(-)-MaackiainCAS# 2035-15-6 |
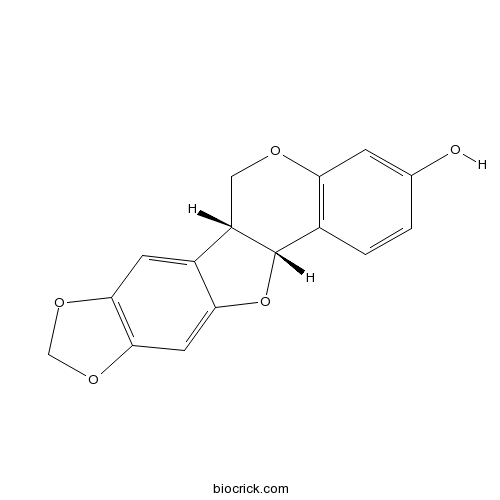
- Maackiain
Catalog No.:BCN1236
CAS No.:19908-48-6
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 2035-15-6 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 91510 | Appearance | White powder |
| Formula | C16H12O5 | M.Wt | 284.3 |
| Type of Compound | Flavonoids | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Synonyms | Inermine; Trifolirhizin aglycone | ||
| Solubility | Soluble in ethanol and methanol; sparingly soluble in water | ||
| SMILES | C1C2C(C3=C(O1)C=C(C=C3)O)OC4=CC5=C(C=C24)OCO5 | ||
| Standard InChIKey | HUKSJTUUSUGIDC-ZBEGNZNMSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C16H12O5/c17-8-1-2-9-12(3-8)18-6-11-10-4-14-15(20-7-19-14)5-13(10)21-16(9)11/h1-5,11,16-17H,6-7H2/t11-,16-/m0/s1 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | (-)-Maackiain, a phytoalexin, which is an anti-allergic compound that suppresses the up-regulation of the histamine H1 receptor (H1R) gene. It shows significant growth inhibitory action on the growth of the human lymphoblastoid cell lines Molt and Raji, and shows a strong larvicidal effect against 4th instar larvae of Aedes aegypti(LC50=21.95±1.34ug/mL). |
| Targets | HSP (e.g. HSP90) | Histamine Receptor |
| In vitro | The effect of the phytoalexins, lubimin, (-)-maackiain, pinosylvin, and the related compounds dehydroloroglossol and hordatine M on human lymphoblastoid cell lines.[Pubmed: 3709764]Experientia. 1986 May 15;42(5):568-70.
|
| In vivo | Pharmacokinetic properties of trifolirhizin, (-)-maackiain, (-)-sophoranone and 2-(2,4-dihydroxyphenyl)-5,6-methylenedioxybenzofuran after intravenous and oral administration of Sophora tonkinensis extract in rats.[Pubmed: 26068519]Xenobiotica. 2015 Jun 11:1-13.1. SKI3301, a standardized dried 50% ethanolic extracts of Sophora tonkinensis, contains four marker compounds (trifolirhizin, TF; (-)-Maackiain, Maack; (-)-sophoranone, SPN, and (2-(2,4-dihydroxyphenyl)-5,6-methylenedioxybenzofuran, ABF), is being developed as an herbal medicine for the treatment of asthma in Korea.
|
| Kinase Assay | Disruption of Heat Shock Protein 90 (Hsp90)-Protein Kinase Cδ (PKCδ) Interaction by (−)-Maackiain Suppresses Histamine H1 Receptor Gene Transcription in HeLa Cells*[Pubmed: 26391399]J. Biol. Chem.,2015, 290(45):27393-402.The histamine H1 receptor (H1R) gene is an allergic disease sensitive gene, and its expression level is strongly correlated with the severity of allergic symptoms. (-)-Maackiain was identified as a Kujin-derived anti-allergic compound that suppresses the up-regulation of the H1R gene. However, the underlying mechanism of H1R gene suppression remains unknown.
|
| Structure Identification | Plant Physiol.,1987 Feb;83(2):365-70.Role of oxygenases in pisatin biosynthesis and in the fungal degradation of maackiain.[Pubmed: 16665251 ]
|

(-)-Maackiain Dilution Calculator

(-)-Maackiain Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 3.5174 mL | 17.5871 mL | 35.1741 mL | 70.3482 mL | 87.9353 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.7035 mL | 3.5174 mL | 7.0348 mL | 14.0696 mL | 17.5871 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.3517 mL | 1.7587 mL | 3.5174 mL | 7.0348 mL | 8.7935 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0703 mL | 0.3517 mL | 0.7035 mL | 1.407 mL | 1.7587 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0352 mL | 0.1759 mL | 0.3517 mL | 0.7035 mL | 0.8794 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
- (+)-Bornyl acetate
Catalog No.:BCN8317
CAS No.:20347-65-3
- SNX 482
Catalog No.:BCC5952
CAS No.:203460-30-4
- 18-Norabieta-8,11,13-triene-4,15-diol
Catalog No.:BCN1504
CAS No.:203455-81-6
- Luteollin 5-glucoside
Catalog No.:BCN5391
CAS No.:20344-46-1
- 7-Oxo-beta-sitosterol
Catalog No.:BCN4891
CAS No.:2034-74-4
- Daphnoretin
Catalog No.:BCN2473
CAS No.:2034-69-7
- H-D-Arg-NH2.2HCl
Catalog No.:BCC2870
CAS No.:203308-91-2
- 3,4-Dimethoxyphenol
Catalog No.:BCN4890
CAS No.:2033-89-8
- 3,4,5-Trimethoxy-trans-cinnamic acid
Catalog No.:BCN3423
CAS No.:20329-98-0
- 3,5-Diacetamido-4-methylbenzoic acid
Catalog No.:BCN1505
CAS No.:6633-37-0
- Solamarine
Catalog No.:BCN3806
CAS No.:20318-30-3
- Tiliroside
Catalog No.:BCN4889
CAS No.:20316-62-5
- Brefeldin A
Catalog No.:BCC4387
CAS No.:20350-15-6
- 2,4,6,6-Tetramethyl-3(6H)-pyridinone
Catalog No.:BCN4893
CAS No.:203524-64-5
- DMNB
Catalog No.:BCC7259
CAS No.:20357-25-9
- Hastacine
Catalog No.:BCN2086
CAS No.:20361-77-7
- Arctiin
Catalog No.:BCN1090
CAS No.:20362-31-6
- Istaroxime
Catalog No.:BCC1660
CAS No.:203737-93-3
- 27-Hydroxycholesterol
Catalog No.:BCN2750
CAS No.:20380-11-4
- MMAD
Catalog No.:BCC1774
CAS No.:203849-91-6
- Fmoc-ß-HoGlu(OtBu)-OH
Catalog No.:BCC3234
CAS No.:203854-49-3
- Helioxanthin derivative 5-4-2
Catalog No.:BCC5414
CAS No.:203935-39-1
- SU5416
Catalog No.:BCC1974
CAS No.:204005-46-9
- PD 176252
Catalog No.:BCC7426
CAS No.:204067-01-6
The effect of the phytoalexins, lubimin, (-)-maackiain, pinosylvin, and the related compounds dehydroloroglossol and hordatine M on human lymphoblastoid cell lines.[Pubmed:3709764]
Experientia. 1986 May 15;42(5):568-70.
We have tested the effect of the phytoalexins lubimin, (-)-Maackiain and pinosylvin and the related compounds dehydroloroglossol and hordatine M on the growth of the human lymphoblastoid cell lines Molt and Raji. (-)-Maackiain, pinosylvin and dehydroloroglossol showed significant growth inhibitory action on the cells. Suppression of [3H] thymidine and [3H] leucine uptake was tested and noted in pinosylvin and dehydroloroglossol. The phytoalexins and related compounds are widespread in plants and provide a potential source of antineoplastic substances.
Disruption of Heat Shock Protein 90 (Hsp90)-Protein Kinase Cdelta (PKCdelta) Interaction by (-)-Maackiain Suppresses Histamine H1 Receptor Gene Transcription in HeLa Cells.[Pubmed:26391399]
J Biol Chem. 2015 Nov 6;290(45):27393-402.
The histamine H1 receptor (H1R) gene is an allergic disease sensitive gene, and its expression level is strongly correlated with the severity of allergic symptoms. (-)-Maackiain was identified as a Kujin-derived anti-allergic compound that suppresses the up-regulation of the H1R gene. However, the underlying mechanism of H1R gene suppression remains unknown. Here, we sought to identify a target protein of (-)-Maackiain and investigate its mechanism of action. A fluorescence quenching assay and immunoblot analysis identified heat shock protein 90 (Hsp90) as a target protein of (-)-Maackiain. A pull-down assay revealed that (-)-Maackiain disrupted the interaction of Hsp90 with PKCdelta, resulting in the suppression of phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate (PMA)-induced up-regulation of H1R gene expression in HeLa cells. Additional Hsp90 inhibitors, including 17-(allylamino)-17-demethoxygeldanamycin, celastrol, and novobiocin also suppressed PMA-induced H1R gene up-regulation. 17-(Allylamino)-17-demethoxygeldanamycin inhibited PKCdelta translocation to the Golgi and phosphorylation of Tyr(311) on PKCdelta. These data suggest that (-)-Maackiain is a novel Hsp90 pathway inhibitor. The underlying mechanism of the suppression of PMA-induced up-regulation of H1R gene expression by (-)-Maackiain and Hsp90 inhibitors is the inhibition of PKCdelta activation through the disruption of Hsp90-PKCdelta interaction. Involvement of Hsp90 in H1R gene up-regulation suggests that suppression of the Hsp90 pathway could be a novel therapeutic strategy for allergic rhinitis.
Role of oxygenases in pisatin biosynthesis and in the fungal degradation of maackiain.[Pubmed:16665251]
Plant Physiol. 1987 Feb;83(2):365-70.
Some isolates of the plant pathogen Nectria haematococca detoxify the isoflavonoid phytoalexin (-)maackiain by hydroxylation at carbon 6a. Precursor feeding studies strongly suggest that the penultimate step in (+)pisatin biosynthesis by Pisum sativum is 6a-hydroxylation of (+)maackiain. We have used (18)O labeling to test the involvement of oxygenases in these two reactions. When fungal metabolism of maackiain took place under (18)O(2), the product was labeled with 99% efficiency; no label was incorporated by metabolism in H(2) (18)O. Pisatin synthesized by pea pods in the presence of (18)O(2) or H(2) (18)O was a mixture of molecules containing up to three labeled oxygen atoms. Primary mass spectra of such mixtures were complex but were greatly simplified by tandem MS. This analysis indicated that the 6a oxygen of pisatin was derived from H(2)O and not from O(2). Labeling patterns for the other five oxygen atoms were consistent with the proposed pathway for biosynthesis of pisatin and related isoflavonoids. We conclude that the fungal hydroxylation of maackiain is catalyzed by an oxygenase, but the biosynthetic route to the 6a hydroxyl of pisatin is unknown.
Pharmacokinetic properties of trifolirhizin, (-)-maackiain, (-)-sophoranone and 2-(2,4-dihydroxyphenyl)-5,6-methylenedioxybenzofuran after intravenous and oral administration of Sophora tonkinensis extract in rats.[Pubmed:26068519]
Xenobiotica. 2015;45(12):1092-104.
1. SKI3301, a standardized dried 50% ethanolic extracts of Sophora tonkinensis, contains four marker compounds (trifolirhizin, TF; (-)-Maackiain, Maack; (-)-sophoranone, SPN, and (2-(2,4-dihydroxyphenyl)-5,6-methylenedioxybenzofuran, ABF), is being developed as an herbal medicine for the treatment of asthma in Korea. This study investigates the pharmacokinetic properties of SKI3301 extract in rats. 2. The dose-proportional AUCs suggest linear pharmacokinetics of TF, Maack, SPN and ABF in the SKI3301 extract intravenous dose range of 5-20 mg/kg. After the oral administration of 200-1000 mg/kg of the extract, TF and Maack exhibited non-linearity due to the saturation of gastrointestinal absorption. However, linear pharmacokinetics of SPN and ABF were observed. 3. The absorptions of TF, Maack, SPN and ABF in the extract were increased relative to those of the respective pure forms due to the increased solubility and/or the decreased metabolism by other components in the SKI3301 extract. 4. No accumulation was observed after multiple dosing, and the steady-state pharmacokinetics of TF, Maack, SPN and ABF were not significantly different from those after a single oral administration of the extract. 5. The pharmacokinetics of TF, SPN and ABF were not significantly different between male and female rats after oral administration of the extract, but a significant gender difference in the pharmacokinetics of Maack in rats was observed. 6. Our findings may help to comprehensively elucidate the pharmacokinetic characteristics of TF, Maack, SPN and ABF and provide useful information for the clinical application of SKI3301 extract.


