SB202190 (FHPI)P38 MAPK inhibitor CAS# 152121-30-7 |
- Skepinone-L
Catalog No.:BCC1953
CAS No.:1221485-83-1
- SB 239063
Catalog No.:BCC1923
CAS No.:193551-21-2
- SD-06
Catalog No.:BCC1937
CAS No.:271576-80-8
- BIRB 796 (Doramapimod)
Catalog No.:BCC2535
CAS No.:285983-48-4
- LY2228820
Catalog No.:BCC2528
CAS No.:862507-23-1
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 152121-30-7 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 5353940 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C20H14N3OF | M.Wt | 331.34 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Synonyms | SB 202190; SB202190; SB-202190; FHPI | ||
| Solubility | DMSO : ≥ 40 mg/mL (120.72 mM) *"≥" means soluble, but saturation unknown. | ||
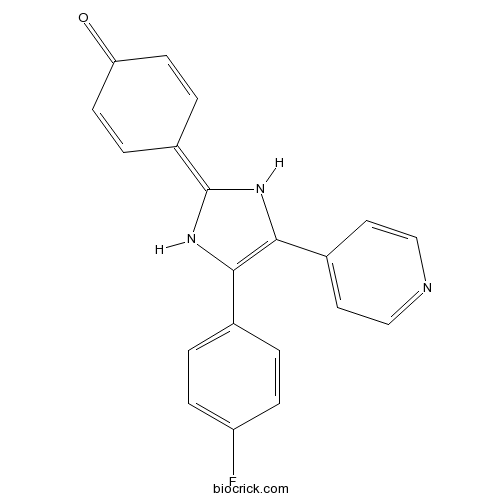
| Chemical Name | 4-[4-(4-fluorophenyl)-5-pyridin-4-yl-1,3-dihydroimidazol-2-ylidene]cyclohexa-2,5-dien-1-one | ||
| SMILES | C1=CC(=O)C=CC1=C2NC(=C(N2)C3=CC=NC=C3)C4=CC=C(C=C4)F | ||
| Standard InChIKey | NJNKPVPFGLGHPA-UHFFFAOYSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C20H14FN3O/c21-16-5-1-13(2-6-16)18-19(14-9-11-22-12-10-14)24-20(23-18)15-3-7-17(25)8-4-15/h1-12,23-24H | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | A highly selective, potent and cell-permeable inhibitor of p38 MAP kinase. Binds within the ATP pocket of the active kinase (Kd = 38 nM, as measured in recombinant human p38), and selectively inhibits the p38α and β isoforms (IC50 = 50 and 100 nM at SAPK2a/p38 and SAPK2b/p38β2 respectively). Promotes stability of naive human pluripotent stem cells in culture. Also available as part of the MAPK Inhibitor. |

SB202190 (FHPI) Dilution Calculator

SB202190 (FHPI) Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 3.018 mL | 15.0902 mL | 30.1805 mL | 60.361 mL | 75.4512 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.6036 mL | 3.018 mL | 6.0361 mL | 12.0722 mL | 15.0902 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.3018 mL | 1.509 mL | 3.018 mL | 6.0361 mL | 7.5451 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0604 mL | 0.3018 mL | 0.6036 mL | 1.2072 mL | 1.509 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0302 mL | 0.1509 mL | 0.3018 mL | 0.6036 mL | 0.7545 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
SB202190 (FHPI) is a potent p38 MAPK inhibitor that specifically inhibits p38α and p38β with IC50 values of 50 and 100 nM, respectively [1].
SB202190 has been reported to potently enhance the growth of leukemia cell lines THP-1 and MV4-11. SB202190 activates the phosphorylation ERK and C-Raf. Studies have shown that the ED50 values of U0126 and FPT inhibitor II were significantly decreased in the presence of SB202190 [2].
SB202190 triggers changes in cell cycle profiles both during HU treatment and caffeine-induced PCC (premature chromosome condensation) in plants. Moreover, SB202190 and caffeine decrease independently HU-induced histone H4 Lys5 acetylation [3].
References:
[1] Davies SP1, Reddy H, Caivano M, Cohen P. Specificity and mechanism of action of some commonly used protein kinase inhibitors. Biochem J. 2000 Oct 1;351(Pt 1):95-105.
[2] Hirosawa M1, Nakahara M, Otosaka R, Imoto A, Okazaki T, Takahashi S. The p38 pathway inhibitor SB202190 activates MEK/MAPK to stimulate the growth of leukemia cells. Leuk Res. 2009 May;33(5):693-9.
[3] Winnicki K1, Maszewski J. SB202190 affects cell response to hydroxyurea-induced genotoxic stress in root meristems of Vicia faba. Plant Physiol Biochem. 2012 Nov;60:129-36.
- N,N'-Di-Boc-1H-pyrazole-1-carboxamidine
Catalog No.:BCC9065
CAS No.:152120-54-2
- 2-chloro-11-cyclopentyl-5H-benzo[e]pyrimido[5,4-b][1,4]diazepin-6(11H)-one
Catalog No.:BCC8568
CAS No.:1521197-43-2
- Teuclatriol
Catalog No.:BCN1676
CAS No.:152110-17-3
- 1,2-Epoxy-1-hydroxymethylpyrrolizidine
Catalog No.:BCN1557
CAS No.:15211-03-7
- 3,4-Dimethoxybenzamide
Catalog No.:BCN6565
CAS No.:1521-41-1
- Dp44mT
Catalog No.:BCC6518
CAS No.:152095-12-0
- Epothilone B (EPO906, Patupilone)
Catalog No.:BCC1092
CAS No.:152044-54-7
- Epothilone A
Catalog No.:BCC1091
CAS No.:152044-53-6
- Sophoricoside
Catalog No.:BCN2294
CAS No.:152-95-4
- Vicine
Catalog No.:BCC8366
CAS No.:152-93-2
- Quinestrol
Catalog No.:BCC9132
CAS No.:152-43-2
- Verapamil HCl
Catalog No.:BCC4747
CAS No.:152-11-4
- SB 203580
Catalog No.:BCC3663
CAS No.:152121-47-6
- PD 169316
Catalog No.:BCC3969
CAS No.:152121-53-4
- A 80426 mesylate
Catalog No.:BCC7336
CAS No.:152148-64-6
- Forrestin A
Catalog No.:BCN1677
CAS No.:152175-76-3
- Aphadilactone B
Catalog No.:BCN7646
CAS No.:1522004-68-7
- Aphadilactone C
Catalog No.:BCN7645
CAS No.:1522004-70-1
- SB 204741
Catalog No.:BCC7035
CAS No.:152239-46-8
- GT 2016
Catalog No.:BCC7357
CAS No.:152241-24-2
- Uncargenin C
Catalog No.:BCN1678
CAS No.:152243-70-4
- Mupinensisone
Catalog No.:BCN4704
CAS No.:152253-67-3
- U 93631
Catalog No.:BCC7471
CAS No.:152273-12-6
- Amyloid β-Peptide (10-20) (human)
Catalog No.:BCC1026
CAS No.:152286-31-2
Inhibitory effect of 4-(4-fluorophenyl)-2-(4-hydroxyphenyl)-5-(4-pyridyl)1H - imidazole on HCMV DNA replication and permissive infection.[Pubmed:10320043]
Antiviral Res. 1999 Apr;41(3):101-11.
We found that Human Cytomegalovirus (HCMV) infection of human fibroblasts resulted in a dramatic increase in p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) phosphorylation. Recently, drug mediated inhibition of p38 has been demonstrated to exhibit anti-viral activity against HIV (Shapiro, L., Heidenreich, K.A., Meintzer, M.D. and Dinarello, C.A., 1998. Role of p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase in HIV type 1 production in vitro. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 95, 7422-7426). Therefore, we examined the effect of a specific p38 kinase inhibitor on HCMV infection. Inhibiting p38 activity in HCMV infected cells by treating cells with 4-(4-fluorophenyl)-2-(4-hydroxyphenyl)-5-(4-pyridyl)1H-imidazole; (FHPI), a p38 inhibitor drug, prevented permissive HCMV infection as measured by plaque assay. In the presence of FHPI, HCMV immediate early gene expression was slightly lower at early times of infection, but there was no inhibition of expression of the early gene UL-84, an HCMV protein essential for viral replication. However, FHPI inhibited HCMV DNA replication and late gene expression. The inhibitory effect of FHPI was reversible, as demonstrated by the induction of HCMV replication upon withdrawal of FHPI. Our data describes FHPI as a novel anti-HCMV compound that inhibits synthesis/activation of cellular and/or viral factors required for initiation of HCMV DNA replication.
Blockade of p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway inhibits inducible nitric-oxide synthase expression in mouse astrocytes.[Pubmed:9353295]
J Biol Chem. 1997 Nov 7;272(45):28373-80.
Treatment of mouse astrocyte cultures with combined interleukin (IL)-1alpha and tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-alpha induced expression of inducible nitric-oxide synthase (iNOS), resulting in sustained release of large amounts of nitric oxide, whereas TNF-alpha and IL-1alpha individually were unable to induce iNOS expression in astrocytes. The role of MAPK cascades and of NF-kappaB activation in the early intracellular signal transduction involved in iNOS transcription in TNF-alpha/IL-1alpha-stimulated astrocytes was investigated. TNF-alpha and IL-1alpha activated all p42/44(MAPK), p38(MAPK), and p54(JNK) pathways as determined by immunoprecipitation kinase assays using specific antibodies and substrates. The p38(MAPK) pathway is specifically involved in TNF-alpha/IL-1alpha-induced iNOS expression, since iNOS protein and nitric oxide release in the presence of a specific inhibitor of p38(MAPK), 4-(4-fluorophenyl)-2-2-(4-hydroxyphenyl)-5-(4-pyridyl)-imidazole (FHPI), were dramatically diminished. In contrast, PD98059, a specific inhibitor of MEK1 had no effect on iNOS expression. p38(MAPK) did not couple NF-kappaB to iNOS transcription, but NF-kappaB had a clear role in iNOS transcription regulation. Northern blot analysis showed that the p38(MAPK) pathway controlled iNOS expression at the transcriptional level, since iNOS mRNA was reduced in the presence of FHPI in TNF-alpha/IL-1alpha-stimulated astrocytes. iNOS expression was investigated with TNF receptor (TNFR)-1- and TNFR-2-deficient mice. The TNF-alpha activity in TNF-alpha/IL-1alpha-stimulated astrocytes was exclusively mediated through TNFR-1, most likely because TNFR-2-mediated signals in astrocytes did not connect to the p38(MAPK) pathway. These data suggest that TNF-alpha/IL-1alpha-induced iNOS expression depends on a yet undetermined second pathway in addition to p38(MAPK).
Derivation of novel human ground state naive pluripotent stem cells.[Pubmed:24172903]
Nature. 2013 Dec 12;504(7479):282-6.
Mouse embryonic stem (ES) cells are isolated from the inner cell mass of blastocysts, and can be preserved in vitro in a naive inner-cell-mass-like configuration by providing exogenous stimulation with leukaemia inhibitory factor (LIF) and small molecule inhibition of ERK1/ERK2 and GSK3beta signalling (termed 2i/LIF conditions). Hallmarks of naive pluripotency include driving Oct4 (also known as Pou5f1) transcription by its distal enhancer, retaining a pre-inactivation X chromosome state, and global reduction in DNA methylation and in H3K27me3 repressive chromatin mark deposition on developmental regulatory gene promoters. Upon withdrawal of 2i/LIF, naive mouse ES cells can drift towards a primed pluripotent state resembling that of the post-implantation epiblast. Although human ES cells share several molecular features with naive mouse ES cells, they also share a variety of epigenetic properties with primed murine epiblast stem cells (EpiSCs). These include predominant use of the proximal enhancer element to maintain OCT4 expression, pronounced tendency for X chromosome inactivation in most female human ES cells, increase in DNA methylation and prominent deposition of H3K27me3 and bivalent domain acquisition on lineage regulatory genes. The feasibility of establishing human ground state naive pluripotency in vitro with equivalent molecular and functional features to those characterized in mouse ES cells remains to be defined. Here we establish defined conditions that facilitate the derivation of genetically unmodified human naive pluripotent stem cells from already established primed human ES cells, from somatic cells through induced pluripotent stem (iPS) cell reprogramming or directly from blastocysts. The novel naive pluripotent cells validated herein retain molecular characteristics and functional properties that are highly similar to mouse naive ES cells, and distinct from conventional primed human pluripotent cells. This includes competence in the generation of cross-species chimaeric mouse embryos that underwent organogenesis following microinjection of human naive iPS cells into mouse morulas. Collectively, our findings establish new avenues for regenerative medicine, patient-specific iPS cell disease modelling and the study of early human development in vitro and in vivo.
Specificity and mechanism of action of some commonly used protein kinase inhibitors.[Pubmed:10998351]
Biochem J. 2000 Oct 1;351(Pt 1):95-105.
The specificities of 28 commercially available compounds reported to be relatively selective inhibitors of particular serine/threonine-specific protein kinases have been examined against a large panel of protein kinases. The compounds KT 5720, Rottlerin and quercetin were found to inhibit many protein kinases, sometimes much more potently than their presumed targets, and conclusions drawn from their use in cell-based experiments are likely to be erroneous. Ro 318220 and related bisindoylmaleimides, as well as H89, HA1077 and Y 27632, were more selective inhibitors, but still inhibited two or more protein kinases with similar potency. LY 294002 was found to inhibit casein kinase-2 with similar potency to phosphoinositide (phosphatidylinositol) 3-kinase. The compounds with the most impressive selectivity profiles were KN62, PD 98059, U0126, PD 184352, rapamycin, wortmannin, SB 203580 and SB 202190. U0126 and PD 184352, like PD 98059, were found to block the mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) cascade in cell-based assays by preventing the activation of MAPK kinase (MKK1), and not by inhibiting MKK1 activity directly. Apart from rapamycin and PD 184352, even the most selective inhibitors affected at least one additional protein kinase. Our results demonstrate that the specificities of protein kinase inhibitors cannot be assessed simply by studying their effect on kinases that are closely related in primary structure. We propose guidelines for the use of protein kinase inhibitors in cell-based assays.
The activation state of p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase determines the efficiency of ATP competition for pyridinylimidazole inhibitor binding.[Pubmed:9753474]
Biochemistry. 1998 Sep 29;37(39):13846-53.
The serine/threonine kinase p38 is a ubiquitous, highly conserved, stress responsive, signal-transducing enzyme. It regulates the production of proinflammatory mediators and is the target of the cytokine synthesis inhibitory pyridinylimidazoles. We have expressed human p38 in Drosophila S2 cells and characterized preparations of mixed unphosphorylated/monophosphorylated (inactive) and homogeneously diphosphorylated (active) forms of the enzyme. We observed that only the active preparation of the enzyme has significant kinase activity when assayed using an ATF2-GST fusion protein as the substrate. We determined that the value of KM[ATP] in this reaction is 25 microM and that the pyridinylimidazole inhibitor of p38 kinase activity, SB203580, competes with ATP. We have found that a tritiated pyridinylimidazole, SB202190, has an equal affinity for both the active and inactive forms of the enzyme and that SB203580 competes with it equally well for binding to either form of the enzyme. However, ATP can compete with the tritiated inhibitor for binding to only the active form of the enzyme. Further, we demonstrate in vivo that at concentrations consistent with its IC50 as a cytokine inhibitor, SB203580 can inhibit stimulus-induced phosphorylation of p38 at the Thr-Gly-Tyr activation motif. Our observations suggest that pyridinylimidazoles may block the biological activity of p38 kinase by binding to the inactive form of p38 and reducing its rate of activation. Under these conditions, ATP would not effectively compete with the inhibitors in vivo.
Induction of apoptosis by SB202190 through inhibition of p38beta mitogen-activated protein kinase.[Pubmed:9632706]
J Biol Chem. 1998 Jun 26;273(26):16415-20.
p38, a subfamily of the mitogen-activated protein kinase, regulates gene expression in response to various extracellular stimuli. The pyridinyl imidazoles like SB202190 are specific inhibitors of p38alpha and p38beta and have been widely used in investigation of the biological functions of p38. Here we show that SB202190 by itself was sufficient to induce cell death, with typical apoptotic features such as nucleus condensation and intranucleosomal DNA fragmentation. SB202190 stimulated the activity of CPP32-like caspases, and its apoptotic effect was completely blocked by the protease inhibitor benzyloxycarbonyl-Val-Ala-Asp-fluoromethyl ketone and expression of bcl-2. In addition, SB202190 was able to potentiate apoptosis induced by Fas(APO-1) ligation or UV irradiation. Expression of p38beta attenuated the apoptotic effect of SB202190 and the cell death induced by Fas ligation and UV irradiation. In contrast, expression of p38alpha induced cell death mildly. These results indicate that SB202190 induces apoptosis through activation of CPP32-like caspases and suggest that distinct members of the p38 subfamily of mitogen-activated protein kinase have different functions in apoptosis.
Characterization of the structure and function of a new mitogen-activated protein kinase (p38beta).[Pubmed:8663524]
J Biol Chem. 1996 Jul 26;271(30):17920-6.
Mitogen-activated protein (MAP) kinase cascades represent one of the major signal systems used by eukaryotic cells to transduce extracellular signals into cellular responses. Four MAP kinase subgroups have been identified in humans: ERK, JNK (SAPK), ERK5 (BMK), and p38. Here we characterize a new MAP kinase, p38beta. p38beta is a 372-amino acid protein most closely related to p38. It contains a TGY dual phosphorylation site, which is required for its kinase activity. Like p38, p38beta is activated by proinflammatory cytokines and environmental stress. A comparison of events associated with the activation of p38beta and p38 revealed differences, most notably in the preferred activation of p38beta by MAP kinase kinase 6 (MKK6), whereas p38 was activated nearly equally by MKK3, MKK4, and MKK6. Moreover, in vitro and in vivo experiments showed a strong substrate preference by p38beta for activating transcription factor 2 (ATF2). Enhancement of ATF2-dependent gene expression by p38beta was approximately20-fold greater than that of p38 and other MAP kinases tested. The data reported here suggest that while closely related, p38beta and p38 may be regulated by differing mechanisms and may exert their actions on separate downstream targets.


