IWP-2Wnt production inhibitor,PORCN inhibitor CAS# 686770-61-6 |
- FH535
Catalog No.:BCC1573
CAS No.:108409-83-2
- CHIR-99021 (CT99021)
Catalog No.:BCC1275
CAS No.:252917-06-9
- XAV-939
Catalog No.:BCC1120
CAS No.:284028-89-3
- Salinomycin
Catalog No.:BCC1916
CAS No.:53003-10-4
- Salinomycin sodium salt
Catalog No.:BCC1917
CAS No.:55721-31-8
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 686770-61-6 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 2155128 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C22H18N4O2S3 | M.Wt | 466.6 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | DMSO : 2 mg/mL (4.29 mM; Need ultrasonic) H2O : < 0.1 mg/mL (insoluble) | ||
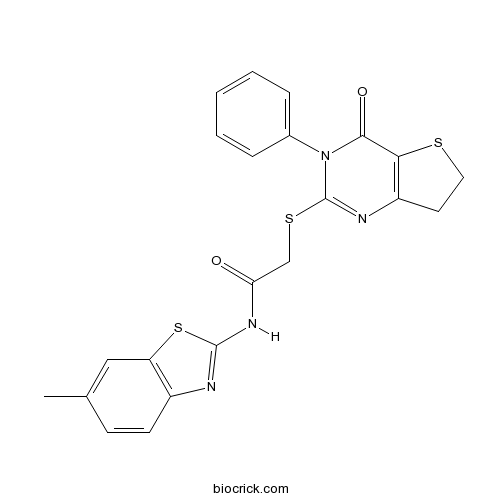
| Chemical Name | N-(6-methyl-1,3-benzothiazol-2-yl)-2-[(4-oxo-3-phenyl-6,7-dihydrothieno[3,2-d]pyrimidin-2-yl)sulfanyl]acetamide | ||
| SMILES | CC1=CC2=C(C=C1)N=C(S2)NC(=O)CSC3=NC4=C(C(=O)N3C5=CC=CC=C5)SCC4 | ||
| Standard InChIKey | WRKPZSMRWPJJDH-UHFFFAOYSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C22H18N4O2S3/c1-13-7-8-15-17(11-13)31-21(23-15)25-18(27)12-30-22-24-16-9-10-29-19(16)20(28)26(22)14-5-3-2-4-6-14/h2-8,11H,9-10,12H2,1H3,(H,23,25,27) | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Inhibitor of Wnt processing and secretion. Inactivates PORCN, a membrane-bound O-acyltransferase (MBOAT), and selectively inhibits palmitoylation of Wnt. Blocks Wnt-dependent phosphorylation of Lrp6 receptor and Dvl2, and β-catenin accumulation. Suppresses self-renewal in R1 embryonic stem cells. |

IWP-2 Dilution Calculator

IWP-2 Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.1432 mL | 10.7158 mL | 21.4316 mL | 42.8633 mL | 53.5791 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.4286 mL | 2.1432 mL | 4.2863 mL | 8.5727 mL | 10.7158 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.2143 mL | 1.0716 mL | 2.1432 mL | 4.2863 mL | 5.3579 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0429 mL | 0.2143 mL | 0.4286 mL | 0.8573 mL | 1.0716 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0214 mL | 0.1072 mL | 0.2143 mL | 0.4286 mL | 0.5358 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
IC50: 27 nM for Wnt pathway activity
The Wnt signaling pathway is important in embryonic devel opment as well as the initiation and progression of a number of types of human cancer. Porcn, a member of the membrane-bound O-acyltransferase (MBOAT) family, adds a palmitoyl group to Wnt proteins that is essential to their signaling ability and is required for Wnt secretion. IWP-2 is a small-molecule antagonist of the Wnt/b-catenin pathway.
In vitro: Expression of Porcn but not Evi alleviated the effects of IWP-2 on pathway activity and Wnt secretion, which suggests that in general IWP-2 may act on Porcn [1].
In vivo: In order to test the in vivo activity of IWP-2, the authors turned to a simple and rapid assay of Wnt/b-catenin pathway activity: regeneration of the zebrafish caudal fin following resection. The addition of IWP-2 to the aquarium water of zebrafish failed to suppress fin regeneration after mechanical resection, which suggests either that IWP-2 have poor bioavailability or that the determinants in the gene product that they target are not conserved in zebrafish [1].
Clinical trial: Up to now, IWP-2 is still in the preclinical development stage.
Reference:
[1] Chen B, Dodge ME, Tang W, Lu J, Ma Z, Fan CW, Wei S, Hao W, Kilgore J, Williams NS, Roth MG, Amatruda JF, Chen C, Lum L. Small molecule-mediated disruption of Wnt-dependent signaling in tissue regeneration and cancer. Nat Chem Biol. 2009 Feb;5(2):100-7.
- (±)-Palmitoylcarnitine chloride
Catalog No.:BCC6718
CAS No.:6865-14-1
- BOP-Cl
Catalog No.:BCC2808
CAS No.:68641-49-6
- CP-945598 HCl
Catalog No.:BCC1082
CAS No.:686347-12-6
- Otenabant
Catalog No.:BCC1828
CAS No.:686344-29-6
- Procerine
Catalog No.:BCN2017
CAS No.:68622-81-1
- Xylobiose
Catalog No.:BCN8424
CAS No.:6860-47-5
- Isorhynchophylline
Catalog No.:BCN6458
CAS No.:6859-1-4
- Isorhyncophylline
Catalog No.:BCN3466
CAS No.:6859-01-4
- PX-478 2HCl
Catalog No.:BCC6502
CAS No.:685898-44-6
- Prometaphanine
Catalog No.:BCN4244
CAS No.:6858-85-1
- Moschamine
Catalog No.:BCN3900
CAS No.:68573-23-9
- Pridinol Methanesulfonate
Catalog No.:BCC3845
CAS No.:6856-31-1
- BC 11-38
Catalog No.:BCC7940
CAS No.:686770-80-9
- IWP 4
Catalog No.:BCC5602
CAS No.:686772-17-8
- Qianhucoumarin G
Catalog No.:BCN3704
CAS No.:68692-61-5
- Retronecine N-oxide
Catalog No.:BCN2035
CAS No.:6870-33-3
- Jacobine
Catalog No.:BCN2087
CAS No.:6870-67-3
- 11β,17α-Dihydroxy-6α-methylpregna-1,4-diene-3,20-dione
Catalog No.:BCC8434
CAS No.:6870-94-6
- 13,18-Dehydroglaucarubinone
Catalog No.:BCN7957
CAS No.:68703-94-6
- Asimilobine
Catalog No.:BCN7076
CAS No.:6871-21-2
- Echitamine
Catalog No.:BCN4245
CAS No.:6871-44-9
- (-)-Lotusine
Catalog No.:BCN8443
CAS No.:6871-67-6
- Arteanoflavone
Catalog No.:BCN6824
CAS No.:68710-17-8
- Xanthoplanine
Catalog No.:BCN4246
CAS No.:6872-88-4
IL-36gamma inhibits differentiation and induces inflammation of keratinocyte via Wnt signaling pathway in psoriasis.[Pubmed:28924372]
Int J Med Sci. 2017 Aug 18;14(10):1002-1007.
Psoriasis is a common inflammatory skin disease characterized by abnormal keratinocyte inflammation and differentiation that has a major impact on patients' quality of life. IL-36gamma, a member of IL-36 cytokine family, is highly expressed in psoriasis and plays an important role in inflammation response and differentiation. However, the function of IL-36gamma in differentiation and inflammation of keratinocyte in psoriasis has not been clearly identified. Thus, this study aimed to investigate the role of IL-36gamma on differentiation and inflammation in HaCaT cells. HaCaT cells were divided into three groups: (1) Control group; (2) IL-36gamma (100 ng/mL) group; (3) IL-36gamma (100 ng/mL) + IWP-2 (1muM) group. Real time PCR was used to detect gene expression; the inflammation cytokines were examined by ELISA. We showed that treatment of HaCaT cells with IL-36gamma significantly upregulated the expression levels of beta-catenin, cyclin D1, and ki-67. IL-36gamma also promoted the production of the inflammatory cytokines IFN-gamma, IL-1beta and IL-6, suppressed the expression of filaggrin, involucrin, keratin 1 and keratin 5. Meanwhile, we demonstrated the role of IWP-2, an inhibitor of the Wnt signaling pathway, in IL-36gamma-treated HaCaT cells. Collectively, our findings suggest that IL-36gamma inhibits differentiation and induces inflammation of keratinocyte via Wnt signaling pathway in psoriasis, this indicated that downregulation of IL-36gamma may be a potential therapeutic option in psoriasis.
Endocrine Therapy of Estrogen Receptor-Positive Breast Cancer Cells: Early Differential Effects on Stem Cell Markers.[Pubmed:28929082]
Front Oncol. 2017 Sep 4;7:184.
INTRODUCTION: Endocrine therapy of breast cancer, which either deprives cancer tissue of estrogen or prevents estrogen pathway signaling, is the most common treatment after surgery and radiotherapy. We have previously shown for the estrogen-responsive MCF-7 cell line that exposure to tamoxifen, or deprivation of estrogen, leads initially to inhibition of cell proliferation, followed after several months by the emergence of resistant sub-lines that are phenotypically different from the parental line. We examined the early responses of MCF-7 cells following either exposure to 4-hydroxytamoxifen or deprivation of estrogen for periods of 2 days-4 weeks. METHODS: Endocrine-sensitive or -resistant breast cancer cell lines were used to examine the expression of the stem cell gene SOX2, and the Wnt effector genes AXIN2 and DKK1 using quantitative PCR analysis. Breast cancer cell lines were used to assess the anti-proliferative effects (as determined by IC50 values) of Wnt pathway inhibitors LGK974 and IWP-2. RESULTS: Hormone therapy led to time-dependent increases of up to 10-fold in SOX2 expression, up to threefold in expression of the Wnt target genes AXIN2 and DKK1, and variable changes in NANOG and OCT4 expression. The cells also showed increased mammosphere formation and increased CD24 surface protein expression. Some but not all hormone-resistant MCF-7 sub-lines, emerging after long-term hormonal stress, showed up to 50-fold increases in SOX2 expression and smaller increases in AXIN2 and DKK1 expression. However, the increase in Wnt target gene expression was not accompanied by an increase in sensitivity to Wnt pathway inhibitors LGK974 and IWP-2. A general trend of lower IC50 values was observed in 3-dimensional spheroid culture conditions (which allowed enrichment of cells with cancer stem cell phenotype) relative to monolayer cultures. The endocrine-resistant cell lines showed no significant increase in sensitivity to Wnt inhibitors. CONCLUSION: Hormone treatment of cultured MCF-7 cells leads within 2 days to increased expression of components of the SOX2 and Wnt pathways and to increased potential for mammosphere formation. We suggest that these responses are indicative of early adaptation to endocrine stress with features of stem cell character and that this facilitates the survival of emerging hormone-resistant cell populations.
Introduction of hsa-miR-103a and hsa-miR-1827 and hsa-miR-137 as new regulators of Wnt signaling pathway and their relation to colorectal carcinoma.[Pubmed:28817181]
J Cell Biochem. 2018 Jul;119(7):5104-5117.
Wnt signaling is hyper-activated in most of human cancers including colorectal carcinoma (CRC). Therefore, the introduction of new regulators for Wnt pathway possesses promising diagnostic and therapeutic applications in cancer medicine. Bioinformatics analysis introduced hsa-miR-103a, hsa-miR-1827, and hsa-miR-137 as potential regulators of Wnt signaling pathway. Here, we intended to examine the effect of these human miRNAs on Wnt signaling pathway components, on the cell cycle progression in CRC originated cell lines and their expression in CRC tissues. RT-qPCR results indicated upregulation of hsa-miR-103a, hsa-miR-1827, and downregulation of hsa-miR-137 in CRC tissues. Overexpression of hsa-miR-103a and hsa-miR-1827 in SW480 cells resulted in elevated Wnt activity, detected by both Top/Flash assay and RT-qPCR analysis. Inhibition of Wnt signaling by using PNU-74654 or IWP-2 small molecules suggested that these miRNAs exerts their effect at the beta-catenin degradation complex level. Then, RT-qPCR, dual luciferase assay, and western blotting analysis indicated that APC and APC2 transcripts were targeted by hsa-miR-103a, hsa-miR-1827 while, Wnt3a and beta-catenin genes were upregulated. However, hsa-miR-137 downregulated Wnt3a and beta-catenin genes. Further, hsa-miR-103a and hsa-miR-1827 overexpression resulted in cell cycle progression and reduced apoptotic rate in SW480 cells, unlike hsa-miR-137 overexpression which resulted in cell cycle suppression, detected by flowcytometry and Anexin analysis. Overall, our data introduced hsa-miR-103a, hsa-miR-1827 as onco-miRNAs and hsa-miR-137 as tumor suppressor which exert their effect through regulation of Wnt signaling pathway in CRC and introduced them as potential target for therapy.
[Zinc finger protein 521 suppresses osteogenic differentiation of rat mesenchymal stem cells by inhibiting the Wnt/beta-catenin signaling pathway].[Pubmed:28707663]
Mol Biol (Mosk). 2017 May-Jun;51(3):464-472.
Zinc finger protein 521 (Zfp521) is involved in a number of cellular processes in a variety of cells and tissues. In the present study, the effects of Zfp521 on osteogenic differentiation of rat mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) were investigated. The results showed that, in rat MSCs, knocking down cellular Zfp521 by short hairpin RNA (shRNA) decreases cell proliferation while promoting ALP activity, calcium accumulation, and the expression of mRNA that encodes bone sialoprotein (BSP), osteocalcin (OCN) and Runx2. Furthermore, in Zfp521-depleted cells, the up-regulation of phospho-Wnt (p-Wnt) and beta-catenin expression levels was detected. However, over-expression of Zfp521 played the opposite role in proliferation and osteogenic differentiation of rat MSCs. To further demonstrate the functions of the Wnt/beta-catenin signaling in Zfp521 regulated-osteogenic differentiation, the activation of Wnt/beta-catenin was blocked with IWP-2 inhibitor. The suppression of the Wnt/beta-catenin pathway completely abrogated the effects of Zfp521 knockdown on osteogenic differentiation of rat MSCs. Therefore, we conclude that Zfp521 regulates osteogenic differentiation of rat MSCs through the suppression of the Wnt/beta-catenin signaling pathway.
DKK1 promotes migration and invasion of non-small cell lung cancer via beta-catenin signaling pathway.[Pubmed:28677426]
Tumour Biol. 2017 Jul;39(7):1010428317703820.
Disregulation of dickkopf-related protein 1 (DKK1) has been reported in a variety of human cancers. However, how DKK1 functions in Non-small cell lung cancer has not been revealed. In the current study, DKK1 was knocked out by the lentivirus-mediated short hairpin RNA interference approach in H1299 and 95C non-small cell lung cancer cell lines. Subsequently, the migration and invasion ability were assessed by wound-healing and transwell assays. In addition, epithelial-mesenchymal transition markers and beta-catenin were examined by Western blot analysis. The signaling pathway downstream of DKK1 was characterized using the Wnt signaling pathway inhibitor, IWP2, and glycogen synthase kinase 3 beta inhibitor, LiCl. Immunofluorescence analysis investigated the subcellular localization of beta-catenin. The results suggested that knockdown of DKK1 caused reduced migration and invasion ability of H1299 and 95C cells. DKK1 silencing resulted in the downregulation of epithelial-mesenchymal transition-related proteins, such as Snail and zinc finger E-box binding homeobox 1. Besides, DKK1 silencing inhibited beta-catenin and promoted the phosphorylation of beta-catenin. Mechanism results indicated that the expression of beta-catenin was reduced in H1299 or 95C cells after being treated with Wnt signaling inhibitor, IWP2. In addition, the inhibition of beta-catenin phosphorylation by glycogen synthase kinase 3 beta inhibitor, LiCl, significantly enhanced the migration and invasion capacities in DKK1-knockdown cell lines. Furthermore, cell immunofluorescence revealed that nuclear beta-catenin was reduced when DKK1 was knocked down. Taken together, these findings suggest that DKK1 induces the occurrence of epithelial-mesenchymal transition and promotes migration and invasion in non-small cell lung cancer cells. Mechanically, beta-catenin plays a vital role in DKK1-induced non-small cell lung cancer cell migration and invasion, and DKK1 inhibits the phosphorylation of beta-catenin, resulting in the increased nuclear localization of beta-catenin.
Robust cardiomyocyte differentiation from human pluripotent stem cells via temporal modulation of canonical Wnt signaling.[Pubmed:22645348]
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2012 Jul 3;109(27):E1848-57.
Human pluripotent stem cells (hPSCs) offer the potential to generate large numbers of functional cardiomyocytes from clonal and patient-specific cell sources. Here we show that temporal modulation of Wnt signaling is both essential and sufficient for efficient cardiac induction in hPSCs under defined, growth factor-free conditions. shRNA knockdown of beta-catenin during the initial stage of hPSC differentiation fully blocked cardiomyocyte specification, whereas glycogen synthase kinase 3 inhibition at this point enhanced cardiomyocyte generation. Furthermore, sequential treatment of hPSCs with glycogen synthase kinase 3 inhibitors followed by inducible expression of beta-catenin shRNA or chemical inhibitors of Wnt signaling produced a high yield of virtually (up to 98%) pure functional human cardiomyocytes from multiple hPSC lines. The robust ability to generate functional cardiomyocytes under defined, growth factor-free conditions solely by genetic or chemically mediated manipulation of a single developmental pathway should facilitate scalable production of cardiac cells suitable for research and regenerative applications.
Embryonic stem cells require Wnt proteins to prevent differentiation to epiblast stem cells.[Pubmed:21841791]
Nat Cell Biol. 2011 Aug 14;13(9):1070-5.
Pluripotent stem cells exist in naive and primed states, epitomized by mouse embryonic stem cells (ESCs) and the developmentally more advanced epiblast stem cells (EpiSCs; ref. 1). In the naive state of ESCs, the genome has an unusual open conformation and possesses a minimum of repressive epigenetic marks. In contrast, EpiSCs have activated the epigenetic machinery that supports differentiation towards the embryonic cell types. The transition from naive to primed pluripotency therefore represents a pivotal event in cellular differentiation. But the signals that control this fundamental differentiation step remain unclear. We show here that paracrine and autocrine Wnt signals are essential self-renewal factors for ESCs, and are required to inhibit their differentiation into EpiSCs. Moreover, we find that Wnt proteins in combination with the cytokine LIF are sufficient to support ESC self-renewal in the absence of any undefined factors, and support the derivation of new ESC lines, including ones from non-permissive mouse strains. Our results not only demonstrate that Wnt signals regulate the naive-to-primed pluripotency transition, but also identify Wnt as an essential and limiting ESC self-renewal factor.
Small molecule-mediated disruption of Wnt-dependent signaling in tissue regeneration and cancer.[Pubmed:19125156]
Nat Chem Biol. 2009 Feb;5(2):100-7.
The pervasive influence of secreted Wnt signaling proteins in tissue homeostasis and tumorigenesis has galvanized efforts to identify small molecules that target Wnt-mediated cellular responses. By screening a diverse synthetic chemical library, we have discovered two new classes of small molecules that disrupt Wnt pathway responses; whereas one class inhibits the activity of Porcupine, a membrane-bound acyltransferase that is essential to the production of Wnt proteins, the other abrogates destruction of Axin proteins, which are suppressors of Wnt/beta-catenin pathway activity. With these small molecules, we establish a chemical genetic approach for studying Wnt pathway responses and stem cell function in adult tissue. We achieve transient, reversible suppression of Wnt/beta-catenin pathway response in vivo, and we establish a mechanism-based approach to target cancerous cell growth. The signal transduction mechanisms shown here to be chemically tractable additionally contribute to Wnt-independent signal transduction pathways and thus could be broadly exploited for chemical genetics and therapeutic goals.


