GLPG0634JAK1 inhibitor CAS# 1206161-97-8 |
- Repaglinide
Catalog No.:BCC2504
CAS No.:135062-02-1
- Dronedarone
Catalog No.:BCN2176
CAS No.:141626-36-0
- NS309
Catalog No.:BCC1809
CAS No.:18711-16-5
- TRAM-34
Catalog No.:BCC1122
CAS No.:289905-88-0
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 1206161-97-8 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 49831257 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C21H23N5O3S | M.Wt | 425.5 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Synonyms | Filgotinib | ||
| Solubility | DMSO : 25 mg/mL (58.75 mM; Need ultrasonic) H2O : < 0.1 mg/mL (insoluble) | ||
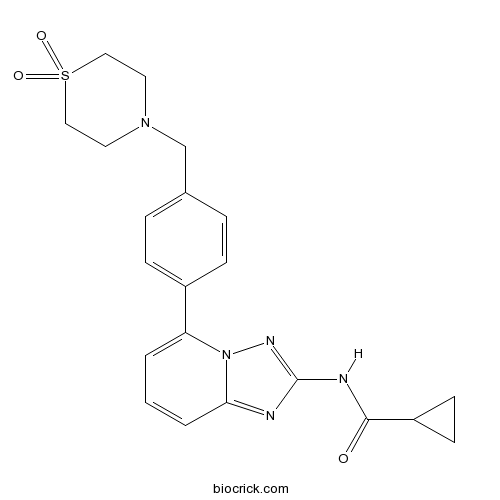
| Chemical Name | N-[5-[4-[(1,1-dioxo-1,4-thiazinan-4-yl)methyl]phenyl]-[1,2,4]triazolo[1,5-a]pyridin-2-yl]cyclopropanecarboxamide | ||
| SMILES | C1CC1C(=O)NC2=NN3C(=N2)C=CC=C3C4=CC=C(C=C4)CN5CCS(=O)(=O)CC5 | ||
| Standard InChIKey | RIJLVEAXPNLDTC-UHFFFAOYSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C21H23N5O3S/c27-20(17-8-9-17)23-21-22-19-3-1-2-18(26(19)24-21)16-6-4-15(5-7-16)14-25-10-12-30(28,29)13-11-25/h1-7,17H,8-14H2,(H,23,24,27) | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | GLPG0634 is a selective JAK1 inhibitor with IC50 of 10 nM, 28 nM, 810 nM, and 116 nM for JAK1, JAK2, JAK3, and TYK2, respectively.In Vitro:GLPG0634 dose-dependently inhibits the differentiation of Th2 cells mediated by IL-4, a cytokine that signals through JAK1 and JAK3. GLPG0634 also inhibits Th1 differentiation with similar potencies of 1 μM or lower[1]. GLPG0634 does not inhibit JAK2 homodimer-mediated signaling induced by EPO or PRL (IC50 > 10 μM)[2].In Vivo:GLPG0634 (3, 10, 30 mg/kg, p.o.) dose-dependently prevents disease progression in the therapeutic rat CIA model. GLPG0634 (50 mg/kg, o.p.) protects bone and cartilage from degradation, effectively reduces infiltration of T cells (CD3+ cells) and macrophages (F4/80+ cells) in the paw, and decreases the serum levels of all cytokines and chemokines measured, including IL-6, IP-10, XCL1, and MCP-1[1]. GLPG0634 (0.1 and 0.3 mg/kg) shows efficacy in the rat CIA model[2]. References: | |||||

GLPG0634 Dilution Calculator

GLPG0634 Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.3502 mL | 11.7509 mL | 23.5018 mL | 47.0035 mL | 58.7544 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.47 mL | 2.3502 mL | 4.7004 mL | 9.4007 mL | 11.7509 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.235 mL | 1.1751 mL | 2.3502 mL | 4.7004 mL | 5.8754 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.047 mL | 0.235 mL | 0.47 mL | 0.9401 mL | 1.1751 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0235 mL | 0.1175 mL | 0.235 mL | 0.47 mL | 0.5875 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
GLPG0634 is a selective inhibitor of JAK1 with IC50 value of 10nM [1].
GLPG0634 is a small molecule inhibitor of JAK1. It shows potent inhibitory activity against both JAK1 and JAK2 with IC50 values of 10nM and 28nM, respectively. In cellular assays, GLPG0634 is most potent in inhibiting the JAK1/JAK3/γc signaling induced by IL-2– and IL-4 as well as the JAK1/TYK2 type II receptor signaling induced by IFN-αB2. However, it shows lower potent to inhibit JAK2 homodimer–mediated signaling induced by EPO or PRL. It demonstrates that GLPG0634 is specific to JAK1. In addition, GLPG0634 is found to inhibit the phosphorylation of STAT1 and STAT5 induced by cytokines. Moreover, GLPG0634 inhibits the differentiation of Th1 and Th2 cells with similar potencies. Th17 differentiation is also affected by GLPG0634 with a lower potency [1].
In the rat model of collagen-induced arthritis (CIA), oral administration of GLPG0634 shows a marked protection from bone damage at dose of 3 mg/kg. It reduces the infiltration of inflammatory cells significantly from 1 mg/kg onward [1].
References:
[1] Van Rompaey L, Galien R, van der Aar E M, et al. Preclinical characterization of GLPG0634, a selective inhibitor of JAK1, for the treatment of inflammatory diseases. The Journal of Immunology, 2013, 191(7): 3568-3577.
- GLPG0634 analogue
Catalog No.:BCC6547
CAS No.:1206101-20-3
- 16-Nor-7,15-dioxodehydroabietic acid
Catalog No.:BCN7295
CAS No.:120591-53-9
- Anastrozole
Catalog No.:BCC4370
CAS No.:120511-73-1
- Desacetyldoronine
Catalog No.:BCN2105
CAS No.:120481-77-8
- SRT3190
Catalog No.:BCC1966
CAS No.:1204707-73-2
- SRT3109
Catalog No.:BCC1965
CAS No.:1204707-71-0
- Epacadostat
Catalog No.:BCC6531
CAS No.:1204669-58-8
- Pinanediol talabostat boronate
Catalog No.:BCC1640
CAS No.:1204669-37-3
- Ganoderenic acid H
Catalog No.:BCN2447
CAS No.:120462-48-8
- Ganoderenic acid F
Catalog No.:BCN2446
CAS No.:120462-47-7
- Lophanthoidin F
Catalog No.:BCN6093
CAS No.:120462-46-6
- Lophanthoidin E
Catalog No.:BCN6092
CAS No.:120462-45-5
- TC Mps1 12
Catalog No.:BCC7974
CAS No.:1206170-62-8
- Mofegiline hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC5412
CAS No.:120635-25-8
- 2beta-Acetoxyferruginol
Catalog No.:BCN7955
CAS No.:1206461-56-4
- 4,4'-Dihydroxy-3,3',9-trimethoxy-9,9'-epoxylignan
Catalog No.:BCN7017
CAS No.:1206464-65-4
- N-Benzylnaltrindole hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC6782
CAS No.:1206487-81-1
- MK-5172 potassium salt
Catalog No.:BCC1764
CAS No.:1206524-86-8
- Geranyl ferulate
Catalog No.:BCN7078
CAS No.:1206615-69-1
- (RS)-PPG
Catalog No.:BCC6975
CAS No.:120667-15-4
- DMH-1
Catalog No.:BCC5329
CAS No.:1206711-16-1
- 2''-Acetylastragalin
Catalog No.:BCN4810
CAS No.:1206734-95-3
- 1-(3,4-Dihydroxyphenyl)-7-(4-hydroxyphenyl)hept-6-en-3-ol
Catalog No.:BCN7143
CAS No.:1206788-61-5
- LY2801653
Catalog No.:BCC1720
CAS No.:1206799-15-6
Filgotinib (GLPG0634/GS-6034), an oral selective JAK1 inhibitor, is effective as monotherapy in patients with active rheumatoid arthritis: results from a randomised, dose-finding study (DARWIN 2).[Pubmed:27993828]
Ann Rheum Dis. 2017 Jun;76(6):1009-1019.
OBJECTIVES: To evaluate the efficacy and safety of different doses of filgotinib, an oral Janus kinase 1 inhibitor, as monotherapy in patients with active rheumatoid arthritis (RA) and previous inadequate response to methotrexate (MTX). METHODS: In this 24-week phase IIb study, patients with moderately to severely active RA were randomised (1:1:1:1) to receive 50, 100 or 200 mg filgotinib once daily, or placebo, after a >/=4-week washout from MTX. The primary end point was the percentage of patients achieving an American College of Rheumatology (ACR)20 response at week 12. RESULTS: Overall, 283 patients were randomised and treated. At week 12, significantly more patients receiving filgotinib at any dose achieved ACR20 responses versus placebo (>/=65% vs 29%, p<0.001). For other key end points at week 12 (ACR50, ACR70, ACR-N, Disease Activity Score based on 28 joints and C reactive protein, Clinical Disease Activity Index, Simplified Disease Activity Index and Health Assessment Questionnaire-Disability Index) significant differences from baseline in favour of filgotinib 100 and 200 mg versus placebo were seen; responses were maintained or improved through week 24. Rapid onset of action was observed for most efficacy end points. Dose-dependent increases in haemoglobin were observed. The percentage of patients with treatment-emergent adverse events (TEAE) was similar in the placebo and filgotinib groups ( approximately 40%). Eight patients on filgotinib and one on placebo had a serious TEAE, and four patients, all of whom received filgotinib, experienced a serious infection. No tuberculosis or opportunistic infections were reported. CONCLUSIONS: Over 24 weeks, filgotinib as monotherapy was efficacious in treating the signs and symptoms of active RA, with a rapid onset of action. Filgotinib was generally well tolerated. TRIAL REGISTRATION NUMBER: NCT01894516.
Filgotinib (GLPG0634/GS-6034), an oral JAK1 selective inhibitor, is effective in combination with methotrexate (MTX) in patients with active rheumatoid arthritis and insufficient response to MTX: results from a randomised, dose-finding study (DARWIN 1).[Pubmed:27993829]
Ann Rheum Dis. 2017 Jun;76(6):998-1008.
OBJECTIVES: To evaluate the efficacy and safety of different doses and regimens of filgotinib, an oral Janus kinase 1 inhibitor, as add-on treatment to methotrexate (MTX) in patients with active rheumatoid arthritis (RA) and inadequate response to MTX. METHODS: In this 24-week phase IIb study, patients with moderate-to-severe active RA receiving a stable dose of MTX were randomised (1:1:1:1:1:1:1) to receive placebo or 50, 100 or 200 mg filgotinib, administered once daily or twice daily. Primary end point was the percentage of patients achieving a week 12 American College of Rheumatology (ACR)20 response. RESULTS: Overall, 594 patients were randomised and treated. At week 12, significantly more patients receiving filgotinib 100 mg once daily or 200 mg daily (both regimens) achieved an ACR20 response versus placebo. For other key end points at week 12 (ACR50, ACR-N, Disease Activity Score based on 28 joints and C reactive protein value, Clinical Disease Activity Index, Simplified Disease Activity Index and Health Assessment Questionnaire-Disability Index), differences in favour of 100 or 200 mg filgotinib daily were seen versus placebo; responses were maintained or improved through to week 24. Rapid onset of action and dose-dependent responses were observed for most efficacy end points and were associated with an increased haemoglobin concentration. No significant differences between once-daily and twice-daily regimens were seen. Treatment-emergent adverse event rates were similar in placebo and filgotinib groups. Serious infections occurred in one and five patients in the placebo and filgotinib groups, respectively. No tuberculosis or opportunistic infections were reported. CONCLUSIONS: Filgotinib as add-on to MTX improved the signs and symptoms of active RA over 24 weeks and was associated with a rapid onset of action. Filgotinib was generally well tolerated. TRIAL REGISTRATION NUMBER: NCT01888874.
Clinical Confirmation that the Selective JAK1 Inhibitor Filgotinib (GLPG0634) has a Low Liability for Drug-drug Interactions.[Pubmed:26693854]
Drug Metab Lett. 2016;10(1):38-48.
OBJECTIVE: The selective Janus kinase 1 inhibitor filgotinib (GLPG0634), which is currently in clinical development for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis (RA) and Crohn's disease, demonstrated encouraging safety and efficacy profiles in RA patients after 4 weeks of daily dosing. As RA patients might be treated with multiple medications simultaneously, possible drug-drug interactions of filgotinib with cytochrome P450 enzymes and with key drug transporters were evaluated in vitro and in clinical studies. METHODS: The enzymes involved in filgotinib's metabolism and the potential interactions of the parent and its active major metabolite with drug-metabolizing enzymes and drug transporters, were identified using recombinant enzymes, human microsomes, and cell systems. Furthermore, filgotinib's interaction potential with CYP3A4 was examined in an open-label study in healthy volunteers, which evaluated the impact of filgotinib co-administration on the CYP3A4-sensitive substrate midazolam. The potential interaction with the common RA drug methotrexate was investigated in a clinical study in RA patients. RESULTS: In vitro, filgotinib and its active metabolite at clinically relevant concentrations did not interact with cytochrome P450 enzymes and uridine 5'-diphospho-glucuronosyltransferases, and did not inhibit key drug transporters. In the clinic, a lack of relevant pharmacokinetic drug interactions by filgotinib and its active metabolite with substrates of CYP3A4, as well as with organic anion transporters involved in methotrexate elimination were found. CONCLUSION: the collective in vivo and in vitro data on drug-metabolizing enzymes and on key drug transporters, support co-administration of filgotinib with commonly used RA drugs to patients without the need for dose adjustments.


