PF-04447943PDE9 inhibitor CAS# 1082744-20-4 |
- GSK256066 2,2,2-trifluoroacetic acid
Catalog No.:BCC1605
CAS No.:1415560-64-3
- Nortadalafil
Catalog No.:BCC1806
CAS No.:171596-36-4
- Bay 60-7550
Catalog No.:BCC1405
CAS No.:439083-90-6
- Oglemilast
Catalog No.:BCC1817
CAS No.:778576-62-8
- AN-2728
Catalog No.:BCC1361
CAS No.:906673-24-3
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 1082744-20-4 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 25115162 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C20H25N7O2 | M.Wt | 395.46 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | DMSO : ≥ 54.6 mg/mL (138.07 mM) *"≥" means soluble, but saturation unknown. | ||
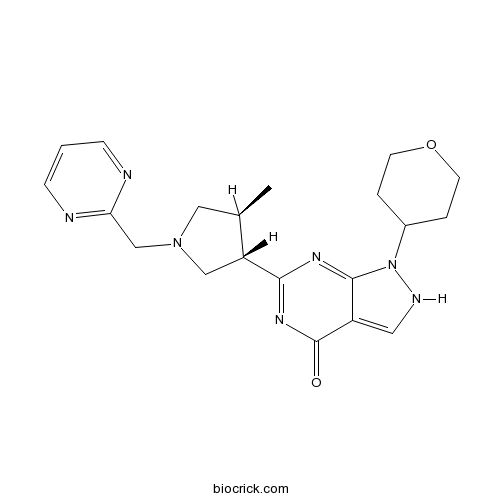
| Chemical Name | 6-[(3S,4S)-4-methyl-1-(pyrimidin-2-ylmethyl)pyrrolidin-3-yl]-1-(oxan-4-yl)-2H-pyrazolo[3,4-d]pyrimidin-4-one | ||
| SMILES | CC1CN(CC1C2=NC(=O)C3=CNN(C3=N2)C4CCOCC4)CC5=NC=CC=N5 | ||
| Standard InChIKey | ACXPOEVOYNJCHF-CZUORRHYSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C20H25N7O2/c1-13-10-26(12-17-21-5-2-6-22-17)11-16(13)18-24-19-15(20(28)25-18)9-23-27(19)14-3-7-29-8-4-14/h2,5-6,9,13-14,16,23H,3-4,7-8,10-12H2,1H3/t13-,16-/m1/s1 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | PF-04447943 is a potent inhibitor of human recombinant PDE9A (IC50=12 nM) with >78-fold selectivity, respectively, over other PDE family members (IC50>1000 nM).In Vitro:Using recombinant human, rhesus, and rat PDE9A2 in a cell free assay PF-04447943 is shown to have a Ki of 2.8±0.26, 4.5±0.13, and 18.1±1.9 nM (n=4, 11 and 9 respectively). PF-04447943 is found to be highly selective over other PDE enzymes (PDE1, Ki=8600±2121 nM, n = 5; PDE2A3, Ki>99,000 nM; PDE3A, Ki>50,000 nM; PDE4A, Ki>29,000 nM; PDE5A, Ki=14,980±5025 nM, n=5; PDE6C, Ki=5324±2612 nM, n=4; PDE7A2, Ki>75,000 nM; PDE8A, Ki>50,000 nM; PDE10, Ki>51,250±20,056 nM, n=4; PDE11, Ki>80,000 nM) and no other significant activity at ~60 other receptors/enzymes. In HEK whole cells expressing rhesus PDE9A2, PF-04447943 inhibits ANP (0.3 μM) stimulated cGMP with an IC50 of 375±36.9 nM (n=16)[2].In Vivo:Based on i.v. and p.o. dosing, pharmacokinetic studies with PF-04447943 in the rat indicates a Tmax of 0.3 h, T1/2 of 4.9 h, Cl of 21.7 mL/min/kg and an oral bioavailability of 47%. Thirty minutes following oral administration in rats (1-30 mg/kg), PF-04447943 concentrations dose-dependently increase in blood, brain and cerebrospinal fluid (CSF). The brain:plasma exposure ratios 30 min after dosing range from 0.13 at the 1 mg/kg dose to 0.33 at the 30 mg/kg dose. CSF levels are approximately 50% of brain levels. In mice, PF-04447943 (3, 10, 30 mg/kg p.o.) dose-dependently increases plasma and brain concentrations of PF-04447943 while the brain to plasma ratio ranged from 0.26 to 0.7 although this is not entirely dose dependent. CSF cGMP levels increase in a dose-dependent manner from a basal level of 3 pmol/mL to 13.3 pmol/mL (3.5-fold) at the 30 mg/kg dose. CSF cGMP levels also increase in a dose-dependent manner from a basal level of 3 pmol/mL in vehicle treated animals to 13.3 pmol/mL (3.5-fold) at the 30 mg/kg dose. CSF cGMP levels are elevated at all doses tested with a maximal effect of 3.5 fold increase above controls at 30 mg/kg[2]. References: | |||||

PF-04447943 Dilution Calculator

PF-04447943 Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.5287 mL | 12.6435 mL | 25.287 mL | 50.574 mL | 63.2175 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.5057 mL | 2.5287 mL | 5.0574 mL | 10.1148 mL | 12.6435 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.2529 mL | 1.2644 mL | 2.5287 mL | 5.0574 mL | 6.3218 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0506 mL | 0.2529 mL | 0.5057 mL | 1.0115 mL | 1.2644 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0253 mL | 0.1264 mL | 0.2529 mL | 0.5057 mL | 0.6322 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
PF-04447943 is a potent and selective inhibitor of PDE9 [1].
Phosphodiesterase 9 (PDE9) selectively degrades cGMP and limits the cGMP-mediated signal transduction which occurs following glutamate binding to NMDA receptors. PDE9 in cortex and hippocampus of rodents and humans play an important role in memory and learning [1].
PF-04447943 have high affinity with Ki of 2.8, 4.5 and 18 nM for human, rhesus and rat recombinant PDE9 respectively and high selectivity for PDE9 versus PDEs1- 8 and 10 -11. In cultured hippocampal neurons, PF-04447943 (30-100 nM) significantly increased neurite outgrowth and synapse formation. Also, PF-04447943 (100 nM) significantly facilitated hippocampal slice LTP evoked by a weak tetanic stimulus [1].
In mice model, PF-04447943 (1 mg/kg) significantly reduced the time spent interacting with the female mouse during the second encounter 24 h later compared to the first encounter, which suggested that PF-04447943 enhanced recognition memory. While, PF-04447943 (3 or 10 mg/kg) didn’t change the interaction times for each encounter. These results suggested that PF-04447943 enhanced memory with an inverted U-shaped dose-response efficacy curve [1].
Reference:
[1]Hutson PH, Finger EN, Magliaro BC, et al. The selective phosphodiesterase 9 (PDE9) inhibitor PF-04447943(6-[(3S,4S)-4-methyl-1-(pyrimidin-2-ylmethyl)pyrrolidin-3-yl]-1-(tetrahydro-2H-pyran-4-yl)-1,5-dihydro-4H-pyrazolo[3,4-d]pyrimidin-4-one) enhances synaptic plasticity and cognitive function in rodents. Neuropharmacology, 2011, 61(4): 665-676.
- PDE-9 inhibitor
Catalog No.:BCC1842
CAS No.:1082743-70-1
- TC-S 7005
Catalog No.:BCC6189
CAS No.:1082739-92-1
- TUG 424
Catalog No.:BCC7776
CAS No.:1082058-99-8
- SKF 83566 hydrobromide
Catalog No.:BCC7121
CAS No.:108179-91-5
- 6-(beta-D-glucopyranosyloxy)-Salicylic acid methyl ester
Catalog No.:BCN1631
CAS No.:108124-75-0
- α-Terthiophene
Catalog No.:BCN8380
CAS No.:1081-34-1
- KT 5720
Catalog No.:BCC8080
CAS No.:108068-98-0
- CP-466722
Catalog No.:BCC3912
CAS No.:1080622-86-1
- Roxindole hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC7116
CAS No.:108050-82-4
- Tilmicosin
Catalog No.:BCC4865
CAS No.:108050-54-0
- Ambocin
Catalog No.:BCN7748
CAS No.:108044-05-9
- Bergenin monohydrate
Catalog No.:BCC8132
CAS No.:108032-11-7
- LY2584702
Catalog No.:BCC6369
CAS No.:1082949-67-4
- A 987306
Catalog No.:BCC7732
CAS No.:1082954-71-9
- Cariprazine hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC1454
CAS No.:1083076-69-0
- 1,7-Bis(4-hydroxyphenyl)hept-6-en-3-ol
Catalog No.:BCN1630
CAS No.:1083195-05-4
- 1,7-Bis(4-hydroxyphenyl)hept-1-en-3-one
Catalog No.:BCN1629
CAS No.:1083200-79-6
- Fmoc-D-Asn-OH
Catalog No.:BCC3083
CAS No.:108321-39-7
- Geneticin, G-418 Sulfate
Catalog No.:BCC1202
CAS No.:108321-42-2
- Ganoderic acid D
Catalog No.:BCN2437
CAS No.:108340-60-9
- Noradrenaline bitartrate monohydrate
Catalog No.:BCC4810
CAS No.:108341-18-0
- Fuligorubin A
Catalog No.:BCN1837
CAS No.:108343-55-1
- FH535
Catalog No.:BCC1573
CAS No.:108409-83-2
- [D-Phe12]-Bombesin
Catalog No.:BCC5844
CAS No.:108437-87-2
The selective phosphodiesterase 9 (PDE9) inhibitor PF-04447943 attenuates a scopolamine-induced deficit in a novel rodent attention task.[Pubmed:22070409]
J Neurogenet. 2011 Dec;25(4):120-6.
Numerous changes occur during aging and Alzheimer's disease (AD) progression, including a decline in cholinergic functioning and cognition, as well as alterations in gene expression and activity in the nitric oxide/cyclic guanosine monophosphate (NO/cGMP) pathway. Donepezil, the current standard of care for Alzheimer's disease, improves cholinergic functioning and has demonstrated effects on multiple domains of cognition, including memory and attention in both preclinical species and patients. We previously found that increasing activation of the NO/cGMP pathway via phosphodiesterase 9 (PDE9) inhibition also improves memory in rodents and suggested that PDE9 might be a promising target for novel treatments for AD. Here we investigated whether PDE9 inhibition also enhances attention using a novel attention task in rats. We validated this task using several pharmacological manipulations and showed that the selective PDE9 inhibitor PF-04447943 produced effects similar to those of donepezil. These data confirm and extend the hypothesis that PDE9 inhibition might serve as a novel treatment for AD and age-related cognitive decline.
A multicenter, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial of the PDE9A inhibitor, PF-04447943, in Alzheimer's disease.[Pubmed:24801218]
Curr Alzheimer Res. 2014;11(5):413-21.
BACKGROUND: PF-04447943 is a potent, selective phosphodiesterase 9A (PDE9A) inhibitor that elevates guanoscine 3',5' - cyclic monophosphate (cGMP) in brain and cerebrospinal fluid. PDE9A inhibition enhances synaptic plasticity and improves memory in preclinical cognition models, and prevents decreases in dendritic spine density in transgenic mice that overexpress amyloid precursor protein (APP) leading to high levels of amyloid beta (Abeta) production (Tg2576). OBJECTIVE: This Phase 2 multicenter study was designed to assess the efficacy, safety and pharmacokinetics of PF-04447943 compared with placebo in mild to moderate probable Alzheimer's disease (AD). METHODS: Subjects in overall good health with Mini Mental State Examination (MMSE) scores of 14-26 were randomized to 12 weeks treatment with PF-04447943 25 mg q12h (n=91) or placebo (n=100). Concomitant acetylcholinesterase inhibitor or memantine use was excluded. The primary outcome was the Alzheimer's Disease Assessment Scale - cognitive subscale (ADAS-cog). The Neuropsychiatric Inventory (NPI), Clinical Global Impression-Improvement scale (CGI-I) and standard safety measures were secondary outcomes. RESULTS: Completion rates were similar, 87% PF-04447943 vs 92% placebo. At week 12 the mean (SE) baseline adjusted decrease from baseline in ADAS cog for PF-04447943-treated patients was -1.91 (0.54). Placebo treated patients had a change of -1.60 (0.50). The difference between treatments was -0.31 (90% CI of -1.52, 0.90). Corresponding values for the NPI were -2.86 (0.72) vs -2.70 (0.67) with a treatment difference of -0.16 (90% CI of -1.78, 1.48). Neither these changes nor the distribution of CGI-I scores were statistically significantly different between groups. The incidence of serious adverse events (AEs) was similar between groups with 2 deaths in the placebo group. The PF-04447943 group reported more gastrointestinal AEs including diarrhea (5.5% vs 3%) and nausea (5.5% vs 1%) and had a higher rate of discontinuation due to AEs (6.6% vs 2%). CONCLUSIONS: Although generally safe and well-tolerated, 12 weeks PF-04447943 treatment did not improve cognition, behavior, and global change compared with placebo.
The selective phosphodiesterase 9 (PDE9) inhibitor PF-04447943 (6-[(3S,4S)-4-methyl-1-(pyrimidin-2-ylmethyl)pyrrolidin-3-yl]-1-(tetrahydro-2H-py ran-4-yl)-1,5-dihydro-4H-pyrazolo[3,4-d]pyrimidin-4-one) enhances synaptic plasticity and cognitive function in rodents.[Pubmed:21619887]
Neuropharmacology. 2011 Sep;61(4):665-76.
Inhibition of phosphodiesterase 9 (PDE9) has been reported to enhance rodent cognitive function and may represent a potential novel approach to improving cognitive dysfunction in Alzheimer's disease. PF-04447943, (6-[(3S,4S)-4-methyl-1-(pyrimidin-2-ylmethyl)pyrrolidin-3-yl]-1-(tetrahydro-2H-py ran-4-yl)-1,5-dihydro-4H-pyrazolo[3,4-d]pyrimidin-4-one), a recently described PDE9 inhibitor, was found to have high affinity (Ki of 2.8, 4.5 and 18 nM) for human, rhesus and rat recombinant PDE9 respectively and high selectivity for PDE9 versus PDEs1-8 and 10-11. PF-04447943 significantly increased neurite outgrowth and synapse formation (as indicated by increased synapsin 1 expression) in cultured hippocampal neurons at low (30-100 nM) but not high (300-1000 nM) concentrations. PF-04447943 significantly facilitated hippocampal slice LTP evoked by a weak tetanic stimulus at a concentration of 100 nM but failed to affect response to the weak tetanus at either 30 or 300 nM, or the LTP produced by a theta burst stimulus. Systemic administration of PF-04447943 (1-30 mg/kg p.o.) dose-dependently increased cGMP in the cerebrospinal fluid 30 min after administration indicating target engagement in the CNS of rats. PF-04447943 (1-3 mg/kg p.o.) significantly improved cognitive performance in three rodent cognition assays (mouse Y maze spatial recognition memory model of natural forgetting, mouse social recognition memory model of natural forgetting and rat novel object recognition with a scopolamine deficit). When administered at a dose of 3 mg/kg p.o., which improved performance in novel object recognition, PF-04447943 significantly increased phosphorylated but not total GluR1 expression in rat hippocampal membranes. Collectively these data indicate that PF-04447943 is a potent, selective brain penetrant PDE9 inhibitor that increased indicators of hippocampal synaptic plasticity and improved cognitive function in a variety of cognition models in both rats and mice. Results with PF-04447943 are consistent with previously published findings using a structurally diverse PDE9 inhibitor, BAY73-6199, and further support the suggestion that PDE9 inhibition may represent a novel approach to the palliative remediation of cognitive dysfunction.
Design and discovery of 6-[(3S,4S)-4-methyl-1-(pyrimidin-2-ylmethyl)pyrrolidin-3-yl]-1-(tetrahydro-2H-pyr an-4-yl)-1,5-dihydro-4H-pyrazolo[3,4-d]pyrimidin-4-one (PF-04447943), a selective brain penetrant PDE9A inhibitor for the treatment of cognitive disorders.[Pubmed:22780914]
J Med Chem. 2012 Nov 8;55(21):9045-54.
6-[(3S,4S)-4-Methyl-1-(pyrimidin-2-ylmethyl)pyrrolidin-3-yl]-1-(tetrahydro-2H-pyr an-4-yl)-1,5-dihydro-4H-pyrazolo[3,4-d]pyrimidin-4-one (PF-04447943) is a novel PDE9A inhibitor identified using parallel synthetic chemistry and structure-based drug design (SBDD) and has advanced into clinical trials. Selectivity for PDE9A over other PDE family members was achieved by targeting key residue differences between the PDE9A and PDE1C catalytic site. The physicochemical properties of the series were optimized to provide excellent in vitro and in vivo pharmacokinetics properties in multiple species including humans. It has been reported to elevate central cGMP levels in the brain and CSF of rodents. In addition, it exhibits procognitive activity in several rodent models and synaptic stabilization in an amyloid precursor protein (APP) transgenic mouse model. Recent disclosures from clinical trials confirm that it is well tolerated in humans and elevates cGMP in cerebral spinal fluid of healthy volunteers, confirming that it is a quality pharmacological tool for testing clinical hypotheses in disease states associated with impairment of cGMP signaling or cognition.


