Forskolinadenylate cyclase activator CAS# 66575-29-9 |
- NKH 477
Catalog No.:BCC7126
CAS No.:138605-00-2
- SQ 22536
Catalog No.:BCC7065
CAS No.:17318-31-9
- NKY 80
Catalog No.:BCC8003
CAS No.:299442-43-6
- KH 7
Catalog No.:BCC7787
CAS No.:330676-02-3
- MDL 12330A hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC7066
CAS No.:40297-09-4
- 1,9-Dideoxyforskolin
Catalog No.:BCC6352
CAS No.:64657-18-7
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 66575-29-9 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 47936 | Appearance | White powder |
| Formula | C22H34O7 | M.Wt | 410.50 |
| Type of Compound | Diterpenoids | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Synonyms | Coleonol; Colforsin | ||
| Solubility | DMSO : 100 mg/mL (243.61 mM; Need ultrasonic) H2O : < 0.1 mg/mL (insoluble) | ||
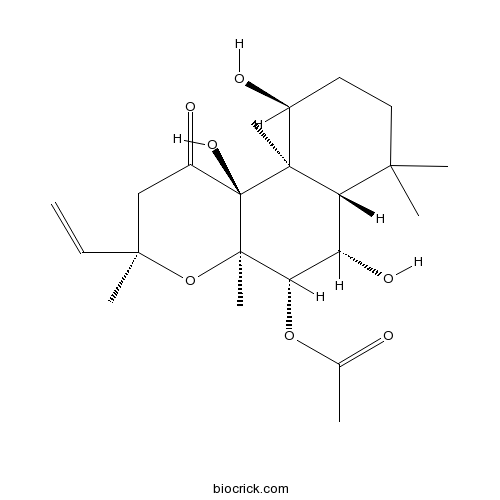
| Chemical Name | [(3R,4aR,5S,6S,6aS,10S,10aR,10bS)-3-ethenyl-6,10,10b-trihydroxy-3,4a,7,7,10a-pentamethyl-1-oxo-5,6,6a,8,9,10-hexahydro-2H-benzo[f]chromen-5-yl] acetate | ||
| SMILES | CC(=O)OC1C(C2C(CCC(C2(C3(C1(OC(CC3=O)(C)C=C)C)O)C)O)(C)C)O | ||
| Standard InChIKey | OHCQJHSOBUTRHG-KGGHGJDLSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C22H34O7/c1-8-19(5)11-14(25)22(27)20(6)13(24)9-10-18(3,4)16(20)15(26)17(28-12(2)23)21(22,7)29-19/h8,13,15-17,24,26-27H,1,9-11H2,2-7H3/t13-,15-,16-,17-,19-,20-,21+,22-/m0/s1 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Forskolin is a ubiquitous activator of eukaryotic adenylyl cyclase (AC) in a wide variety of cell types, commonly used to raise levels of cAMP in the study and research of cell physiology. Forskolin has antitumor, antioxidant and antiinflammatory actions, it may cause genotoxic effects. Chronic administration of Forskolin can decrease fasting blood glucose levels, it is effective in preventing diet induced obesity. |
| Targets | cAMP | Akt | ERK | Adenylyl cyclase | cGMP | FFA | PP2A | Caspase |
| In vitro | Forskolin: genotoxicity assessment in Allium cepa.[Pubmed: 25726172]Mutat Res Genet Toxicol Environ Mutagen. 2015 Jan 1;777:29-32.Forskolin, a diterpene, 7β-acetoxy-8,13-epoxy-1α,6β,9α-trihydroxy-labd-14-en-11-one (C22H34O7) isolated from Coleus forskohlii, exerts multiple physiological effects by stimulating the enzyme adenylate cyclase and increasing cyclic adenosine monophosphate (cAMP) concentrations. Forskolin is used in the treatment of hypertension, congestive heart failure, eczema, and other diseases.
Effect of leukemia inhibitory factor and forskolin on establishment of rat embryonic stem cell lines.[Pubmed: 24317016]J Reprod Dev. 2014 Mar 7;60(1):78-82.This study was designed to investigate whether supplementation of 2i medium with leukemia inhibitory factor (LIF) and/or Forskolin would support establishment of germline-competent rat embryonic stem (ES) cell lines.
|
| In vivo | The effects of forskolin and rolipram on cAMP, cGMP and free fatty acid levels in diet induced obesity.[Pubmed: 24520882]Biotech Histochem. 2014 Jul;89(5):388-92.Obesity is a major health problem. We investigated the effects of Forskolin and rolipram in the diet of animals in which obesity had been induced.
|
| Kinase Assay | Hyperphosphorylation of PP2A in colorectal cancer and the potential therapeutic value showed by its forskolin-induced dephosphorylation and activation.[Pubmed: 24997451]Biochim Biophys Acta. 2014 Sep;1842(9):1823-9.The tumor suppressor protein phosphatase 2A (PP2A) is frequently inactivated in human cancer and phosphorylation of its catalytic subunit (p-PP2A-C) at tyrosine-307 (Y307) has been described to inhibit this phosphatase. However, its molecular and clinical relevance in colorectal cancer (CRC) remains unclear. |
| Animal Research | Effect of chronic administration of forskolin on glycemia and oxidative stress in rats with and without experimental diabetes.[Pubmed: 24688307]Int J Med Sci. 2014 Mar 11;11(5):448-52.Forskolin is a diterpene derived from the plant Coleus forskohlii. Forskolin activates adenylate cyclase, which increases intracellular cAMP levels. The antioxidant and antiinflammatory action of Forskolin is due to inhibition of macrophage activation with a subsequent reduction in thromboxane B2 and superoxide levels. These characteristics have made Forskolin an effective medication for heart disease, hypertension, diabetes, and asthma.
|

Forskolin Dilution Calculator

Forskolin Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.4361 mL | 12.1803 mL | 24.3605 mL | 48.7211 mL | 60.9013 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.4872 mL | 2.4361 mL | 4.8721 mL | 9.7442 mL | 12.1803 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.2436 mL | 1.218 mL | 2.4361 mL | 4.8721 mL | 6.0901 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0487 mL | 0.2436 mL | 0.4872 mL | 0.9744 mL | 1.218 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0244 mL | 0.1218 mL | 0.2436 mL | 0.4872 mL | 0.609 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
Forskolin is a cell-permeable activator of adenylyl cyclase [1].
Adenylate cyclase is an enzyme that catalyzes the conversion of adenosine triphosphate (ATP) to 3',5'-cyclic AMP (cAMP) and pyrophosphate.
Forskolin is a cell-permeable activator of adenylyl cyclase. In rat cerebral cortical membranes, forskolin reversibly and rapidly activated adenylate cyclase with EC50 value of 5-10 μM. GTP and GDP increased the responses to forskolin. In rat cerebral cortical slices, forskolin rapidly increased cAMP by 35-fold with IC50 values of 25 μM [1]. Forskolin inhibited the inactivation of adenylate cyclases induced by N-ethylmaleimide with Kd values of 7.6 and 6.3 μM for the platelet and brain adenylate cyclases, respectively. Also, forskolin protected adenylate cyclases against thermal inactivation. Forskolin activated the platelet adenylate cyclase with IC50 and Kd values of 3-10 μM and 9-11 μM, respectively [2]. In pig epidermal cells, forskolin activated epidermal adenylate cyclase with Ka value of 2-3×10-5 M and induced cAMP accumulations, which then inhibited mitotic in a dose-dependent way [3].
References:
[1]. Seamon KB, Padgett W, Daly JW. Forskolin: unique diterpene activator of adenylate cyclase in membranes and in intact cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A, 1981, 78(6): 3363-3367.
[2]. Awad JA, Johnson RA, Jakobs KH, et al. Interactions of forskolin and adenylate cyclase. Effects on substrate kinetics and protection against inactivation by heat and N-ethylmaleimide. J Biol Chem, 1983, 258(5): 2960-2965.
[3]. Takeda J, Adachi K, Halprin KM, et al. Forskolin activates adenylate cyclase activity and inhibits mitosis in in vitro in pig epidermis. J Invest Dermatol, 1983, 81(3): 236-240.
- Tsugafolin
Catalog No.:BCN4026
CAS No.:66568-97-6
- ent-3beta-Hydroxykaur-16-en-19-oic acid
Catalog No.:BCN6472
CAS No.:66556-91-0
- CL 218872
Catalog No.:BCC7162
CAS No.:66548-69-4
- Augustifolin
Catalog No.:BCN3232
CAS No.:66548-01-4
- Ansamitocin P-3
Catalog No.:BCN8373
CAS No.:66547-09-9
- Propacetamol hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC9129
CAS No.:66532-86-3
- Benzoin isopropyl ether
Catalog No.:BCC8856
CAS No.:6652-28-4
- MSOP
Catalog No.:BCC6801
CAS No.:66515-29-5
- Bicifadine hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC7925
CAS No.:66504-75-4
- Amantadine HCl
Catalog No.:BCC4465
CAS No.:665-66-7
- JW 55
Catalog No.:BCC2453
CAS No.:664993-53-7
- H-D-Lys(Boc)-OMe.HCl
Catalog No.:BCC2990
CAS No.:66494-53-9
- Dihydrorotenone
Catalog No.:BCN2726
CAS No.:6659-45-6
- Agaric acid
Catalog No.:BCC9216
CAS No.:666-99-9
- Boc-Phenylalaninol
Catalog No.:BCC2718
CAS No.:66605-57-0
- RU 24969
Catalog No.:BCC5423
CAS No.:66611-26-5
- Risperidone hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC4205
CAS No.:666179-74-4
- Risperidone mesylate
Catalog No.:BCC4206
CAS No.:666179-96-0
- 2',4'-Dihydroxy-3,7':4,8'-diepoxylign-7-ene
Catalog No.:BCN6645
CAS No.:666250-52-8
- GW842166X
Catalog No.:BCC4413
CAS No.:666260-75-9
- Biotin Hydrazide
Catalog No.:BCC3582
CAS No.:66640-86-6
- Acetyl Angiotensinogen (1-14), porcine
Catalog No.:BCC1023
CAS No.:66641-26-7
- N-trans-Feruloyltyramine
Catalog No.:BCN4213
CAS No.:66648-43-9
- N-Feruloyloctopamine
Catalog No.:BCN4604
CAS No.:66648-44-0
Hyperphosphorylation of PP2A in colorectal cancer and the potential therapeutic value showed by its forskolin-induced dephosphorylation and activation.[Pubmed:24997451]
Biochim Biophys Acta. 2014 Sep;1842(9):1823-9.
BACKGROUND: The tumor suppressor protein phosphatase 2A (PP2A) is frequently inactivated in human cancer and phosphorylation of its catalytic subunit (p-PP2A-C) at tyrosine-307 (Y307) has been described to inhibit this phosphatase. However, its molecular and clinical relevance in colorectal cancer (CRC) remains unclear. METHODS: p-PP2A-C Y307 was determined by immunoblotting in 7 CRC cell lines and 35 CRC patients. CRC cells were treated with the PP2A activator Forskolin alone or combined with the PP2A inhibitor okadaic acid, 5-fluorouracil and oxaliplatin. We examined cell growth, colonosphere formation, caspase activity and AKT and ERK activation. RESULTS: PP2A-C was found hyperphosphorylated in CRC cell lines. Forskolin dephosphorylated and activated PP2A, impairing proliferation and colonosphere formation, and inducing activation of caspase 3/7 and changes in AKT and ERK phosphorylation. Moreover, Forskolin showed additive effects with 5-fluorouracil and oxaliplatin treatments. Analysis of p-PP2A-C Y307 in primary tumors confirmed the presence of this alteration in a subgroup of CRC patients. CONCLUSIONS: Our data show that PP2A-C hyperphosphorylation is a frequent event that contributes to PP2A inhibition in CRC. Antitumoral effects of Forskolin-mediated PP2A activation suggest that the analysis of p-PP2A-C Y307 status could be used to identify a subgroup of patients who would benefit from treatments based on PP2A activators.
Effect of chronic administration of forskolin on glycemia and oxidative stress in rats with and without experimental diabetes.[Pubmed:24688307]
Int J Med Sci. 2014 Mar 11;11(5):448-52.
Forskolin is a diterpene derived from the plant Coleus forskohlii. Forskolin activates adenylate cyclase, which increases intracellular cAMP levels. The antioxidant and antiinflammatory action of Forskolin is due to inhibition of macrophage activation with a subsequent reduction in thromboxane B2 and superoxide levels. These characteristics have made Forskolin an effective medication for heart disease, hypertension, diabetes, and asthma. Here, we evaluated the effects of chronic Forskolin administration on blood glucose and oxidative stress in 19 male Wistar rats with streptozotocin-induced diabetes compared to 8 healthy male Wistar rats. Rats were treated with Forskolin, delivered daily for 8 weeks. Glucose was assessed by measuring fasting blood glucose in diabetic rats and with an oral glucose tolerance test (OGTT) in healthy rats. Oxidative stress was assessed by measuring 8-hydroxydeoxyguanosine (8OHdG) in 24-h urine samples. In diabetic rats, without Forskolin, fasting blood glucose was significantly higher at the end than at the beginning of the experiment (8 weeks). In both healthy and diabetic rats, Forskolin treatment lowered the fasting glucose at the end of the experiment but no effect was found on oral glucose tolerance. The 8-OHdG levels tended to be less elevated in Forskolin-treated than in untreated group. Our results showed that chronic administration of Forskolin decreased fasting blood glucose levels; however, the reductions of 8-OHdG were not statistically significant.
The effects of forskolin and rolipram on cAMP, cGMP and free fatty acid levels in diet induced obesity.[Pubmed:24520882]
Biotech Histochem. 2014 Jul;89(5):388-92.
Obesity is a major health problem. We investigated the effects of Forskolin and rolipram in the diet of animals in which obesity had been induced. We used 50 female albino Wistar rats that were assigned randomly into five groups as follows: group 1, control; group 2, high fat diet; group 3, high fat diet + Forskolin; group 4, high fat diet + rolipram; and group 5, high fat diet + rolipram + Forskolin. The rats were fed for 10 weeks and rolipram and Forskolin were administered during last two weeks. The animals were sacrificed and blood samples were obtained. Serum cAMP, cGMP and free fatty acids (FFA) levels were measured using ELISA assays. We also measured weight gain during the 10 week period. cAMP and FFA levels of groups 3, 4 and 5 were significantly higher than those of groups 1 and 2. We found no significant differences in serum cGMP levels among the groups. The weight gain in groups 3, 4 and 5 was significantly less than for group 2. We also found that the weight gain in group 5 was significantly less than in groups 3 and 4. We found that both Forskolin and rolipram stimulated lipolysis and inhibited body weight increase by increasing cAMP levels. Also, combination therapy using the two agents may be more effective in preventing diet induced obesity than either agent alone. We found also that these agents did not effect cellular cGMP levels in diet induced obesity.
Forskolin: genotoxicity assessment in Allium cepa.[Pubmed:25726172]
Mutat Res Genet Toxicol Environ Mutagen. 2015 Jan 1;777:29-32.
Forskolin, a diterpene, 7beta-acetoxy-8,13-epoxy-1alpha,6beta,9alpha-trihydroxy-labd-14-en-11-one (C22H34O7) isolated from Coleus forskohlii, exerts multiple physiological effects by stimulating the enzyme adenylate cyclase and increasing cyclic adenosine monophosphate (cAMP) concentrations. Forskolin is used in the treatment of hypertension, congestive heart failure, eczema, and other diseases. A cytogenetic assay was performed in Allium cepa to assess possible genotoxic effects of Forskolin. Forskolin was tested at concentrations 5-100 muM for exposure periods of 24 or 48 h. Treated samples showed significant reductions in mitotic index (p < 0.05) and increases in the frequency of chromosome aberrations (p < 0.01) at both exposure times. The treated meristems showed chromosome aberrations including sticky metaphases, sticky anaphases, laggard, anaphase bridges, micronuclei, polyploidy, fragments, breaks, and C-mitosis. Forskolin may cause genotoxic effects and further toxicological evaluations should be conducted to ensure its safety.
Pluripotent stem cells induced from mouse somatic cells by small-molecule compounds.[Pubmed:23868920]
Science. 2013 Aug 9;341(6146):651-4.
Pluripotent stem cells can be induced from somatic cells, providing an unlimited cell resource, with potential for studying disease and use in regenerative medicine. However, genetic manipulation and technically challenging strategies such as nuclear transfer used in reprogramming limit their clinical applications. Here, we show that pluripotent stem cells can be generated from mouse somatic cells at a frequency up to 0.2% using a combination of seven small-molecule compounds. The chemically induced pluripotent stem cells resemble embryonic stem cells in terms of their gene expression profiles, epigenetic status, and potential for differentiation and germline transmission. By using small molecules, exogenous "master genes" are dispensable for cell fate reprogramming. This chemical reprogramming strategy has potential use in generating functional desirable cell types for clinical applications.
cAMP induces neuronal differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells via activation of extracellular signal-regulated kinase/MAPK.[Pubmed:16056139]
Neuroreport. 2005 Aug 22;16(12):1357-61.
Mesenchymal stem cells are able to trans-differentiate into nonmesodermal lineage cells. Here, we identified downstream signaling molecules required for acquisition of neuron-like traits by mesenchymal stem cells following the elevation of intracellular cAMP levels. We found that Forskolin induced neuron-like morphology and expression of neuron-specific enolase and neurofilament-200 in mesenchymal stem cells. Forskolin sequentially activated protein kinase A and B-regulation of alpha-fetoprotein (Raf), which led to phosphorylation of extracellular signal-regulated kinase. Importantly, blockade of extracellular signal-regulated kinase phosphorylation with a mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) kinase inhibitor abrogated the Forskolin-induced morphological changes and induction of neuronal proteins. These results indicate that extracellular signal-regulated kinase/MAPK mediates both cAMP-induced early cytoskeletal rearrangement and the later induction of neuronal markers in mesenchymal stem cells.
Forskolin: a specific stimulator of adenylyl cyclase or a diterpene with multiple sites of action?[Pubmed:2692256]
Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1989 Nov;10(11):442-7.
Forskolin, a naturally occurring diterpene, directly stimulates adenylyl cyclase and has been used extensively to increase cAMP and to elicit cAMP-dependent physiological responses. More recently, Forskolin has been shown to inhibit a number of membrane transport proteins and channel proteins through a mechanism that does not involve the production of cAMP. Many of these channel proteins are predicted to have similar topographies in the membrane bilayer and it is tempting to speculate that Forskolin may be binding at structurally homologous sites. Kenneth Seamon and colleagues discuss the cAMP-independent effects of Forskolin and the structural similarity between Forskolin and other physiologically important substances such as hexoses and steroids with respect to potential Forskolin binding sites.
Structure-activity relationships for activation of adenylate cyclase by the diterpene forskolin and its derivatives.[Pubmed:6681845]
J Med Chem. 1983 Mar;26(3):436-9.
Forskolin (7 beta-acetoxy-8,13-epoxy-1 alpha, 6 beta, 9 alpha-trihydroxylabd-14-en-11-one), a diterpene from the Indian plant Coleus forskohlii, activates cyclic AMP generating systems in a number of mammalian tissues in a rapid and reversible fashion. Derivatives of Forskolin have been tested for their ability to stimulate membrane adenylate cyclase from rat brain and rabbit heart, as well as cyclic AMP generation in guinea pig brain vesicular preparations, a model system for intact cells. Derivatives at the 6 beta- and 7 beta-hydroxy functions retain activity, but none have greater activity than that of Forskolin. Reduction of the 11-keto function affords an active 11 beta-hydroxy derivative. Reduction of the 14,15-vinyl (alpha) substituent reduces activity, while epoxidation abolishes activity. Derivatization or lack of the 1 alpha- and 9 alpha-hydroxy functions results in a marked reduction in activity, emphasizing the importance of the alpha aspect of the molecule. However, the 1 alpha, 6 beta-di-O-acetyl derivative does retain activity. None of the inactive derivatives, which include the 14,15-epoxy, the 1,9-dideoxy, and the 1,6-diketo derivatives, antagonize the stimulatory effects of Forskolin.


