Fmoc-Lys(Me,Boc)-OHCAS# 951695-85-5 |
- PF-4708671
Catalog No.:BCC5031
CAS No.:1255517-76-0
- BIX 02565
Catalog No.:BCC4303
CAS No.:1311367-27-7
- BI-D1870
Catalog No.:BCC5030
CAS No.:501437-28-1
- CMK
Catalog No.:BCC1489
CAS No.:821794-90-5
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

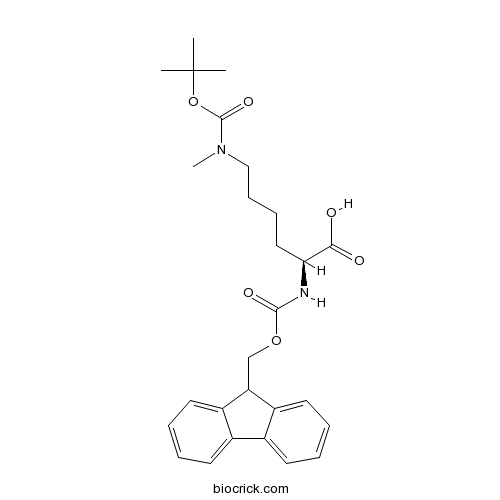
| Cas No. | 951695-85-5 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 44118847 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C27H34N2O6 | M.Wt | 482.56866 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | Soluble in Chloroform,Dichloromethane,Ethyl Acetate,DMSO,Acetone,etc. | ||
| Chemical Name | (2S)-2-(9H-fluoren-9-ylmethoxycarbonylamino)-6-[methyl-[(2-methylpropan-2-yl)oxycarbonyl]amino]hexanoic acid | ||
| SMILES | CC(C)(C)OC(=O)N(C)CCCCC(C(=O)O)NC(=O)OCC1C2=CC=CC=C2C3=CC=CC=C13 | ||
| Standard InChIKey | JHMSFOFHTAYQLS-QHCPKHFHSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C27H34N2O6/c1-27(2,3)35-26(33)29(4)16-10-9-15-23(24(30)31)28-25(32)34-17-22-20-13-7-5-11-18(20)19-12-6-8-14-21(19)22/h5-8,11-14,22-23H,9-10,15-17H2,1-4H3,(H,28,32)(H,30,31)/t23-/m0/s1 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||

Fmoc-Lys(Me,Boc)-OH Dilution Calculator

Fmoc-Lys(Me,Boc)-OH Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.0722 mL | 10.3612 mL | 20.7224 mL | 41.4449 mL | 51.8061 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.4144 mL | 2.0722 mL | 4.1445 mL | 8.289 mL | 10.3612 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.2072 mL | 1.0361 mL | 2.0722 mL | 4.1445 mL | 5.1806 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0414 mL | 0.2072 mL | 0.4144 mL | 0.8289 mL | 1.0361 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0207 mL | 0.1036 mL | 0.2072 mL | 0.4144 mL | 0.5181 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
Fmoc-Lys(Me,Boc)-OH
- Herpetone
Catalog No.:BCN2812
CAS No.:951677-22-8
- DY131
Catalog No.:BCC1539
CAS No.:95167-41-2
- Artemetin acetate
Catalog No.:BCN4501
CAS No.:95135-98-1
- Desformylflustrabromine hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC7651
CAS No.:951322-11-5
- Boc-N-Me-Tyr-OH.DCHA
Catalog No.:BCC3355
CAS No.:95105-25-2
- 2'-Deoxyuridine
Catalog No.:BCC8278
CAS No.:951-78-0
- PF-670462
Catalog No.:BCC1856
CAS No.:950912-80-8
- trans-4-Hydroxy-2-nonenoic acid
Catalog No.:BCN7959
CAS No.:95087-42-6
- Quizartinib (AC220)
Catalog No.:BCC2548
CAS No.:950769-58-1
- PCI-34051
Catalog No.:BCC2148
CAS No.:950762-95-5
- B-Raf IN 1
Catalog No.:BCC5439
CAS No.:950736-05-7
- 6-O-Methacryloyltrilobolide
Catalog No.:BCN7599
CAS No.:950685-51-5
- Sibiricin
Catalog No.:BCN4502
CAS No.:95188-34-4
- PF-477736
Catalog No.:BCC4421
CAS No.:952021-60-2
- Parishin E
Catalog No.:BCN3814
CAS No.:952068-57-4
- Atovaquone
Catalog No.:BCC4890
CAS No.:95233-18-4
- Neocaesalpin L
Catalog No.:BCN7650
CAS No.:952473-86-8
- 11-Oxomogroside III
Catalog No.:BCN3169
CAS No.:952481-53-7
- Hydrangenoside A dimethyl acetal
Catalog No.:BCN4553
CAS No.:952485-00-6
- Yadanzioside F
Catalog No.:BCN6406
CAS No.:95258-11-0
- Yadanziolide C
Catalog No.:BCN6719
CAS No.:95258-12-1
- Yadanziolide B
Catalog No.:BCN6720
CAS No.:95258-13-2
- Yadanziolide A
Catalog No.:BCN6721
CAS No.:95258-14-3
- Yadanzioside A
Catalog No.:BCN6718
CAS No.:95258-15-4
Inhibition of cruzipain visualized in a fluorescence quenched solid-phase inhibitor library assay. D-amino acid inhibitors for cruzipain, cathepsin B and cathepsin L.[Pubmed:9620612]
J Pept Sci. 1998 Apr;4(2):83-91.
A PEGA-resin was derivatized with a 3:1 mixture of hydroxymethyl benzoic acid and Fmoc-Lys(Boc)-OH and the fluorogenic substrate Ac-Y(NO2)KLRFSKQK(Abz)-PEGA was assembled on the lysine using the active ester approach. Following esterification of the hydroxymethyl benzoic acid with Fmoc-Val-OH a library XXX-k/r-XXXV containing approximately 200,000 beads was assembled by split synthesis. The resulting 'one bead, two peptides' library was subjected to extensive hydrolysis with cruzipain. One hundred darker beads were isolated and the 14 most persistently dark beads were collected and sequenced. The putative inhibitor peptides and several analogues were synthesized and found to be competitive microM to nM inhibitors of cruzipain in solution. The inhibitory activity was found to be unspecific to cruzipain when compared with cathepsins B and L and specific when compared with kallikrein. One of the inhibitors was docked into the active site of cathepsin B and was found most probably to bind to the enzyme cavity in an unusual manner, owing to the inserted D-amino acid residue.
Comparison of modification sites in glycated crystallin in vitro and in vivo.[Pubmed:25636230]
Anal Bioanal Chem. 2015 Mar;407(9):2557-67.
Glycation of alpha-crystallin is responsible for age- and diabetic-related cataracts, which are the main cause of blindness worldwide. We optimized the method of identification of lysine residues prone to glycation using the combination of LC-MS, isotopic labeling, and modified synthetic peptide standards with the glycated lysine derivative (Fmoc-Lys(i,i-Fru,Boc)-OH). The in vitro glycation of bovine lens alpha-crystallin was conducted by optimized method with the equimolar mixture of [(12)C6]- and [(13)C6]D-glucose. The in vivo glycation was studied on human lens crystallin. The glycated protein was subjected to proteolysis and analyzed using LC-MS. The results of in vitro and in vivo glycation of alpha-crystallin reveal a different distribution of the modified lysine residues. More Amadori products were detected as a result of the in vitro reaction due to forced glycation conditions. The developed method allowed us to identify the glycation sites in crystallin from eye lenses obtained from patients suffering from the cataract. We identified K166 in the A chain and K166 in the B chain of alpha-crystallin as major glycation sites during the in vitro reaction. We found also two in vivo glycated lysine residues: K92 in the B chain and K166 in the A chain, which are known as locations for Amadori products. These modification sites were confirmed by the LC-MS experiment using two synthetic standards. This study demonstrates the applicability of the LC-MS methods combined with the isotopic labeling and synthetic peptide standards for analysis of post-translational modifications in the biological material.
DNA binding behavior of peptides carrying acridinyl units: First example of effective poly-intercalation.[Pubmed:12836315]
Nucleic Acids Res Suppl. 2001;(1):163-4.
Bis-, tris-, tetrakis-, and pentakis-acridinyl (Acr) peptides 2-5 were synthesized from Fomc-Lys(Acr)-OH and Fmoc-Lys(Boc)-OH with the peptide synthesizer. The molar absorptivity of these peptides saturated with an increase in the number of the acridinyl unit in the peptide, suggesting intramolecular stacking of the acridinyl units. It was found from Scatchard analysis by means of spectrophotometry that all the peptides can bind to double stranded DNA with very high affinity even under high salt conditions (0.4 M NaCl) and the logarithmic binding constant increased in proportion to the number of the acridinyl unit in the peptide. This result suggested effective poly-intercalation of all the acridinyl units into double stranded DNA.


