SolamarineCAS# 20318-30-3 |
- Solasonine
Catalog No.:BCN2302
CAS No.:19121-58-5
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 20318-30-3 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 70680623 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C45H73NO16 | M.Wt | 884.1 |
| Type of Compound | Alkaloids | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Synonyms | alpha-Solamarine | ||
| Solubility | Soluble in Chloroform,Dichloromethane,Ethyl Acetate,DMSO,Acetone,etc. | ||
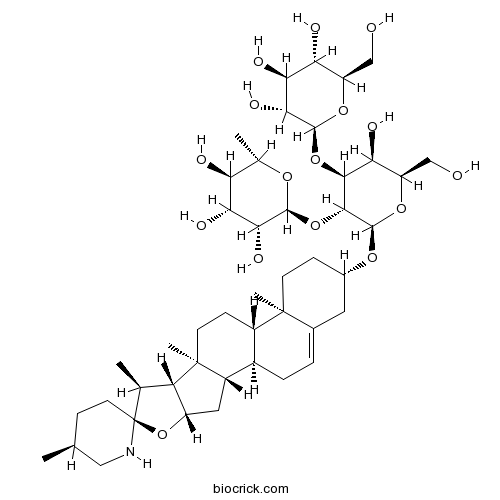
| Chemical Name | (2S,3R,4R,5R,6S)-2-[(2R,3R,4S,5S,6R)-5-hydroxy-6-(hydroxymethyl)-2-[(1S,2S,4S,5'S,6S,7S,8R,9S,12S,13R,16S)-5',7,9,13-tetramethylspiro[5-oxapentacyclo[10.8.0.02,9.04,8.013,18]icos-18-ene-6,2'-piperidine]-16-yl]oxy-4-[(2S,3R,4S,5S,6R)-3,4,5-trihydroxy-6-(hydroxymethyl)oxan-2-yl]oxyoxan-3-yl]oxy-6-methyloxane-3,4,5-triol | ||
| SMILES | CC1CCC2(C(C3C(O2)CC4C3(CCC5C4CC=C6C5(CCC(C6)OC7C(C(C(C(O7)CO)O)OC8C(C(C(C(O8)CO)O)O)O)OC9C(C(C(C(O9)C)O)O)O)C)C)C)NC1 | ||
| Standard InChIKey | QCTMYNGDIBTNSK-AQZQQWEISA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C45H73NO16/c1-19-8-13-45(46-16-19)20(2)30-27(62-45)15-26-24-7-6-22-14-23(9-11-43(22,4)25(24)10-12-44(26,30)5)57-42-39(61-40-36(54)34(52)31(49)21(3)56-40)38(33(51)29(18-48)59-42)60-41-37(55)35(53)32(50)28(17-47)58-41/h6,19-21,23-42,46-55H,7-18H2,1-5H3/t19-,20-,21-,23-,24+,25-,26-,27-,28+,29+,30-,31-,32+,33-,34+,35-,36+,37+,38-,39+,40-,41-,42+,43-,44-,45-/m0/s1 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||

Solamarine Dilution Calculator

Solamarine Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 1.1311 mL | 5.6555 mL | 11.3109 mL | 22.6219 mL | 28.2773 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.2262 mL | 1.1311 mL | 2.2622 mL | 4.5244 mL | 5.6555 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.1131 mL | 0.5655 mL | 1.1311 mL | 2.2622 mL | 2.8277 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0226 mL | 0.1131 mL | 0.2262 mL | 0.4524 mL | 0.5655 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0113 mL | 0.0566 mL | 0.1131 mL | 0.2262 mL | 0.2828 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
- Tiliroside
Catalog No.:BCN4889
CAS No.:20316-62-5
- Procyanidin B1
Catalog No.:BCN6314
CAS No.:20315-25-7
- Solamargine
Catalog No.:BCN2305
CAS No.:20311-51-7
- Saponarin
Catalog No.:BCN2280
CAS No.:20310-89-8
- Clofazimine
Catalog No.:BCC4651
CAS No.:2030-63-9
- Aporheine
Catalog No.:BCN4802
CAS No.:2030-53-7
- NF 279
Catalog No.:BCC6964
CAS No.:202983-32-2
- NF 340
Catalog No.:BCC7785
CAS No.:202982-98-7
- Conantokin-R
Catalog No.:BCC5980
CAS No.:202925-60-8
- glucagon receptor antagonists 2
Catalog No.:BCC1594
CAS No.:202917-18-8
- glucagon receptor antagonists 3
Catalog No.:BCC1595
CAS No.:202917-17-7
- 7-Benzyloxyindole
Catalog No.:BCC8778
CAS No.:20289-27-4
- 3,5-Diacetamido-4-methylbenzoic acid
Catalog No.:BCN1505
CAS No.:6633-37-0
- 3,4,5-Trimethoxy-trans-cinnamic acid
Catalog No.:BCN3423
CAS No.:20329-98-0
- 3,4-Dimethoxyphenol
Catalog No.:BCN4890
CAS No.:2033-89-8
- H-D-Arg-NH2.2HCl
Catalog No.:BCC2870
CAS No.:203308-91-2
- Daphnoretin
Catalog No.:BCN2473
CAS No.:2034-69-7
- 7-Oxo-beta-sitosterol
Catalog No.:BCN4891
CAS No.:2034-74-4
- Luteollin 5-glucoside
Catalog No.:BCN5391
CAS No.:20344-46-1
- 18-Norabieta-8,11,13-triene-4,15-diol
Catalog No.:BCN1504
CAS No.:203455-81-6
- SNX 482
Catalog No.:BCC5952
CAS No.:203460-30-4
- (+)-Bornyl acetate
Catalog No.:BCN8317
CAS No.:20347-65-3
- (-)-Maackiain
Catalog No.:BCN4892
CAS No.:2035-15-6
- Brefeldin A
Catalog No.:BCC4387
CAS No.:20350-15-6
A New Cytotoxic Steroidal Glycoalkaloid from the Methanol Extract of Blumea lacera Leaves.[Pubmed:26626252]
J Pharm Pharm Sci. 2015;18(4):616-33.
PURPOSE: Blumea lacera (B. lacera) (Asteraceae) is a well-known Bangladeshi medicinal plant. This study aimed to identify and characterize constituents associated with the significant cytotoxic activity of this plant that we reported previously. Here, we describe the isolation and characterization of a new steroidal glycoalkaloid (SGA) 1, the evaluation of its cytotoxic activity, apoptotic potential, and effect on cell cycle in comparison to analogous steroidal glycoalkaloids (SGAs). METHODS: SGA 1 was isolated using C18 SPE and HPLC, and subsequently structurally characterized using 1D and 2D NMR, MS and other spectroscopic methods, along with a comparative inspection of the literature. Cytotoxic activity of 1 and seven SGA analogues and steroidal alkaloids (SAs), (beta-Solamarine, alpha-solanine, beta-solamargine, alpha-solasonine, khasianine, solasodine, tomatidine HCl) were evaluated for their cytotoxicity against two healthy (NIH3T3 and VERO) and four human cancer (AGS, HT-29, MCF-7 and MDA-MB-231) cell lines using the MTT assay. Cytotoxic SGAs were further evaluated for apoptosis-inducing potential and cell cycle arresting ability against breast cancer cells (MCF-7) using the FITC Annexin V and propidium iodide (PI) assay. RESULTS: Bioactivity guided fractionation of the methanol extract of B. lacera led to isolation of compound 1: (25R)-3beta-{O-beta-D-glucopyranosyl-(1 --> 4)-O-alpha-L-rhamnopyranosyl-(1 --> 4)-[O-alpha-L-rhamnopyranosyl-(1 --> 2)]-alpha-L-rhamnopyranosyl}-22alphaN-spirosol-5-ene. SGA 1 was the most cytotoxic compound against a number of human cancer cell lines with an IC50 of 2.62 microM against MCF-7 cells. It displayed the highest apoptotic potential (32% AV+/PI-) on MCF-7 cells compared to other cytotoxic SGA analogues and a slight, but significant cell cycle arresting effect. CONCLUSIONS: A new SGA 1 was isolated from B. lacera and its cytotoxic activity, as well as that of other SAGs, was evaluated. SAR investigations on SGA 1, in relation to SGA analogues, show that the number and nature of sugar moieties along with the linkages of the sugar to the aglycone are crucial for cytotoxic and apoptotic activity. This article is open to POST-PUBLICATION REVIEW. Registered readers (see "For Readers") may comment by clicking on ABSTRACT on the issue's contents page.
Molluscicidal activity of Solanum elaeagnifolium seeds against Galba truncatula intermediate host of Fasciola hepatica: Identification of beta-solamarine.[Pubmed:26429590]
Pharm Biol. 2016;54(4):726-31.
CONTEXT: The persistence of fascioliasis in many developing countries urges the search for simple, cheap, and effective substances. In this view, plants provide interesting molluscicidal activities thanks to the secondary metabolites they produce. The genus Solanum is known for its potent effect on vector snails. OBJECTIVE: The molluscicidal activity of Solanum elaeagnifolium Cav. (Solanaceae) seeds against Galba truncatula Mull. (Lymnaeidae), intermediate host of Fasciola hepatica L. (Fasciolidae), was evaluated. MATERIALS AND METHODS: Solanum elaeagnifolium seeds were powdered and successively extracted using n-hexane, methylene chloride, acetone, and methanol, for 20 h each. After filtration, solvents were evaporated. An acid-base treatment was conducted on seed methanolic extract to isolate total alkaloids and beta-Solamarine. Total saponins fraction was obtained after successive macerations and evaporations. The molluscicidal activity was evaluated by subjecting snails, in groups of 10, for 48 h to 500 mL of extracts, fractions, and pure product aqueous solutions, each containing amounts, ranging from 1 to 50 mg of plant material in 5 mg increments. RESULTS: The methanolic extract of seeds, beta-Solamarine isolated for the first time from this plant and total saponins fraction showed very potent activities on snails, giving respective median lethal concentrations (LC50) of 1.18, 0.49, and 0.94 mg/L. Total alkaloids fraction obtained from the methanolic extract was less active giving an LC50 value of 14.67 mg/L. DISCUSSION AND CONCLUSION: This study emphasizes that glycoalkaloids and saponins of Solanum elaeagnifolium are potent molluscicidal agents. Seed methanolic extract, beta-Solamarine, and total saponins fraction may be used as molluscicides.


