | Sesquiterpenoids | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | Soluble in Chloroform,Dichloromethane,Ethyl Acetate,DMSO,Acetone,etc. | ||
| Chemical Name | 2-hydroxy-12-(2-hydroxypropan-2-yl)-7-methylspiro[4,10-dioxatetracyclo[7.2.1.02,7.03,5]dodecane-6,2'-oxirane]-11-one | ||
| SMILES | CC12CC3C(C(C1(C4C(C25CO5)O4)O)C(=O)O3)C(C)(C)O | ||
| Standard InChIKey | LGZSARJAXHVXEV-UHFFFAOYSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C15H20O6/c1-12(2,17)7-6-4-13(3)14(5-19-14)9-10(21-9)15(13,18)8(7)11(16)20-6/h6-10,17-18H,4-5H2,1-3H3 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | 1. Coriatin and corianin demonstrate synergistic effect to insecticidal activity of tutin againstarmyworm. |

Coriatin Dilution Calculator

Coriatin Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 3.375 mL | 16.8748 mL | 33.7496 mL | 67.4992 mL | 84.3739 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.675 mL | 3.375 mL | 6.7499 mL | 13.4998 mL | 16.8748 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.3375 mL | 1.6875 mL | 3.375 mL | 6.7499 mL | 8.4374 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0675 mL | 0.3375 mL | 0.675 mL | 1.35 mL | 1.6875 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0337 mL | 0.1687 mL | 0.3375 mL | 0.675 mL | 0.8437 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
- Zingiberen newsaponin
Catalog No.:BCN2942
CAS No.:91653-50-8
- Senkyunolide C
Catalog No.:BCC9141
CAS No.:91652-78-7
- Clinodiside A
Catalog No.:BCN1048
CAS No.:916347-31-4
- Acetylvirolin
Catalog No.:BCN7041
CAS No.:916264-22-7
- Gopherenediol
Catalog No.:BCN6582
CAS No.:916236-79-8
- AC 55541
Catalog No.:BCC3951
CAS No.:916170-19-9
- TCS 1102
Catalog No.:BCC4063
CAS No.:916141-36-1
- Benidipine HCl
Catalog No.:BCC4395
CAS No.:91599-74-5
- Momordicine I
Catalog No.:BCN3058
CAS No.:91590-76-0
- Dovitinib (TKI258) Lactate
Catalog No.:BCC6473
CAS No.:915769-50-5
- WAY 316606
Catalog No.:BCC2052
CAS No.:915759-45-4
- ABC294640
Catalog No.:BCC4192
CAS No.:915385-81-8
- Clematomandshurica saponin B
Catalog No.:BCN7810
CAS No.:916649-91-7
- Clematiunicinoside E
Catalog No.:BCN7809
CAS No.:916649-92-8
- TC-I 15
Catalog No.:BCC6216
CAS No.:916734-43-5
- 5,7,4'-Trihydroxy-8-methylflavanone
Catalog No.:BCN2844
CAS No.:916917-28-7
- Enniatin B
Catalog No.:BCN4774
CAS No.:917-13-5
- 2-[(Acetylthio)methyl]-phenylpropionic acid
Catalog No.:BCC8507
CAS No.:91702-98-6
- CYT997 (Lexibulin)
Catalog No.:BCC4601
CAS No.:917111-44-5
- Bromfenac Sodium
Catalog No.:BCC4641
CAS No.:91714-93-1
- MPC 6827 hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC8040
CAS No.:917369-31-4
- Letermovir
Catalog No.:BCC1700
CAS No.:917389-32-3
- Cyclo(Ile-Leu)
Catalog No.:BCN2434
CAS No.:91741-17-2
- Platycoside M1
Catalog No.:BCN3238
CAS No.:917482-67-8
[Determination of coriatin and corianin in plasma and urine using ultra-performance liquid chromatography-triple quadrupole mass spectrometry].[Pubmed:30693722]
Se Pu. 2019 Feb 8;37(2):149-154.
An ultra-performance liquid chromatography-triple quadrupole mass spectrometry (UPLC-MS/MS) method has been developed for the determination of Coriatin and corianin in plasma and urine, which are the biomarkers of poisoning caused by Coriaria sinica Maxim. Plasma and urine samples were extracted and purified using a solid supported liquid/liquid extraction method. Chromatographic separation was performed on a Cortecs C18 column (100 mmx2.1 mm, 1.6 mum) using a gradient elution of methanol and water. Coriatin and corianin were detected using negative electrospray ionization tandem mass spectrometry in multiple reaction monitoring (MRM) mode and quantified via a matrix working standard curve internal standard method; florfenicol was used as the internal standard. The assay was linear in the calibration range of 0.03-5.0 mug/L for Coriatin and 0.3-50 mug/L for corianin in plasma, and 0.1-10 mug/L and 1-100 mug/L for Coriatin and corianin in urine, respectively. The average recoveries were 86.2%-110% for Coriatin and corianin in plasma and urine with relative standard deviations of 5.1%-14.6% (n=6). The limits of detection (S/N=3) for Coriatin and corianin were 0.01 mug/L and 0.1 mug/L in plasma, and 0.03 mug/L and 0.3 mug/L in urine, respectively. The method is simple, sensitive and accurate for the determination of Coriatin and corianin in plasma and urine for toxicological purposes.
Phytochemistry and biology of Loranthus parasiticus Merr, a commonly used herbal medicine.[Pubmed:24467533]
Am J Chin Med. 2014;42(1):23-35.
Loranthus parasiticus Merr (L. parasiticus) is a member of Loranthaceae family and is an important medicinal plant with a long history of Chinese traditional use. L. parasiticus, also known as Sang Ji Sheng (in Chinese), benalu teh (in Malay) and baso-kisei (in Japanese), is a semiparasitic plant, which is mostly distributed in the southern and southwestern regions of China. This review aims to provide a comprehensive overview of the ethnomedicinal use, phytochemistry and pharmacological activity of L. parasiticus and to highlight the needs for further investigation and greater global development of the plant's medicinal properties. To date, pharmacological studies have demonstrated significant biological activities, which support the traditional use of the plant as a neuroprotective, tranquilizing, anticancer, immunomodulatory, antiviral, diuretic and hypotensive agent. In addition, studies have identified antioxidative, antimutagenic, antiviral, antihepatotoxic and antinephrotoxic activity. The key bioactive constituents in L. parasiticus include coriaria lactone comprised of sesquiterpene lactones: coriamyrtin, tutin, corianin, and Coriatin. In addition, two proanthocyanidins, namely, AC trimer and (+)-catechin, have been recently discovered as novel to L. parasiticus. L. parasiticus usefulness as a medicinal plant with current widespread traditional use warrants further research, clinical trials and product development to fully exploit its medicinal value.
[Studies on chemical constituents from the root of Coriaria nepalensis wall (Coriaria sinica Maxim)].[Pubmed:12016873]
Yao Xue Xue Bao. 1998 Sep;33(9):688-92.
The root of Coriaria nepalensis Wall (Coriaria sinica Maxim) is a Chinese herbal medicine and has been used to treat numbness, toothache due to wind and heat, phlegm-retention syndrome, traumatic injury and acute conjunctivitis. Nine compounds were isolated from the root of Coriaria nepalensis Wall and they were identified as braylin (I), norbraylin (II), dihydrocoriamyrtin (III), coriamyrtin (IV), tutin (V), Coriatin (VI), apotutin (VII), hydroxyCoriatin (VIII) and gallic acid (IX) on the basis of their physicochemical properties and IR, UV, MS, 1HNMR, 13CNMR data. I, II were isolated from the title plant for the first time; III was obtained from plant origin for the first time, and VII, VIII were new compounds.


