FH535Wnt/B-catenin inhibitor CAS# 108409-83-2 |
- Pioglitazone HCl
Catalog No.:BCC2278
CAS No.:112529-15-4
- Rosiglitazone
Catalog No.:BCC2264
CAS No.:122320-73-4
- T0070907
Catalog No.:BCC2261
CAS No.:313516-66-4
- GW0742
Catalog No.:BCC2267
CAS No.:317318-84-6
- Clofibric Acid
Catalog No.:BCC4652
CAS No.:882-09-7
- Troglitazone
Catalog No.:BCC2016
CAS No.:97322-87-7
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

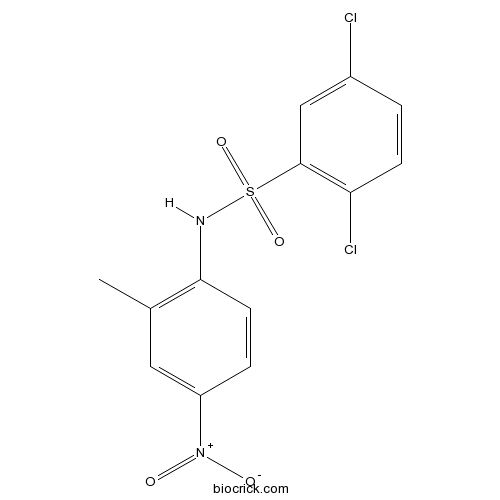
| Cas No. | 108409-83-2 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 3463933 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C13H10Cl2N2O4S | M.Wt | 361.2 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | DMSO : 33.33 mg/mL (92.28 mM; Need ultrasonic) H2O : < 0.1 mg/mL (insoluble) | ||
| Chemical Name | 2,5-dichloro-N-(2-methyl-4-nitrophenyl)benzenesulfonamide | ||
| SMILES | CC1=C(C=CC(=C1)[N+](=O)[O-])NS(=O)(=O)C2=C(C=CC(=C2)Cl)Cl | ||
| Standard InChIKey | AXNUEXXEQGQWPA-UHFFFAOYSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C13H10Cl2N2O4S/c1-8-6-10(17(18)19)3-5-12(8)16-22(20,21)13-7-9(14)2-4-11(13)15/h2-7,16H,1H3 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Inhibitor of Wnt/β-catenin signaling and dual antagonist of PPARγ/δ activity. Suppresses β-catenin/Tcf-mediated transcription; inhibits β-catenin and GRIP1 recruitment to PPARγ and δ. Exhibits antiproliferative effects in transformed colon, lung and liver cancer cell lines. |

FH535 Dilution Calculator

FH535 Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.7685 mL | 13.8427 mL | 27.6855 mL | 55.371 mL | 69.2137 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.5537 mL | 2.7685 mL | 5.5371 mL | 11.0742 mL | 13.8427 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.2769 mL | 1.3843 mL | 2.7685 mL | 5.5371 mL | 6.9214 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0554 mL | 0.2769 mL | 0.5537 mL | 1.1074 mL | 1.3843 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0277 mL | 0.1384 mL | 0.2769 mL | 0.5537 mL | 0.6921 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
FH535 is a small molecule inhibitor of Wnt/B-catenin with IC50 values of 15.4μM, 10.9μM, 9.3μM, respectively in LCSC, Huh7, PLC cell lines [1].
FH535 can inhibit the growth of colon, lung, and hepatocellular carcinoma line but not normal fibroblasts. It makes FH535 potentially be a promising therapeutic approach for cancer cells. It is reported that FH535 has ability to inhibit growth, migration, and invasion of TN breast cancer cell lines (MDA-MB-231 and HCC38) without affecting adhesive abilities of cells to type I collagen [2].
FH535 is also an inhibitor of peroxisome proliferator–activated receptor (PPAR). It plays a role as a dual PPARγ and PPARδ antagonist that is able to inhibit GRIP1 and β-catenin recruitment [3].
References:
[1] Roberto R. Galuppo, Roberto Gedaly, Paul Angulo, Michael F. et al. FH535 inhibits wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway in liver cancer stem cells and HCC cell lines. Hepatology. 2013, October: 466A.
[2] Joji Iida, Jesse Dorchak, John R. Lehman, Rebecca Clancy, Chunqing Luo, Yaqin Chen, Stella Somiari, Rachel E. Ellsworth, Hai Hu, Richard J. Mural, Craig D. Shriver. FH535 Inhibited Migration and Growth of Breast Cancer
Cells. PLOS ONE. 2012, 7(9): 1-11.
[3] Shlomo Handeli and Julian A. Simon. A small-molecule inhibitor of Tcf/β-catenin signaling down-regulates PPARγ and PPARδ activities. Molecular Cancer Therapeutics. 2008, 7:521-529.
- Fuligorubin A
Catalog No.:BCN1837
CAS No.:108343-55-1
- Noradrenaline bitartrate monohydrate
Catalog No.:BCC4810
CAS No.:108341-18-0
- Ganoderic acid D
Catalog No.:BCN2437
CAS No.:108340-60-9
- Geneticin, G-418 Sulfate
Catalog No.:BCC1202
CAS No.:108321-42-2
- Fmoc-D-Asn-OH
Catalog No.:BCC3083
CAS No.:108321-39-7
- 1,7-Bis(4-hydroxyphenyl)hept-1-en-3-one
Catalog No.:BCN1629
CAS No.:1083200-79-6
- 1,7-Bis(4-hydroxyphenyl)hept-6-en-3-ol
Catalog No.:BCN1630
CAS No.:1083195-05-4
- Cariprazine hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC1454
CAS No.:1083076-69-0
- A 987306
Catalog No.:BCC7732
CAS No.:1082954-71-9
- LY2584702
Catalog No.:BCC6369
CAS No.:1082949-67-4
- PF-04447943
Catalog No.:BCC1850
CAS No.:1082744-20-4
- PDE-9 inhibitor
Catalog No.:BCC1842
CAS No.:1082743-70-1
- [D-Phe12]-Bombesin
Catalog No.:BCC5844
CAS No.:108437-87-2
- [D-Phe12,Leu14]-Bombesin
Catalog No.:BCC6020
CAS No.:108437-88-3
- Ilexsaponin A
Catalog No.:BCN7867
CAS No.:108524-93-2
- Ilexgenin A
Catalog No.:BCC9233
CAS No.:108524-94-3
- Eupahualin C
Catalog No.:BCN7234
CAS No.:108525-39-9
- 23S-hydroxy-11,15-dioxo-ganoderic acid DM
Catalog No.:BCN8131
CAS No.:1085273-49-9
- Pyridostatin
Catalog No.:BCC1875
CAS No.:1085412-37-8
- Lumichrome
Catalog No.:BCN7083
CAS No.:1086-80-2
-
4-Hydroxy-Teriflunomide
Catalog No.:BCC4734
CAS No.:
- GSK2126458
Catalog No.:BCC3884
CAS No.:1086062-66-9
- Mizolastine
Catalog No.:BCC4521
CAS No.:108612-45-9
- Purpureaside C
Catalog No.:BCN3865
CAS No.:108648-07-3
FH535 suppresses the proliferation and motility of hepatocellular carcinoma cells.[Pubmed:26530115]
Int J Oncol. 2016 Jan;48(1):110-4.
The Wnt signaling pathway is activated in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). This study investigated the effects of FH535, an inhibitor of the Wnt signaling pathway, on the proliferation and motility of HCC cells. HLF cells and PLC/PRF/5 cells, HCC cells, were subjected to 3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-5-(3-carboxymethoxyphenyl)-2-(4-sulfophenyl)-2H-tetr azolium, inner salt (MTS) assay with the addition of FH535. RNA was isolated from the cells and subjected to real-time quantitative PCR. Hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) staining was performed to analyze apoptosis. A scratch assay was performed to analyze cell motility. Cell proliferation significantly decreased (P<0.05). The expression levels of cyclin D1 significantly decreased in both cell lines (P<0.05). Pyknotic nuclei were observed in the cells cultured with FH535 (50 microM). In the scratch assay, the distance between the growing edges of cells and the scratched line significantly decreased with the addition of FH535 at 50 microM (P<0.05). The expression levels of matrix metalloproteinase 9 significantly decreased at 50 microM (P<0.05). FH535 suppressed the proliferation of HCC cells by downregulating the expression of cyclin D1 and by inducing apoptosis. Further, it suppressed cell motility by downregulating the expression of matrix metalloproteinase.
Wnt signaling inhibitor FH535 selectively inhibits cell proliferation and potentiates imatinib-induced apoptosis in myeloid leukemia cell lines.[Pubmed:27766528]
Int J Hematol. 2017 Feb;105(2):196-205.
Wnt signaling pathway plays a major role in leukemogenesis of myeloid leukemia. Aberrancy in its regulation results in hyperactivity of the pathway contributing to leukemia propagation and maintenance. To investigate effects of Wnt pathway inhibition in leukemia, we used human leukemia cell lines (i.e., K562, HL60, THP1, and Jurkat) and several Wnt inhibitors, including XAV939, IWP2 and FH535. Our results showed that leukemia cell lines (>95 % cells) had increased endogenous levels of beta-catenin as compared to mononuclear cells from healthy donors (0 %). Among the tested inhibitors, FH535 demonstrated a markedly suppressive effect (IC50 = 358 nM) on mRNA levels of beta-catenin target genes (LEF1, CCND1, and cMYC). In addition, FH535 significantly potentiated imatinib-induced apoptosis. Evaluation of erythrocyte and megakaryocyte lineage using flow cytometry demonstrated that the potentiation mechanism is independent of the developmental stage, and is more likely due to crosstalk between other pathways and beta-catenin. FH535 also displayed antiproliferative properties in other cell lines used in this study. In summary, FH535 showed significantly high antiproliferative effects at submicromolar dosages, and additionally enhanced imatinib-induced apoptosis in human leukemia cell lines. Our results highlight its potential antileukemic promise when used in conjunction with other conventional therapeutic regimens.
FH535, a beta-catenin pathway inhibitor, represses pancreatic cancer xenograft growth and angiogenesis.[Pubmed:27323403]
Oncotarget. 2016 Jul 26;7(30):47145-47162.
The WNT/beta-catenin pathway plays an important role in pancreatic cancer carcinogenesis. We evaluated the correlation between aberrant beta-catenin pathway activation and the prognosis pancreatic cancer, and the potential of applying the beta-catenin pathway inhibitor FH535 to pancreatic cancer treatment. Meta-analysis and immunohistochemistry showed that abnormal beta-catenin pathway activation was associated with unfavorable outcome. FH535 repressed pancreatic cancer xenograft growth in vivo. Gene Ontology (GO) analysis of microarray data indicated that target genes responding to FH535 participated in stemness maintenance. Real-time PCR and flow cytometry confirmed that FH535 downregulated CD24 and CD44, pancreatic cancer stem cell (CSC) markers, suggesting FH535 impairs pancreatic CSC stemness. GO analysis of beta-catenin chromatin immunoprecipitation sequencing data identified angiogenesis-related gene regulation. Immunohistochemistry showed that higher microvessel density correlated with elevated nuclear beta-catenin expression and unfavorable outcome. FH535 repressed the secretion of the proangiogenic cytokines vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF), interleukin (IL)-6, IL-8, and tumor necrosis factor-alpha, and also inhibited angiogenesis in vitro and in vivo. Protein and mRNA microarrays revealed that FH535 downregulated the proangiogenic genes ANGPT2, VEGFR3, IFN-gamma, PLAUR, THPO, TIMP1, and VEGF. FH535 not only represses pancreatic CSC stemness in vitro, but also remodels the tumor microenvironment by repressing angiogenesis, warranting further clinical investigation.
Sorafenib and FH535 in combination act synergistically on hepatocellular carcinoma by targeting cell bioenergetics and mitochondrial function.[Pubmed:28179093]
Dig Liver Dis. 2017 Jun;49(6):697-704.
Treatment of advanced hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) remains a challenge due to the high tumor heterogeneity. In the present study, we aim to evaluate the impact of the beta-catenin inhibitor, FH535, alone or in combination with the Ras/Raf/MAPK inhibitor Sorafenib, on the bioenergetics profiles of the HCC cell lines Huh7 and PLC/PRF/5. Single low-dose treatments with FH535 or Sorafenib promoted different effects on mitochondrial respiration and glycolysis in a cell type specific manner. However, the combination of these drugs significantly reduced both mitochondrial respiration and glycolytic rates regardless of the HCC cells. The significant changes in mitochondrial respiration observed in cells treated with the Sorafenib-FH535 combination may correspond to differential targeting of ETC complexes and changes in substrate utilization mediated by each drug. Moreover, the bioenergetics changes and the loss of mitochondrial membrane potential that were evidenced by treatment of HCC cells with the combination of FH535 and Sorafenib, preceded the induction of cell apoptosis. Overall, our results demonstrated that Sorafenib-FH535 drug combination induce the disruption of the bioenergetics of HCC by the simultaneous targeting of mitochondrial respiration and glycolytic flux that leads the synergistic effect on inhibition of cell proliferation. These findings support the therapeutic potential of combinatory FH535-Sorafenib treatment of the HCC heterogeneity by the simultaneous targeting of different molecular pathways.
A small-molecule inhibitor of Tcf/beta-catenin signaling down-regulates PPARgamma and PPARdelta activities.[Pubmed:18347139]
Mol Cancer Ther. 2008 Mar;7(3):521-9.
Activation of the Wnt/beta-catenin signaling pathway occurs in several types of cancers and thus it is an attractive target for anticancer drug development. To identify compounds that inhibit this pathway, we screened a chemical library using a cell-based beta-catenin/Tcf-responsive reporter. We identified FH535, a compound that suppresses both Wnt/beta-catenin and peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor (PPAR) signaling. FH535 antagonizes both PPARgamma and PPARdelta ligand-dependent activation and shows structural similarity to GW9662, a known PPARgamma antagonist. The effect of FH535 on beta-catenin/Tcf activity is reduced in cells carrying a deletion of the PPARdelta gene, as well as by the PPARgamma agonist lysophosphatidic acid. Mechanistically, FH535 inhibits recruitment of the coactivators beta-catenin and GRIP1 but not the corepressors NCoR and SMRT. Its repression of beta-catenin recruitment, in comparison with GW9662, is linked to FH535's unique capability to inhibit the Wnt/beta-catenin signaling pathway. The antiproliferation effect of the compound observed on some transformed colon lung and liver cell lines is suggestive of its potential therapeutic value in the treatment of cancer.


