NF 279Potent and selective P2X1 antagonist CAS# 202983-32-2 |
- Tubastatin A HCl
Catalog No.:BCC3877
CAS No.:1310693-92-5
- Entinostat (MS-275,SNDX-275)
Catalog No.:BCC3595
CAS No.:209783-80-2
- M344
Catalog No.:BCC2162
CAS No.:251456-60-7
- Panobinostat (LBH589)
Catalog No.:BCC3601
CAS No.:404950-80-7
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 202983-32-2 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 5311315 | Appearance | Powder |
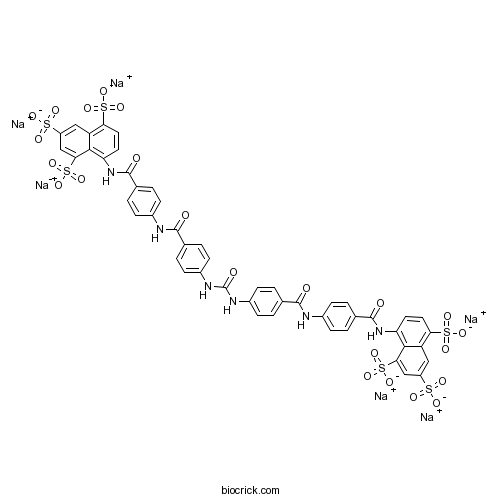
| Formula | C49H30N6Na6O23S6 | M.Wt | 1401.1 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | Soluble to 25 mM in water | ||
| Chemical Name | 8,8'-[Carbonylbis(imino-4,1-phenylen | ||
| SMILES | C1=CC(=CC=C1C(=O)NC2=C3C(=CC(=CC3=C(C=C2)S(=O)(=O)[O-])S(=O)(=O)[O-])S(=O)(=O)[O-])NC(=O)C4=CC=C(C=C4)NC(=O)NC5=CC=C(C=C5)C(=O)NC6=CC=C(C=C6)C(=O)NC7=C8C(=CC(=CC8=C(C=C7)S(=O)(=O)[O-])S(=O)(=O)[O-])S(=O)(=O)[O-].[Na+].[Na+].[Na+].[Na+].[Na+].[Na+] | ||
| Standard InChIKey | RJMCMLNRWDKUDB-UHFFFAOYSA-H | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C49H36N6O23S6.6Na/c56-45(50-29-9-1-27(2-10-29)47(58)54-37-17-19-39(81(67,68)69)35-21-33(79(61,62)63)23-41(43(35)37)83(73,74)75)25-5-13-31(14-6-25)52-49(60)53-32-15-7-26(8-16-32)46(57)51-30-11-3-28(4-12-30)48(59)55-38-18-20-40(82(70,71)72)36-22-34(80(64,65)66)24-42(44(36)38)84(76,77)78;;;;;;/h1-24H,(H,50,56)(H,51,57)(H,54,58)(H,55,59)(H2,52,53,60)(H,61,62,63)(H,64,65,66)(H,67,68,69)(H,70,71,72)(H,73,74,75)(H,76,77,78);;;;;;/q;6*+1/p-6 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | A potent and selective P2X1 antagonist (IC50 = 19 nM). Displays good selectivity over P2X2,(IC50 = 0.76 μM), P2X3 (IC50 = 1.62μM), P2X4 (IC50 > 300 μM), P2Y receptors and ecto-nucleotidases. |

NF 279 Dilution Calculator

NF 279 Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 0.7137 mL | 3.5686 mL | 7.1372 mL | 14.2745 mL | 17.8431 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.1427 mL | 0.7137 mL | 1.4274 mL | 2.8549 mL | 3.5686 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.0714 mL | 0.3569 mL | 0.7137 mL | 1.4274 mL | 1.7843 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0143 mL | 0.0714 mL | 0.1427 mL | 0.2855 mL | 0.3569 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0071 mL | 0.0357 mL | 0.0714 mL | 0.1427 mL | 0.1784 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
- NF 340
Catalog No.:BCC7785
CAS No.:202982-98-7
- Conantokin-R
Catalog No.:BCC5980
CAS No.:202925-60-8
- glucagon receptor antagonists 2
Catalog No.:BCC1594
CAS No.:202917-18-8
- glucagon receptor antagonists 3
Catalog No.:BCC1595
CAS No.:202917-17-7
- 7-Benzyloxyindole
Catalog No.:BCC8778
CAS No.:20289-27-4
- 4-Benzyloxyindole
Catalog No.:BCC8700
CAS No.:20289-26-3
- 8-Hydroxy-3,5,7,3',4',5'-hexamethoxyflavone
Catalog No.:BCN1506
CAS No.:202846-95-5
- Rosmarinic acid
Catalog No.:BCN5893
CAS No.:20283-92-5
- Safinamide Mesylate
Catalog No.:BCC2320
CAS No.:202825-46-5
- Ralfinamide mesylate
Catalog No.:BCC7844
CAS No.:202825-45-4
- BMS 191011
Catalog No.:BCC7448
CAS No.:202821-81-6
- Licoagrochalcone A
Catalog No.:BCC8197
CAS No.:202815-28-9
- Aporheine
Catalog No.:BCN4802
CAS No.:2030-53-7
- Clofazimine
Catalog No.:BCC4651
CAS No.:2030-63-9
- Saponarin
Catalog No.:BCN2280
CAS No.:20310-89-8
- Solamargine
Catalog No.:BCN2305
CAS No.:20311-51-7
- Procyanidin B1
Catalog No.:BCN6314
CAS No.:20315-25-7
- Tiliroside
Catalog No.:BCN4889
CAS No.:20316-62-5
- Solamarine
Catalog No.:BCN3806
CAS No.:20318-30-3
- 3,5-Diacetamido-4-methylbenzoic acid
Catalog No.:BCN1505
CAS No.:6633-37-0
- 3,4,5-Trimethoxy-trans-cinnamic acid
Catalog No.:BCN3423
CAS No.:20329-98-0
- 3,4-Dimethoxyphenol
Catalog No.:BCN4890
CAS No.:2033-89-8
- H-D-Arg-NH2.2HCl
Catalog No.:BCC2870
CAS No.:203308-91-2
- Daphnoretin
Catalog No.:BCN2473
CAS No.:2034-69-7
Effects of acute administration of and tachyphylaxis to alpha,beta-methylene ATP in the guinea-pig small intestine.[Pubmed:16364052]
Basic Clin Pharmacol Toxicol. 2005 Dec;97(6):369-73.
The aim of the present study was to assess the acute motility effects and desensitizing activity of the stable ATP analogue and P(2X) purinoceptor agonist alpha,beta-methylene ATP (alpha,beta-meATP) and the effect of alpha,beta-meATP desensitization on nerve-mediated cholinergic responses in the guinea-pig ileum in vitro. It was confirmed that alpha,beta-meATP (1-30 microM) causes neurally-mediated, cholinergic (tetrodotoxin- and atropine-sensitive) longitudinal contractions. These responses were not influenced by the ganglionic blocking drug hexamethonium (50 microM), or a combination of the adrenergic neurone blocking drug guanethidine (3 microM), the opioid receptor antagonist naloxone (0.5 microM) and the nitric oxide synthase inhibitor N(G)-nitro-L-arginine (L-NOARG; 100 microM), but were strongly reduced or abolished by the P2 purinoceptor antagonist PPADS (30 microM) or by tachyphylaxis evoked by 10 microM alpha,beta-meATP. The contractile effect of alpha,beta-meATP (3 microM) was moderately inhibited by 10 microM and strongly suppressed by 30 microM of NF 279, an antagonist predominantly affecting P2X1 purinoceptors, but left uninfluenced by the P2X(5,7) receptor antagonist Brilliant blue G. No relaxant effect of alpha,beta-meATP was detected in the concentration range of 1-30 microM. Tachyphylaxis to alpha,beta-meATP (1-10 microM) caused a moderate inhibition of the cholinergic (atropine-sensitive) contractile response of the ileum to electrical field stimulation (5 Hz for 5 sec.). This reduction was unaltered in the presence of guanethidine, naloxone and L-NOARG. Responses to nicotine (1 or 2 microM) were not reduced by alpha,beta-meATP tachyphylaxis. It is suggested that alpha,beta-meATP-sensitive P(2X) purinoceptors are involved in the prejunctional modulation of cholinergic neurotransmission between the myenteric plexus and longitudinal smooth muscle in the guinea-pig small intestine.
Pharmacologic characterization of intrinsic mechanisms controlling tone and relaxation of porcine lower esophageal sphincter.[Pubmed:16303917]
J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2006 Mar;316(3):1238-48.
The neurotransmitters mediating relaxation of lower esophageal sphincter (LES) were studied using circular LES strips from adult pigs in organ baths. LES relaxation by sodium nitroprusside (1 nM-3 microM), vasoactive intestinal peptide (VIP) and pituitary adenylate cyclase-activating peptide (PACAP; 1 nM-1 microM), ATP (10 microM-30 mM), and tricarbonyldichlororuthenum dimer (1 microM-1 mM) was unaffected by tetrodotoxin (1 microM) or l-N(G)-nitroarginine methyl ester (l-NAME; 100 microM). Calcitonin gene-related peptide (CGRP; 1 nM-1 microM) did not affect LES tone. ATP relaxation was blocked by 1 microM apamin and the P2Y(1) antagonist MRS 2179 (N6-methyl 2'-deoxyadenosine 3',5'-bisphosphate; 10 microM). Apamin inhibited PACAP relaxation. VIP and PACAP relaxation was blocked by 10 U/ml alpha-chymotrypsin. L-NAME (-62.52 +/- 13.13%) and 1H-[1,2,4]oxadiazole-[4,3-alpha]quinoxalin-1-one (ODQ; 10 microM, -67.67 +/- 6.80%) similarly inhibited electrical LES relaxation, and apamin blocked non-nitrergic relaxation. Nicotine relaxation (100 microM) was inhibited by L-NAME (-60.37 +/- 10.8%) and ODQ (-41.90 +/- 7.89%), and apamin also blocked non-nitrergic relaxation. Non-nitrergic and apamin-sensitive LES relaxation by electrical stimulation or nicotine was strongly inhibited by MRS 2179, slightly inhibited by alpha-chymotrypsin and the P2X(1,2,3) receptor antagonist NF 279 (8,8 cent-[carbonylbis(imino-4,1-phenylenecarbonylimino-4,1-phenylenecarbonylimino)]bi s-1,3,5-naphthalenetrisulfonic acid hexasodium salt; 10 microM), and unaffected by tin protoporphyrin IX (100 microM). Porcine LES relaxation after stimulation of intrinsic inhibitory motor neurons is mediated by two main neuromuscular pathways: nitric oxide through guanylate cyclase signaling and apamin-insensitive mechanisms and by non-nitrergic apamin-sensitive neurotransmission mainly mediated by ATP, ADP, or a related purine acting on P2Y1 receptors and a minor contribution of purinergic P2X1,2,3 receptors and PACAP. Nitrergic and purinergic co-transmitters show parallel effects of similar magnitude without major interplay. Our study shows no role for CGRP and only a minor one for VIP and carbon monoxide in porcine LES relaxation.
Functional evidence that ATP or a related purine is an inhibitory NANC neurotransmitter in the mouse jejunum: study on the identity of P2X and P2Y purinoceptors involved.[Pubmed:14530212]
Br J Pharmacol. 2003 Nov;140(6):1108-16.
1. Conflicting views exist on whether ATP is a neurotransmitter in the enteric nervous system. We investigated the role of ATP in enteric transmission in circular muscle strips of the mouse jejunum. 2. On PGF2alpha-precontracted muscle strips and in the presence of atropine and guanethidine, electrical field stimulation (EFS, 1-8 Hz) of nonadrenergic noncholinergic (NANC) nerves induced transient relaxations that were abolished by the nerve-conductance blocker tetrodotoxin. The NO synthase blocker l-nitroarginine (l-NOARG) partially inhibited the NANC relaxations to EFS, but fast-twitch relaxations to EFS were still observed in the presence of l-NOARG. 3. In the presence of l-NOARG, ATP, the P2X receptor agonist alphabetaMeATP and the P2Y receptor agonist ADPbetaS relaxed jejunal muscle strips. Tetrodotoxin did not affect the relaxation to ATP and ADPbetaS, but inhibited that to alphabetaMeATP. 4. The l-NOARG-resistant NANC relaxations to EFS were almost abolished by apamin, a blocker of small-conductance Ca2+ activated K+ channels, and by suramin and PPADS, blockers of P2 purinoceptors. Relaxations to ATP were almost abolished by apamin and suramin but not affected by PPADS. 5. Desensitisation of alphabetaMeATP-sensitive P2X receptors, the P2X receptor blocker Evans blue and the P2X1,2,3 receptor blocker NF 279 inhibited the l-NOARG-resistant NANC relaxations to EFS and that to alphabetaMeATP without affecting the relaxation to ADPbetaS. Brilliant blue G, a P2X2,5,7 receptor blocker, did not affect the relaxations to EFS. 6. Desensitisation of P2Y receptors and MRS 2179, a P2Y1 receptor blocker, virtually abolished the l-NOARG-resistant NANC relaxations to EFS and the relaxation to ADPbetaS without affecting the relaxation to alphabetaMeATP. 7. Dipyridamole, an adenosine uptake inhibitor, or theophylline and 8-phenyltheophylline, blockers of P1 and A1 purinoceptors, respectively, did not affect the purinergic NANC relaxations to EFS. 8. Our results suggest that ATP or a related purine acts as an inhibitory NANC neurotransmitter in the mouse jejunum, activating P2 but not P1 purinoceptors. Relaxations to the purinergic NANC neurotransmitter mainly involve P2Y receptors of the P2Y1 subtype that are located postjunctionally. Purinergic NANC neurotransmission also involves P2X receptors, most likely of the P2X1 and P2X3 subtype, located pre- and/or postjunctionally.
Antagonism by the suramin analogue NF279 on human P2X(1) and P2X(7) receptors.[Pubmed:10650169]
Eur J Pharmacol. 2000 Jan 17;387(3):245-52.
The effect of the suramin analogue 8,8'-(carbonylbis(imino-4, 1-phenylenecarbonylimino-4,1-phenylenecarbonylimino))bis(1,3 , 5-naphthalenetrisulfonic acid) (NF279) was analyzed on human P2X(1) and P2X(7) receptor subtypes (human P2X(1) and human P2X(7)) heterologously expressed in Xenopus oocytes using the two-microelectrode voltage-clamp technique. At activating ATP concentrations of 1 microM (human P2X(1)) and 10 microM ATP (human P2X(7)), IC(50) values of 0.05 microM and 2.8 microM were found for human P2X(1) and human P2X(7) receptors, respectively. An increase in the activating [ATP] shifted the NF279 concentration-inhibition curve rightwards for both receptors. NF279 slowed the activation of both human P2X(1) and human P2X(7) as well as the desensitization of human P2X(1). The data support a model in which desensitization of P2X(1) is dependent on preceding activation of these P2X receptors. It is concluded that NF279 acts as a competitive antagonist with much higher potency at human P2X(1) than at P2X(7) receptors. NF279 may hence be suited to discriminate between both receptors in native tissues.
The suramin analogue NF279 is a novel and potent antagonist selective for the P2X(1) receptor.[Pubmed:10963748]
Neuropharmacology. 2000 Aug 23;39(11):2044-53.
The suramin analogue 8,8'-(carbonylbis(imino-4, 1-phenylenecarbonylimino-4,1-phenylenecarbonylimino)) bis(1,3,5-naphthalenetrisul fonic acid) (NF279) was analysed with respect to its potency and P2X receptor subtype selectivity. Two-electrode voltage-clamp measurements were performed with Xenopus laevis oocytes expressing homomultimeric rat P2X(1), P2X(2), P2X(3) and human P2X(4) receptors. For the fast desensitising P2X(1) and P2X(3) receptors, IC(50) values strongly depended on whether oocytes were pre-incubated with NF279 prior to ATP superfusion or exposed to NF279 simultaneously with ATP. With a 10 s pre-incubation period of NF279, IC(50) values of 19 nM and 1.62 microM were obtained for rat P2X(1) and P2X(3), respectively. Without pre-incubation, IC(50) values amounted to 2 microM and 85.5 microM for P2X(1) and P2X(3), respectively. For the non-desensitising rat P2X(2) receptor NF279 appeared to act as a competitive antagonist with an IC(50) value of 0.76 microM and a K(B) value of 0.36 microM, as derived from Schild analysis. P2X(4) receptors were the least sensitive subtypes for NF279 (IC(50)>300 microM). The antagonism was fully reversible at all P2X subtypes analysed. Our results indicate that NF279 is a potent P2X(1) receptor-selective and reversible antagonist.
NF279: a novel potent and selective antagonist of P2X receptor-mediated responses.[Pubmed:9683026]
Eur J Pharmacol. 1998 May 29;350(1):R5-6.
8,8'-(Carbonylbis(imino-4, 1 -phenylenecarbonylimino-4,1-phenylenecarbonylimino))bis(1,3, 5-naphthalenetrisulfonic acid) (NF279) antagonized P2X receptor-mediated contractions in rat vas deferens, evoked by alpha,beta-methylene ATP (10 microM; pIC50=5.71) without affecting responses mediated via alpha1A-adrenoceptors, adenosine A1 and A2B receptors, histamine H1, muscarinic M3 and nicotinic receptors. The low inhibitory potency of NF279 on P2Y receptors in guinea-pig taenia coli (pA2=4.10) and at ecto-nucleotidases in folliculated Xenopus laevis oocytes (IC50 > 100 microM) indicates that NF279 is a novel specific and selective P2X receptor antagonist.


