DMNBDNA-PK inhibitor CAS# 20357-25-9 |
- ML347
Catalog No.:BCC5331
CAS No.:1062368-49-3
- LDN-212854
Catalog No.:BCC5330
CAS No.:1432597-26-6
- PD 169316
Catalog No.:BCC3969
CAS No.:152121-53-4
- Imperatorin
Catalog No.:BCN5574
CAS No.:482-44-0
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 20357-25-9 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 88505 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C9H9NO5 | M.Wt | 211.15 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | Soluble to 25 mM in ethanol with gentle warming and to 100 mM in DMSO | ||
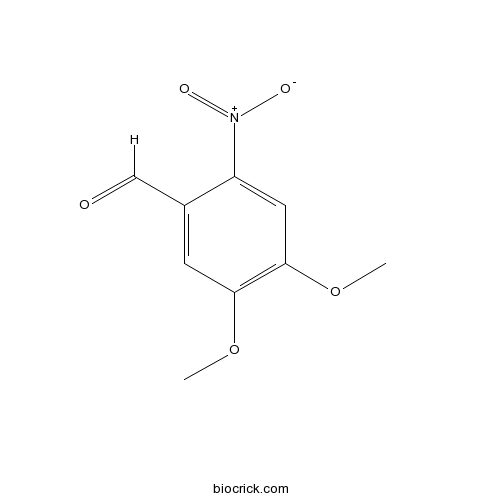
| Chemical Name | 4,5-dimethoxy-2-nitrobenzaldehyde | ||
| SMILES | COC1=C(C=C(C(=C1)C=O)[N+](=O)[O-])OC | ||
| Standard InChIKey | YWSPWKXREVSQCA-UHFFFAOYSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C9H9NO5/c1-14-8-3-6(5-11)7(10(12)13)4-9(8)15-2/h3-5H,1-2H3 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Inhibitor of DNA-dependent protein kinase (DNA-PK) (IC50 = 15 μM), an enzyme involved in the non-homologous end-joining (NHEJ) pathway of double-stranded DNA break (DSB) repair in human cells. Displays 100-fold higher potency than its analog vanillin and does not affect PKC activity. Produces lethal effects on cisplatin-treated D5037 cells upon continuous exposure. |

DMNB Dilution Calculator

DMNB Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 4.736 mL | 23.6798 mL | 47.3597 mL | 94.7194 mL | 118.3992 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.9472 mL | 4.736 mL | 9.4719 mL | 18.9439 mL | 23.6798 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.4736 mL | 2.368 mL | 4.736 mL | 9.4719 mL | 11.8399 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0947 mL | 0.4736 mL | 0.9472 mL | 1.8944 mL | 2.368 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0474 mL | 0.2368 mL | 0.4736 mL | 0.9472 mL | 1.184 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
- 2,4,6,6-Tetramethyl-3(6H)-pyridinone
Catalog No.:BCN4893
CAS No.:203524-64-5
- Brefeldin A
Catalog No.:BCC4387
CAS No.:20350-15-6
- (-)-Maackiain
Catalog No.:BCN4892
CAS No.:2035-15-6
- (+)-Bornyl acetate
Catalog No.:BCN8317
CAS No.:20347-65-3
- SNX 482
Catalog No.:BCC5952
CAS No.:203460-30-4
- 18-Norabieta-8,11,13-triene-4,15-diol
Catalog No.:BCN1504
CAS No.:203455-81-6
- Luteollin 5-glucoside
Catalog No.:BCN5391
CAS No.:20344-46-1
- 7-Oxo-beta-sitosterol
Catalog No.:BCN4891
CAS No.:2034-74-4
- Daphnoretin
Catalog No.:BCN2473
CAS No.:2034-69-7
- H-D-Arg-NH2.2HCl
Catalog No.:BCC2870
CAS No.:203308-91-2
- 3,4-Dimethoxyphenol
Catalog No.:BCN4890
CAS No.:2033-89-8
- 3,4,5-Trimethoxy-trans-cinnamic acid
Catalog No.:BCN3423
CAS No.:20329-98-0
- Hastacine
Catalog No.:BCN2086
CAS No.:20361-77-7
- Arctiin
Catalog No.:BCN1090
CAS No.:20362-31-6
- Istaroxime
Catalog No.:BCC1660
CAS No.:203737-93-3
- 27-Hydroxycholesterol
Catalog No.:BCN2750
CAS No.:20380-11-4
- MMAD
Catalog No.:BCC1774
CAS No.:203849-91-6
- Fmoc-ß-HoGlu(OtBu)-OH
Catalog No.:BCC3234
CAS No.:203854-49-3
- Helioxanthin derivative 5-4-2
Catalog No.:BCC5414
CAS No.:203935-39-1
- SU5416
Catalog No.:BCC1974
CAS No.:204005-46-9
- PD 176252
Catalog No.:BCC7426
CAS No.:204067-01-6
- (2-Aminoethyl)phosphonic acid
Catalog No.:BCN1762
CAS No.:2041-14-7
- Anabasamine
Catalog No.:BCN2148
CAS No.:20410-87-1
- 4'-Hydroxy-2-O-methylanigorufone
Catalog No.:BCN7179
CAS No.:204134-70-3
Amplifying fluorescent polymer sensors for the explosives taggant 2,3-dimethyl-2,3-dinitrobutane (DMNB).[Pubmed:16158118]
Chem Commun (Camb). 2005 Sep 28;(36):4572-4.
Structural and electronic effects on the efficiency of DMNB detection with fluorescent conjugated polymers are described.
Silicon quantum dot sensors for an explosive taggant, 2,3-dimethyl-2,3-dinitrobutane (DMNB).[Pubmed:27188402]
Chem Commun (Camb). 2016 Jul 7;52(53):8207-10.
Silicon quantum dots obtained by the reaction of magnesium silicide with ethylenediamine dihydrochloride were utilized to investigate the sensing mechanism and sensitivity for DMNB detection applications. Sensing DMNB provided us with evidence that Si QDs with a higher lying conduction band have better sensitivity compared to CdSe QDs.
Fluorescent detection of nitroaromatics and 2,3-dimethyl 2,3-dinitrobutane (DMNB) by a zinc complex: (salophen)Zn.[Pubmed:17472370]
Inorg Chem. 2007 May 28;46(11):4422-9.
Fluorescent sensors for the detection of chemical explosives are in great demand. It is shown herein that the fluorescence of ZnL* (H2L=N,N'-phenylene-bis-(3,5-di-tert-butylsalicylideneimine)) is quenched in solution by nitroaromatics and 2,3-dimethyl-2,3-dinitrobutane (DMNB), chemical signatures of explosives. The relationship between the structure and fluorescence of ZnL is explored, and crystal structures of three forms of ZnL(base), (base=ethanol, tetrahydrofuran, pyridine) are reported, with the base=ethanol structure exhibiting a four-centered hydrogen bonding array. Solution structures are monitored by 1H NMR and molecular weight determination, revealing a dimeric structure in poor donor solvents which converts to a monomeric structure in the presence of good donor solvents or added Lewis bases to form five-coordinate ZnL(base). Fluorescence wavelengths and quantum yields in solution are nearly insensitive to monomer-dimer interconversion, as well as to the identity of the Lewis base; in contrast, the emission wavelength in the solid state varies for different ZnL(base) due to pi-stacking. Nitroaromatics and DMNB are moderately efficient quenchers of ZnL*, with Stern-Volmer constants KSV=2-49 M-1 in acetonitrile solution.
Vanillins--a novel family of DNA-PK inhibitors.[Pubmed:14500812]
Nucleic Acids Res. 2003 Oct 1;31(19):5501-12.
Non-homologous DNA end-joining (NHEJ) is a major pathway of double strand break (DSB) repair in human cells. Here we show that vanillin (3-methoxy-4-hydroxybenzaldehyde)--a naturally occurring food component and an acknowledged antimutagen, anticlastogen and anticarcinogen--is an inhibitor of NHEJ. Vanillin blocked DNA end-joining by human cell extracts by directly inhibiting the activity of DNA-PK, a crucial NHEJ component. Inhibition was selective and vanillin had no detectable effect on other steps of the NHEJ process, on an unrelated protein kinase or on DNA mismatch repair by cell extracts. Subtoxic concentrations of vanillin did not affect the ATM/ATR-dependent phosphorylation of Chk2 or the S-phase checkpoint response after ionising radiation. They significantly potentiated the cytotoxicity of cisplatin, but did not affect sensitivity to UVC. A limited screen of structurally related compounds identified two substituted vanillin derivatives that were 100- and 50-fold more potent than vanillin as DNA-PK inhibitors. These compounds also sensitised cells to cisplatin. The inhibition of NHEJ is consistent with the antimutagenic and other biological properties of vanillin, possibly altering the balance between DSB repair by NHEJ and homologous recombination.


