PD 169316P38 MAPK inhibitor CAS# 152121-53-4 |
- Skepinone-L
Catalog No.:BCC1953
CAS No.:1221485-83-1
- SB202190 (FHPI)
Catalog No.:BCC1093
CAS No.:152121-30-7
- SB 239063
Catalog No.:BCC1923
CAS No.:193551-21-2
- SD-06
Catalog No.:BCC1937
CAS No.:271576-80-8
- LY2228820
Catalog No.:BCC2528
CAS No.:862507-23-1
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 152121-53-4 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 4712 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C20H13FN4O2 | M.Wt | 360.34 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | DMSO : 12.5 mg/mL (34.69 mM; Need ultrasonic) H2O : < 0.1 mg/mL (insoluble) | ||
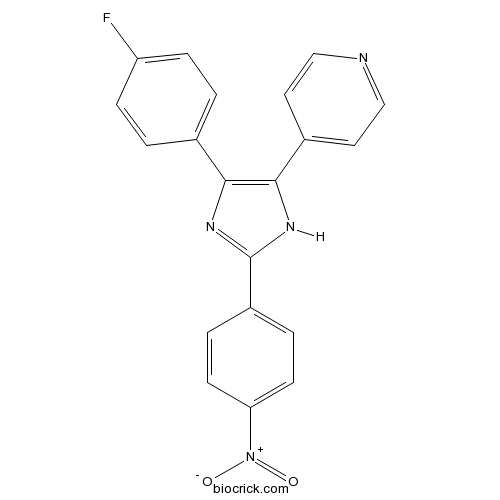
| Chemical Name | 4-[4-(4-fluorophenyl)-2-(4-nitrophenyl)-1H-imidazol-5-yl]pyridine | ||
| SMILES | C1=CC(=CC=C1C2=NC(=C(N2)C3=CC=NC=C3)C4=CC=C(C=C4)F)[N+](=O)[O-] | ||
| Standard InChIKey | BGIYKDUASORTBB-UHFFFAOYSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C20H13FN4O2/c21-16-5-1-13(2-6-16)18-19(14-9-11-22-12-10-14)24-20(23-18)15-3-7-17(8-4-15)25(26)27/h1-12H,(H,23,24) | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | PD 169316 is a potent, cell-permeable and selective p38 MAP kinase inhibitor, with IC50 of 89 nM.In Vitro:PD169316 (10 μM) inhibits TGFβ and Activin A, but not BMP4 signaling in CaOV3 cells. PD169316 (0.2-20 μM) inhibits TGFβ-induced Smad2 nuclear translocation, Smad7 mRNA induction, and reporter gene activity in CaOV3 cells[1]. PD169316 (10 μM) shows a significantly increased rate of proliferation in Nestin knockdown cells, and can rescue the effect of Nestin knockdown on cell viability in the absence of EGF[2]. PD169316 significantly inhibits p38 MAP kinase activity with no significant change in ERK activity in PC12 cells. PD169316 (10 μM) blocks apoptosis induced by trophic factor withdrawal in differentiated PC12 cells[3].In Vivo:PD169316 (30 ng/5 μL) or in combination with U0126 improves spatial learning in MWM in Aβ-injected rats, 20 days after Aβ-injection. Pretreatment with U0126 and PD169316 decreases the levels of phosphorylated form of ERK and p38 to about 77.7 and 64.2%, respectively, and causes a significant increase in c-fos, p-CREB, NRF-1 and TFAM protein levels, compared to the Aβ-injected group[4]. References: | |||||

PD 169316 Dilution Calculator

PD 169316 Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.7752 mL | 13.8758 mL | 27.7516 mL | 55.5031 mL | 69.3789 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.555 mL | 2.7752 mL | 5.5503 mL | 11.1006 mL | 13.8758 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.2775 mL | 1.3876 mL | 2.7752 mL | 5.5503 mL | 6.9379 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0555 mL | 0.2775 mL | 0.555 mL | 1.1101 mL | 1.3876 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0278 mL | 0.1388 mL | 0.2775 mL | 0.555 mL | 0.6938 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
IC50: A potent, selective and cell-permeable suppressor of p38 MAP kinase, with the IC50 value of 89 nM.
PD169316, a specific p38 MAPK inhibitor, blocks signal transduction mediated by both TGF-β and Activin A, but not bone morphogenetic protein (BMP) 4. Suppression on TGF-β signaling in a dose-dependent manner may then reduce Smad2 and Smad3 phosphorylation, block nuclear translocation and increase the expression of TGF-β target gene. [1]
In vitro: It was reported that pretreatment of CaOV3 cells with 10 M PD169316 caused a significant decrease in Smad2 and Smad3 phosphorylation which was mediated by TGF-β. The inhibitory effect of PD 169316 was proved to act in a dose-dependent manner. Study also demonstrated that PD169316 at 5 M or higher dose directly suppressed TGF-β signaling activity. [1]
In vivo: Based on an amyloid β (Aβ) rat model of Alzheimer's disease, the effect of PD 169316 on apoptosis induced by amyloid beta was examined. It was demonstrated that caspase-3 and Bax/Bcl-2 ratio, two marks of apoptosis, were significantly decreased in the rats pre-treated with PD169316 intracerebroventricularly. This study suggested the potential neuroprotective role of PD 169316 against the neuronal toxicity induced by Aβ. [2]
Clinical trial: So far, no clinical trial has been conducted.
References:
[1]Fu YX, O’Connor LM, Shepherd TG and Nachtigal MW. The p38 MAPK inhibitor, PD169316, inhibits transforming growth factor β-induced Smad signaling in human ovarian cancer cells. Biochem Bioph Res Co. 2003. 310: 3917.
[2]Ashabi G, Alamdary SZ, Ramin M and Khodagholi F. Reduction of hippocampal apoptosis by intracerebroventricular administration of extracellular signal-regulated protein kinase and/or P38 inhibitors in amyloid beta rat model of Alzheimer’s disease: involvement of nuclear-related factor-2 and nuclear factor-κb. Basic Clin. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2013 Aug. 112: 145–55.
- SB 203580
Catalog No.:BCC3663
CAS No.:152121-47-6
- SB202190 (FHPI)
Catalog No.:BCC1093
CAS No.:152121-30-7
- N,N'-Di-Boc-1H-pyrazole-1-carboxamidine
Catalog No.:BCC9065
CAS No.:152120-54-2
- 2-chloro-11-cyclopentyl-5H-benzo[e]pyrimido[5,4-b][1,4]diazepin-6(11H)-one
Catalog No.:BCC8568
CAS No.:1521197-43-2
- Teuclatriol
Catalog No.:BCN1676
CAS No.:152110-17-3
- 1,2-Epoxy-1-hydroxymethylpyrrolizidine
Catalog No.:BCN1557
CAS No.:15211-03-7
- 3,4-Dimethoxybenzamide
Catalog No.:BCN6565
CAS No.:1521-41-1
- Dp44mT
Catalog No.:BCC6518
CAS No.:152095-12-0
- Epothilone B (EPO906, Patupilone)
Catalog No.:BCC1092
CAS No.:152044-54-7
- Epothilone A
Catalog No.:BCC1091
CAS No.:152044-53-6
- Sophoricoside
Catalog No.:BCN2294
CAS No.:152-95-4
- Vicine
Catalog No.:BCC8366
CAS No.:152-93-2
- A 80426 mesylate
Catalog No.:BCC7336
CAS No.:152148-64-6
- Forrestin A
Catalog No.:BCN1677
CAS No.:152175-76-3
- Aphadilactone B
Catalog No.:BCN7646
CAS No.:1522004-68-7
- Aphadilactone C
Catalog No.:BCN7645
CAS No.:1522004-70-1
- SB 204741
Catalog No.:BCC7035
CAS No.:152239-46-8
- GT 2016
Catalog No.:BCC7357
CAS No.:152241-24-2
- Uncargenin C
Catalog No.:BCN1678
CAS No.:152243-70-4
- Mupinensisone
Catalog No.:BCN4704
CAS No.:152253-67-3
- U 93631
Catalog No.:BCC7471
CAS No.:152273-12-6
- Amyloid β-Peptide (10-20) (human)
Catalog No.:BCC1026
CAS No.:152286-31-2
- (S)-4-(4-Aminobenzyl)-2(1H)-oxazolidinone
Catalog No.:BCC8400
CAS No.:152305-23-2
- Gnetulin
Catalog No.:BCN3401
CAS No.:152340-24-4
Pd-Catalyzed Acyl C-O Bond Activation for Selective Ring-Opening of alpha-Methylene-beta-lactones with Amines.[Pubmed:28375015]
Org Lett. 2017 Apr 21;19(8):1966-1969.
A Pd-catalyzed ring-opening of beta-lactones with various types of amines (primary, secondary, and aryl) to provide beta-hydroxy amides with excellent selectivity toward acyl C-O bond cleavage is reported. The utility of this protocol is demonstrated in an asymmetric kinetic resolution providing enantioenriched alpha-methylene-beta-lactones.
CD8 T-cell regulation by T regulatory cells and the programmed cell death protein 1 pathway.[Pubmed:28375543]
Immunology. 2017 Jun;151(2):146-153.
The primary function of the immune system is to protect the host from infectious microorganisms and cancers. However, a major component of the immune response involves the direct elimination of cells in the body and the induction of systemic inflammation, which may result in life-threatening immunopathology. Therefore, the immune system has developed complex mechanisms to regulate itself with a specialized subset of CD4 T lymphocytes (referred to as regulatory T cells) and immune checkpoint pathways, such as the programmed cell death protein 1 pathway. These immune regulatory mechanisms can be exploited by pathogens and tumours to establish persistence in the host, warranting a deeper understanding of how to fine-tune immune responses during these chronic diseases. Here, I discuss various features of immune regulatory pathways and what important aspects must be considered in the next generation of therapies to reverse immune exhaustion, understanding that this process is a natural mechanism to prevent the host from destroying itself.
Pd(II)-Catalyzed Direct ortho-C-H Acylation of Aromatic Ketones by Oxidative Decarboxylation of alpha-Oxocarboxylic Acids.[Pubmed:28374587]
Org Lett. 2017 Apr 21;19(8):2082-2085.
A Pd-catalyzed decarboxylative acylation of aromatic ketones with alpha-oxocarboxylic acids was developed, and 1,2-diacylbenzenes were formed in up to 90% yield with excellent ortho-selectivity. This work demonstrates the first successful attempt to direct C-H acylation of aromatic ketones without the need for prederivatization to imines. The acylation reaction was inhibited by radical scavengers such as TEMPO, and 2,2,6,6-tetramethylpiperidin-1-yl benzoate, the adduct of TEMPO and a benzoyl radical, has been isolated and characterized. This finding is compatible with the intermediacy of acyl radicals. A mechanism involving the reaction of the palladacyclic complexes of aryl ketones with acyl radicals is proposed.
Isocyanide insertion across the Pd-C bond of allenyl and propargyl palladium complexes bearing phosphoquinoline as a spectator ligand. Synthesis of a palladium complex bearing a coordinated cyclobutenyl fragment.[Pubmed:28374876]
Dalton Trans. 2017 Apr 19;46(16):5210-5217.
We have studied the insertion of p-toluenesulfonylmethyl isocyanide (TosMIC) on selected allenyl and propargyl complexes of palladium bearing diphenylphosphine quinoline as a spectator ligand. The fast process gives different products depending on the tautomer involved in the reaction. Thus, the unsubstituted allenyl species yields an insertion complex with the isocyanide coordinated between the metal and the first allenyl carbon. On the other hand, a mixture of phenyl substituted allenyl and propargyl palladium complexes yields a novel species characterized by a cyclo-butenyl fragment directly coordinated to palladium. The solid state structure of such a complex together with an exhaustive kinetic study of the whole process is reported.


