FH1(BRD-K4477)Enhance cultured hepatocyte function CAS# 2719-05-3 |
- BAY 87-2243
Catalog No.:BCC4131
CAS No.:1227158-85-1
- PX 12
Catalog No.:BCC2436
CAS No.:141400-58-0
- DMOG
Catalog No.:BCC2433
CAS No.:89464-63-1
- KC7F2
Catalog No.:BCC2434
CAS No.:927822-86-4
- IOX2(Glycine)
Catalog No.:BCC2229
CAS No.:931398-72-0
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 2719-05-3 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 94990 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C17H18N2O2 | M.Wt | 282.34 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Synonyms | NSC 12407, BRD-K4477 | ||
| Solubility | DMSO : 13 mg/mL (46.04 mM; Need ultrasonic and warming) | ||
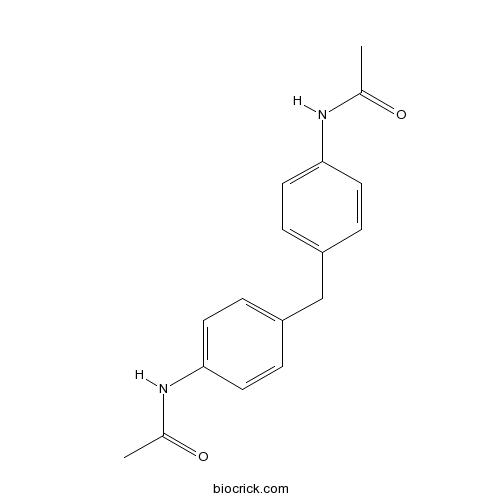
| Chemical Name | N-[4-[(4-acetamidophenyl)methyl]phenyl]acetamide | ||
| SMILES | CC(=O)NC1=CC=C(C=C1)CC2=CC=C(C=C2)NC(=O)C | ||
| Standard InChIKey | OEXMNSOPAKOPEF-UHFFFAOYSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C17H18N2O2/c1-12(20)18-16-7-3-14(4-8-16)11-15-5-9-17(10-6-15)19-13(2)21/h3-10H,11H2,1-2H3,(H,18,20)(H,19,21) | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Enhances differentiation of induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs) to hepatocytes; also promotes the maturation of iPSC-derived hepatocytes. |

FH1(BRD-K4477) Dilution Calculator

FH1(BRD-K4477) Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 3.5418 mL | 17.7091 mL | 35.4183 mL | 70.8366 mL | 88.5457 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.7084 mL | 3.5418 mL | 7.0837 mL | 14.1673 mL | 17.7091 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.3542 mL | 1.7709 mL | 3.5418 mL | 7.0837 mL | 8.8546 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0708 mL | 0.3542 mL | 0.7084 mL | 1.4167 mL | 1.7709 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0354 mL | 0.1771 mL | 0.3542 mL | 0.7084 mL | 0.8855 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
FH1 is a small molecule that can enhance the functions of cultured hepatocytes [1].
FH1 belongs to the function-only hits which are screened out by their ability to permit renewable sourcing of functional human hepatocytes. Besides that, FH1 can promote differentiation of iPS-derived hepatocytes towards a more mature phenotype. It doubles albumin secretion during the differentiation of iPS cells into iHeps. Cultures treated with FH1 contain larger colonies of iHeps were with more pronounced hepatocyte morphologies. Moreover, treatment of FH1 also resulted in the increase of CYP3A4 levels and the decrease of AFP secretion [1].
References:
[1] Shan J, Schwartz R E, Ross N T, et al. Identification of small molecules for human hepatocyte expansion and iPS differentiation. Nature chemical biology, 2013.
- LY 393558
Catalog No.:BCC7660
CAS No.:271780-64-4
- Thonningianin A
Catalog No.:BCN2774
CAS No.:271579-11-4
- SD-06
Catalog No.:BCC1937
CAS No.:271576-80-8
- 3-Tritylmercapto-Propionicacid
Catalog No.:BCC2846
CAS No.:27144-18-9
- Thevetin B
Catalog No.:BCN4046
CAS No.:27127-79-3
- MMK 1
Catalog No.:BCC6037
CAS No.:271246-66-3
- Paradol
Catalog No.:BCC1837
CAS No.:27113-22-0
- Solasurine
Catalog No.:BCN2694
CAS No.:27028-76-8
- H-D-Glu(OMe)-OMe.HCl
Catalog No.:BCC2941
CAS No.:27025-25-8
- 2'-Methoxykurarinone
Catalog No.:BCN2986
CAS No.:270249-38-2
- alpha-Hederin
Catalog No.:BCN5159
CAS No.:27013-91-8
- 17-Hydroxy-1a,2a-methylenepregna-4,6-diene-3,20-dione acetate
Catalog No.:BCC8442
CAS No.:2701-50-0
- 2-Acetamidothiazole
Catalog No.:BCC8509
CAS No.:2719-23-5
- Ampelopsin
Catalog No.:BCN5160
CAS No.:27200-12-0
- Bis[4-(2-hydroxyethoxy)phenyl] sulfone
Catalog No.:BCC8888
CAS No.:27205-03-4
- Polydatin
Catalog No.:BCN5949
CAS No.:27208-80-6
- Miltirone
Catalog No.:BCN5356
CAS No.:27210-57-7
- Pedunsaponin C
Catalog No.:BCN8193
CAS No.:272120-53-3
- Decursidate
Catalog No.:BCN4044
CAS No.:272122-56-2
- Cyanidin 3-Arabinoside
Catalog No.:BCC8157
CAS No.:27214-72-8
- Neoandrographolide
Catalog No.:BCN4657
CAS No.:27215-14-1
- N-(2,6-Dimethylphenyl)-2-piperidinecarboxamide
Catalog No.:BCC9051
CAS No.:27262-40-4
- Levobupivacaine HCl
Catalog No.:BCC4675
CAS No.:27262-48-2
- Phyllostine
Catalog No.:BCN4773
CAS No.:27270-89-9
Identification of small molecules for human hepatocyte expansion and iPS differentiation.[Pubmed:23728495]
Nat Chem Biol. 2013 Aug;9(8):514-20.
Cell-based therapies hold the potential to alleviate the growing burden of liver diseases. Such therapies require human hepatocytes, which, within the stromal context of the liver, are capable of many rounds of replication. However, this ability is lost ex vivo, and human hepatocyte sourcing has limited many fields of research for decades. Here we developed a high-throughput screening platform for primary human hepatocytes to identify small molecules in two different classes that can be used to generate renewable sources of functional human hepatocytes. The first class induced functional proliferation of primary human hepatocytes in vitro. The second class enhanced hepatocyte functions and promoted the differentiation of induced pluripotent stem cell-derived hepatocytes toward a more mature phenotype than what was previously obtainable. The identification of these small molecules can help address a major challenge affecting many facets of liver research and may lead to the development of new therapeutics for liver diseases.


