PD 176252GRP (BB2) and NMB (BB1) receptor antagonist CAS# 204067-01-6 |
- AZD4547
Catalog No.:BCC3711
CAS No.:1035270-39-3
- NVP-BGJ398 phosphate
Catalog No.:BCC1814
CAS No.:1310746-10-1
- Pazopanib (GW-786034)
Catalog No.:BCC1286
CAS No.:444731-52-6
- Nintedanib (BIBF 1120)
Catalog No.:BCC3661
CAS No.:656247-17-5
- BGJ398
Catalog No.:BCC1278
CAS No.:872511-34-7
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 204067-01-6 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 9829828 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C32H36N6O5 | M.Wt | 584.67 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | Soluble to 100 mM in DMSO | ||
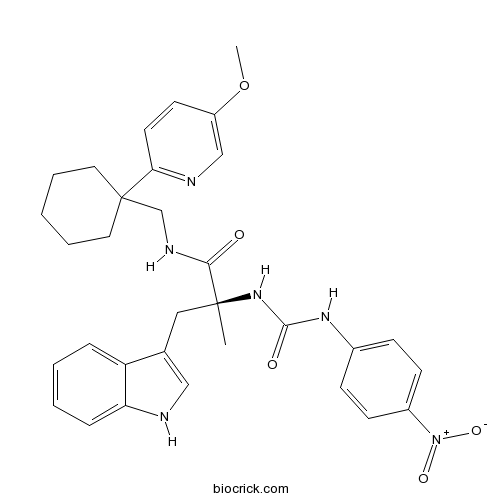
| Chemical Name | (2S)-3-(1H-indol-3-yl)-N-[[1-(5-methoxypyridin-2-yl)cyclohexyl]methyl]-2-methyl-2-[(4-nitrophenyl)carbamoylamino]propanamide | ||
| SMILES | CC(CC1=CNC2=CC=CC=C21)(C(=O)NCC3(CCCCC3)C4=NC=C(C=C4)OC)NC(=O)NC5=CC=C(C=C5)[N+](=O)[O-] | ||
| Standard InChIKey | NNFUWNLENRUDHR-HKBQPEDESA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C32H36N6O5/c1-31(18-22-19-33-27-9-5-4-8-26(22)27,37-30(40)36-23-10-12-24(13-11-23)38(41)42)29(39)35-21-32(16-6-3-7-17-32)28-15-14-25(43-2)20-34-28/h4-5,8-15,19-20,33H,3,6-7,16-18,21H2,1-2H3,(H,35,39)(H2,36,37,40)/t31-/m0/s1 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Non-peptide gastrin-releasing peptide receptor (GRP-R, BB2) and neuromedin B receptor (NMB-R, BB1) antagonist (Ki values are 0.17 and 1.0 nM for BB1 and BB2 respectively). Inhibits proliferation of rat C6 glioma cells (IC50 = 2 μM) and inhibits NCI-H1299 xenograft proliferation in nude mice (IC50 = 5 μM). |

PD 176252 Dilution Calculator

PD 176252 Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 1.7104 mL | 8.5518 mL | 17.1037 mL | 34.2073 mL | 42.7592 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.3421 mL | 1.7104 mL | 3.4207 mL | 6.8415 mL | 8.5518 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.171 mL | 0.8552 mL | 1.7104 mL | 3.4207 mL | 4.2759 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0342 mL | 0.171 mL | 0.3421 mL | 0.6841 mL | 0.8552 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0171 mL | 0.0855 mL | 0.171 mL | 0.3421 mL | 0.4276 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
- SU5416
Catalog No.:BCC1974
CAS No.:204005-46-9
- Helioxanthin derivative 5-4-2
Catalog No.:BCC5414
CAS No.:203935-39-1
- Fmoc-ß-HoGlu(OtBu)-OH
Catalog No.:BCC3234
CAS No.:203854-49-3
- MMAD
Catalog No.:BCC1774
CAS No.:203849-91-6
- 27-Hydroxycholesterol
Catalog No.:BCN2750
CAS No.:20380-11-4
- Istaroxime
Catalog No.:BCC1660
CAS No.:203737-93-3
- Arctiin
Catalog No.:BCN1090
CAS No.:20362-31-6
- Hastacine
Catalog No.:BCN2086
CAS No.:20361-77-7
- DMNB
Catalog No.:BCC7259
CAS No.:20357-25-9
- 2,4,6,6-Tetramethyl-3(6H)-pyridinone
Catalog No.:BCN4893
CAS No.:203524-64-5
- Brefeldin A
Catalog No.:BCC4387
CAS No.:20350-15-6
- (-)-Maackiain
Catalog No.:BCN4892
CAS No.:2035-15-6
- (2-Aminoethyl)phosphonic acid
Catalog No.:BCN1762
CAS No.:2041-14-7
- Anabasamine
Catalog No.:BCN2148
CAS No.:20410-87-1
- 4'-Hydroxy-2-O-methylanigorufone
Catalog No.:BCN7179
CAS No.:204134-70-3
- Caesalmin E
Catalog No.:BCN7247
CAS No.:204185-91-1
- Boc-Ser-OH.H2O
Catalog No.:BCC2599
CAS No.:204191-40-2
- Oseltamivir phosphate
Catalog No.:BCC4690
CAS No.:204255-11-8
- RS 45041-190 hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC5682
CAS No.:204274-74-8
- NS 2028
Catalog No.:BCC6212
CAS No.:204326-43-2
- Fmoc-β-Homo-Phe-OH
Catalog No.:BCC2629
CAS No.:204384-69-0
- BCH
Catalog No.:BCC7993
CAS No.:20448-79-7
- Talnetant hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC1982
CAS No.:204519-66-4
- Epitaraxerol
Catalog No.:BCN4677
CAS No.:20460-33-7
PD 176252--the first high affinity non-peptide gastrin-releasing peptide (BB2) receptor antagonist.[Pubmed:9873586]
Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 1998 Sep 22;8(18):2589-94.
In this paper we describe the development of a novel series of non-peptide, "balanced" neuromedin-B preferring (BB1)/gastrin-releasing peptide preferring (BB2) receptor ligands as exemplified by PD 176252. PD 176252, which exhibits nanomolar affinity for both the BB1 (Ki = 0.15 nM) and BB2 (Ki = 1.0 nM) receptors, has been demonstrated to be a competitive antagonist at these bombesin receptor subtypes.
Gastrin-releasing peptide/neuromedin B receptor antagonists PD176252, PD168368, and related analogs are potent agonists of human formyl-peptide receptors.[Pubmed:20943772]
Mol Pharmacol. 2011 Jan;79(1):77-90.
N-Formyl peptide receptors (FPRs) are G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs) involved in host defense and sensing cellular dysfunction. Thus, FPRs represent important therapeutic targets. In the present studies, we screened 32 ligands (agonists and antagonists) of unrelated GPCRs for their ability to induce intracellular Ca(2)+ mobilization in human neutrophils and HL-60 cells transfected with human FPR1, FPR2, or FPR3. Screening of these compounds demonstrated that antagonists of gastrin-releasing peptide/neuromedin B receptors (BB(1)/BB(2)) PD168368 [(S)-a-methyl-a-[[[(4-nitrophenyl)amino]carbonyl]amino]-N-[[1-(2-pyridinyl) cyclohexyl]methyl]-1H-indole-3-propanamide] and PD176252 [(S)-N-[[1-(5-methoxy-2-pyridinyl)cyclohexyl]methyl]-a-methyl-a-[[-(4-nitrophenyl )amino]carbonyl]amino-1H-indole-3-propanamide] were potent mixed FPR1/FPR2 agonists, with nanomolar EC(5)(0) values. Cholecystokinin-1 receptor agonist A-71623 [Boc-Trp-Lys(epsilon-N-2-methylphenylaminocarbonyl)-Asp-(N-methyl)-Phe-NH(2)] was also a mixed FPR1/FPR2 agonist, but with a micromolar EC(5)(0). Screening of 56 Trp- and Phe-based PD176252/PD168368 analogs and 41 related nonpeptide/nonpeptoid analogs revealed 22 additional FPR agonists. Most were potent mixed FPR1/FPR2/FPR3 agonists with nanomolar EC(5)(0) values for FPR2, making them among the most potent nonpeptide FPR2 agonists reported to date. In addition, these agonists were also potent chemoattractants for murine and human neutrophils and activated reactive oxygen species production in human neutrophils. Molecular modeling of the selected agonists using field point methods allowed us to modify our previously reported pharmacophore model for the FPR2 ligand binding site. This model suggests the existence of three hydrophobic/aromatic subpockets and several binding poses of FPR2 agonists in the transmembrane region of this receptor. These studies demonstrate that FPR agonists could include ligands of unrelated GPCR and that analysis of such compounds can enhance our understanding of pharmacological effects of these ligands.
Nonpeptide gastrin releasing peptide receptor antagonists inhibit the proliferation of lung cancer cells.[Pubmed:12909192]
Eur J Pharmacol. 2003 Aug 1;474(1):21-9.
The ability of nonpeptide antagonists to interact with gastrin releasing peptide receptors on lung cancer cells was investigated. PD176252 (3-(1H-Indol-3-yl)-N-[1-(5-methoxy-pyridin-2-yl)-cyclohexylmethyl]-2-methyl-2-[3- (4-nitro-phenyl)-ureido]-propionamide) and PD168368 (3-(1H-Indol-3-yl)-2-methyl-2-[3(4-nitro-phenyl)-ureido]-N-(1-pyridin-2-yl-cycloh exylmethyl)-propionamide) inhibited specific 125I-gastrin releasing peptide binding to NCI-H1299 cells with IC50 values of 20 and 1500 nM, respectively. Similar binding results were obtained using NCI-H157, H345 and N592 human lung cancer cells. PD176252 inhibited the ability of 1 nM bombesin to cause elevation of cytosolic calcium in Fura-2 loaded NCI-H345 or H1299 cells, whereas it had no effect on basal cytosolic calcium. PD176252 antagonized the ability of 10 nM bombesin to cause elevation of c-fos mRNA in NCI-H1299 cells. Also, PD176252 inhibited the ability of 100 nM bombesin to cause tyrosine phosphorylation of focal adhesion kinase in NCI-H1299 cells. Using a [3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyl-2H-tetrazolium bromide] assay, PD176252 was more potent than PD168368 at inhibiting NCI-H1299 proliferation. Also, 1 microM PD176252 significantly inhibited lung cancer colony number in vitro. PD176252 in a dose-dependent manner inhibited NCI-H1299 xenograft growth in nude mice in vivo. These results indicate that PD176252 is a gastrin releasing peptide receptor antagonist, which inhibits the proliferation of lung cancer cells.
Nonpeptide neuromedin B receptor antagonists inhibit the proliferation of C6 cells.[Pubmed:11104826]
Eur J Pharmacol. 2000 Dec 8;409(2):133-42.
The ability of nonpeptide antagonists to interact with neuromedin B receptors on C6 cells was investigated. 2-[3-(2, 6-Diisopropyl-phenyl)-ureido]3-(1H-indol-3-yl)-2-methyl-N-(1-pyridin- 2-yl-cyclohexylmethyl)-proprionate (PD165929), 3-(1H-indol-3-yl)-2-methyl-2-[3(4-nitro-phenyl)-ureido]-N-(1-pyridin- 2-yl-cyclohexylmethyl)-propionamide (PD168368) and 3-(1H-indol-3-yl)-N-[1-(5-methoxy-pyridin-2-yl)-cyclohexylmethyl]- 2-m ethyl-2-[3-(4-nitro-phenyl)-ureido]-propionamide (PD176252) inhibited (125I-Tyr0)neuromedin B binding with IC50 values of 2000, 40 and 50 nM, respectively. Because neuromedin B is a G-protein coupled serpentine receptor, the effects of neuromedin B antagonists on second messenger production and proliferation were investigated. PD168368 inhibited the ability of 10 nM neuromedin B to cause elevation of cytosolic Ca2+, whereas it had no effect on basal cytosolic Ca2+. PD168368 inhibited the ability of 100 nM neuromedin B to cause elevation of c-fos mRNA. Also, PD168368 in a dose-dependent manner inhibited the ability of 100 nM neuromedin B to cause phosphorylation of focal adhesion kinase. Using a [3-(4,5 dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyl-2H-tetrazolium bromide] assay, the order of antagonist potency to inhibit C6 proliferation was PD168368=PD176252>PD165929. Also, 1 microM PD168368 and PD176252 significantly inhibited colony number using a proliferation assay in vitro. PD168368 significantly inhibited C6 xenograft growth in nude mice in vivo. These results indicate that PD168368 is a C6 cell neuromedin B receptor antagonist, which inhibits proliferation.


