DOXO-EMCHProdrug of doxorubicin CAS# 151038-96-9 |
- Gatifloxacin
Catalog No.:BCC1064
CAS No.:112811-59-3
- Dexrazoxane HCl (ICRF-187, ADR-529)
Catalog No.:BCC1087
CAS No.:149003-01-0
- Doxorubicin (Adriamycin) HCl
Catalog No.:BCC1117
CAS No.:25316-40-9
- Etoposide
Catalog No.:BCC1151
CAS No.:33419-42-0
- Genistein
Catalog No.:BCN5499
CAS No.:446-72-0
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 151038-96-9 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 9576002 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C37H42N4O13 | M.Wt | 750.75 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Synonyms | Doxorubicin-EMCH | ||
| Solubility | DMSO | ||
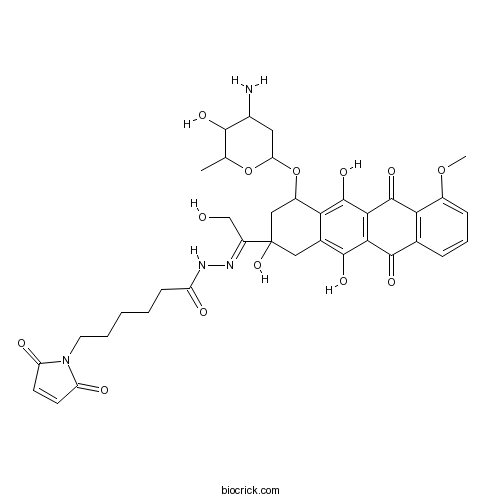
| Chemical Name | N-[(E)-[1-[4-(4-amino-5-hydroxy-6-methyloxan-2-yl)oxy-2,5,12-trihydroxy-7-methoxy-6,11-dioxo-3,4-dihydro-1H-tetracen-2-yl]-2-hydroxyethylidene]amino]-6-(2,5-dioxopyrrol-1-yl)hexanamide | ||
| SMILES | CC1C(C(CC(O1)OC2CC(CC3=C(C4=C(C(=C23)O)C(=O)C5=C(C4=O)C=CC=C5OC)O)(C(=NNC(=O)CCCCCN6C(=O)C=CC6=O)CO)O)N)O | ||
| Standard InChIKey | OBMJQRLIQQTJLR-JRZNSJKLSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C37H42N4O13/c1-17-32(46)20(38)13-27(53-17)54-22-15-37(51,23(16-42)39-40-24(43)9-4-3-5-12-41-25(44)10-11-26(41)45)14-19-29(22)36(50)31-30(34(19)48)33(47)18-7-6-8-21(52-2)28(18)35(31)49/h6-8,10-11,17,20,22,27,32,42,46,48,50-51H,3-5,9,12-16,38H2,1-2H3,(H,40,43)/b39-23+ | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | DOXO-EMCH is a 6-maleimidocaproyl hydrazone derivative of Doxorubicin, is an albumin binding prodrug.In Vitro:DOXO-EMCH is an an acid-sensitive prodrug of Doxorubicin that binds rapidly and selectively to the cysteine-34 position of circulating albumin[1].In Vivo:DOXO-EMCH is a 6-maleimidocaproyl hydrazone derivative of Doxorubicin. DOXO-EMCH unlike its free Doxorubicin parent, achieves complete remissions in a murine renal cell carcinoma model and in 2 breast carcinoma xenograft models. Moreover, DOXO-EMCH is also superior to Doxorubicin with regard to drug toxicity in mice, rats and dogs, and exhibits a good safety profile[2]. References: | |||||

DOXO-EMCH Dilution Calculator

DOXO-EMCH Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 1.332 mL | 6.66 mL | 13.32 mL | 26.64 mL | 33.3 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.2664 mL | 1.332 mL | 2.664 mL | 5.328 mL | 6.66 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.1332 mL | 0.666 mL | 1.332 mL | 2.664 mL | 3.33 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0266 mL | 0.1332 mL | 0.2664 mL | 0.5328 mL | 0.666 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0133 mL | 0.0666 mL | 0.1332 mL | 0.2664 mL | 0.333 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
DOXO-EMCH (151038-96-9) is defined as Double bond geometry unknown, also can be called as INNO-206 (1361644-26-9) with Double bond geometry (2E). INNO-206 (Aldoxorubicin) is the 6-maleimidocaproyl hydrazone derivative prodrug of the anthracycline antibiotic doxorubicin (DOXO-EMCH) with antineoplastic activity. Following intravenous administration, doxorubicin prodrug INNO-206 binds selectively to the cysteine-34 position of albumin via its maleimide moiety. Doxorubicin is released from the albumin carrier after cleavage of the acid-sensitive hydrazone linker within the acidic environment of tumors and, once located intracellularly, intercalates DNA, inhibits DNA synthesis, and induces apoptosis. Albumin tends to accumulate in solid tumors as a result of high metabolic turnover, rapid angiogenesis, hyervasculature, and impaired lymphatic drainage. Because of passive accumulation within tumors, this agent may improve the therapeutic effects of doxorubicin while minimizing systemic toxicity. In a phase I study, INNO-206 showed a good safety profile at doses up to 260 mg/m2 doxorubicin equivalents. Although not the primary end point of the phase I study, INNO-206 was able to induce tumor regressions in breast cancer, small cell lung cancer and sarcoma.
- H-Phe-OtBu.HCl
Catalog No.:BCC3011
CAS No.:15100-75-1
- Boc-Lys(Boc)-OH.DCHA
Catalog No.:BCC3413
CAS No.:15098-69-8
- 7,8-Didehydrocimigenol
Catalog No.:BCN3343
CAS No.:150972-72-8
- 2,4,4'-Trihydroxydihydrochalcone
Catalog No.:BCN7365
CAS No.:15097-74-2
- Tirofiban hydrochloride monohydrate
Catalog No.:BCC2003
CAS No.:150915-40-5
- D-allo-Ile-OH
Catalog No.:BCC2966
CAS No.:1509-35-9
- Aurantiamide benzoate
Catalog No.:BCN8043
CAS No.:150881-02-0
- Euonymine
Catalog No.:BCN3084
CAS No.:150881-01-9
- Bis(phenylacetyl) disulfide
Catalog No.:BCC8887
CAS No.:15088-78-5
- Uralenol-3-methylether
Catalog No.:BCN7993
CAS No.:150853-98-8
- Micromelin
Catalog No.:BCN1672
CAS No.:15085-71-9
- Boc-Orn(Fmoc)-OH
Catalog No.:BCC3429
CAS No.:150828-96-9
- L-701,252
Catalog No.:BCC6755
CAS No.:151057-13-5
- Moxifloxacin
Catalog No.:BCC4227
CAS No.:151096-09-2
- Haloperidol hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC4251
CAS No.:1511-16-6
- 4-Difluoromethoxy-3-hydroxybenzaldehyde
Catalog No.:BCC8706
CAS No.:151103-08-1
- 8-(6-Hydroperoxy-3,7-dimethyl-2,7-octadienyloxy)psoralen
Catalog No.:BCN1558
CAS No.:151121-39-0
- CL 316243 disodium salt
Catalog No.:BCC7091
CAS No.:151126-84-0
- 4'-Hydroxy-2,4-dimethoxychalcone
Catalog No.:BCC8708
CAS No.:151135-64-7
- Borapetoside D
Catalog No.:BCN6612
CAS No.:151200-48-5
- Borapetoside E
Catalog No.:BCN6571
CAS No.:151200-49-6
- Borapetoside F
Catalog No.:BCN6413
CAS No.:151200-50-9
- Poricoic acid AM
Catalog No.:BCN8499
CAS No.:151200-92-9
- Primin
Catalog No.:BCN2729
CAS No.:15121-94-5
The 6-maleimidocaproyl hydrazone derivative of doxorubicin (DOXO-EMCH) is superior to free doxorubicin with respect to cardiotoxicity and mitochondrial damage.[Pubmed:17131338]
Int J Cancer. 2007 Feb 15;120(4):927-34.
Doxorubicin causes a chronic cardiomyopathy in which genetic and functional lesions of mitochondria accumulate in the long-term and explain in part the delayed onset of heart dysfunction. DOXO-EMCH a 6-maleimidocaproyl hydrazone derivative of doxorubicin, is an albumin binding prodrug which has entered clinical trials because of its superior antitumor and toxicological profile. In the present work, we examined the chronic cardiotoxicity of DOXO-EMCH in direct comparison with doxorubicin. Rats (11 weeks of age) were treated with intravenous doxorubicin (0.8 mg/kg weekly for 7 weeks), an equimolar dose of DOXO-EMCH (1.1 mg/kg), or with 3.3 mg/kg of DOXO-EMCH. Controls received saline. Animals were euthanized at 48th week. Rats exposed to doxorubicin had a severe clinical, and histopathological cardiomyopathy with depressed myocardial activity of cytochrome c-oxidase (COX, 26% of controls), reduced expression of the mtDNA-encoded COX II subunit, decreased mtDNA copy numbers (46% of controls), and high levels of malondialdehyde and superoxide (787% of controls). All parameters were highly correlated with myocardial damage. Both DOXO-EMCH groups did not differ from controls with regard to clinical symptomatology, mortality and mitochondrial enzymes, although the myocardia of the high-dose group had slightly increased histopathological abnormalities, depressed mtDNA copies (74% of controls) and elevated superoxide levels (347% of controls). Doxorubicin-exposed hearts and to a lesser extent the myocardia of both DOXO-EMCH groups contained mtDNA-deletions. In summary both DOXO-EMCH doses were superior over doxorubicin with respect to clinical and histopathological evidence of cardiomyopathy, myocardial COX-activity, COX II expression, mtDNA-content, mtDNA mutation loads and superoxide production in rats.
Acute and repeat-dose toxicity studies of the (6-maleimidocaproyl)hydrazone derivative of doxorubicin (DOXO-EMCH), an albumin-binding prodrug of the anticancer agent doxorubicin.[Pubmed:17334177]
Hum Exp Toxicol. 2007 Jan;26(1):19-35.
The (6-maleimidocaproyl)hydrazone derivative of doxorubicin (DOXO-EMCH) is an albumin-binding prodrug of doxorubicin with acid-sensitive properties that demonstrates superior antitumor efficacy in murine tumor models, and has been evaluated in a phase I study. In order to establish the toxicity profile of this prodrug, acute and repeat-dose toxicity studies were performed with DOXO-EMCH in CD1-mice, Sprague-Dawley rats and Beagle dogs. Although the objective of the acute toxicity studies was not the determination of LD50 values, the LD50 of DOXO-EMCH was >60 mg/kg doxorubicin equivalents in both male and female mice (the LD50 of doxorubicin in CD-1 mice is -12 mg/kg). In Sprague-Dawley rats, the LD50 was 23.4 and 45.9 mg/kg doxorubicin equivalents for males and females, respectively. For comparison, the LD50 of doxorubicin in Sprague-Dawley rats is -10.5 mg/kg. The major clinical sign noted following intravenous administration of DOXO-EMCH in mice and rats was a dose-dependent peripheral neuropathy which, in general, developed as a delayed toxicity 1-3 weeks after application. The observed neurotoxicity has been well documented for Sprague-Dawley rats treated with doxorubicin at a dose of 5 and 10 mg/kg. In Beagle dogs, LD10 was not reached for DOXO-EMCH at 4.5 mg/kg doxorubicin equivalents. A four-cycle intravenous study with DOXO-EMCH at dose levels of 4 x 2.5, 5.0 or 7.5 mg/kg doxorubicin equivalents in rats revealed approximately three-fold less side effects on the hemolymphoreticular system when compared to 4 x 2.5 mg/kg doxorubicin dose, whereas effects on the testes/oligospermia seem to be comparable between both drugs at equitoxic dose. A No Observable Adverse Effect Level (NOAEL) for DOXO-EMCH of 4 x 2.5 mg/kg doxorubicin equivalents was established in this study. This dose is equivalent to the maximum tolerated dose (MTD) of doxorubicin in rats. In a two-cycle study over a period of 6 weeks in Beagle dogs (intravenous administration of DOXO-EMCH at dose levels of 1.5, 3.0 or 4.5 mg/kg doxorubicin equivalents), dose-related systemic histamine-like reactions within the first 3 hours after injection were noted in all treated groups. Only transient and temporary effects on hematology, urinary function, as well as on histopathology in mid- and/or high-dose animals, were observed. The low dose of 2 x 1.5 mg/kg was considered to be the NOAEL in this study, which is equivalent to twice the MTD o f doxorubicin i nBeagle dogs. In summary, the toxicity studies with DOXO-EMCH in mice, rats or dogs have not identified any other special toxicity when compared to the toxicity data for doxorubicin. Preclinical tolerance of DOXO-EMCH was higher in mice, rats and dogs compared to doxorubicin. A dose of 20 mg/m2 doxorubicin equivalents was recommended as the starting dose for a phase I study with DOXO-EMCH.
DOXO-EMCH (INNO-206): the first albumin-binding prodrug of doxorubicin to enter clinical trials.[Pubmed:17501697]
Expert Opin Investig Drugs. 2007 Jun;16(6):855-66.
The (6-maleimidocaproyl)hydrazone derivative of doxorubicin (DOXO-EMCH) is an albumin-binding prodrug of doxorubicin with acid-sensitive properties that demonstrates superior antitumor efficacy in murine tumor models and a favorable toxicity profile in mice, rats and dogs, including significantly reduced cardiotoxicity. After intravenous administration, DOXO-EMCH binds rapidly to the Cys-34 position of circulating albumin and accumulates in solid tumors due to passive targeting. In a clinical Phase I study, the dose of doxorubicin could be increased by a factor of 4.5-340 mg/m(2) when 75 mg/m(2) of free doxorubicin is considered to be the dose that can be administered as a single agent concomitant with the typical spectrum of side effects (i.e., myelotoxicity and mucositis). DOXO-EMCH was able to induce tumor regressions in anthracycline-sensitive tumors (i.e., breast cancer, small cell lung cancer and sarcoma). Phase II studies will be initiated at the beginning of 2007.


