Ganoderic acid DCAS# 108340-60-9 |
- Ganoderic acid C1
Catalog No.:BCN3035
CAS No.:95311-97-0
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 108340-60-9 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 102004379 | Appearance | White powder |
| Formula | C30H42O7 | M.Wt | 514.66 |
| Type of Compound | Triterpenoids | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | Soluble in methanol; insoluble in water | ||
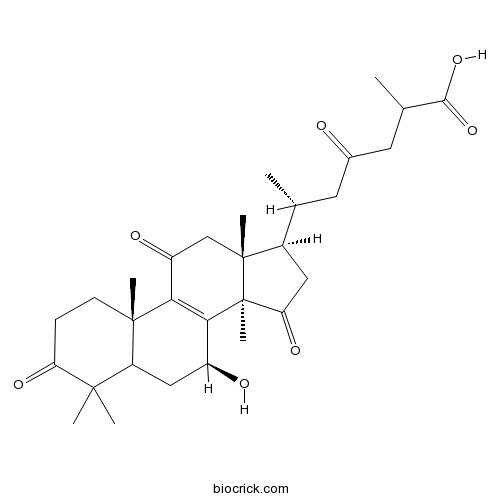
| Chemical Name | (6R)-6-[(7S,10S,13R,14R,17R)-7-hydroxy-4,4,10,13,14-pentamethyl-3,11,15-trioxo-1,2,5,6,7,12,16,17-octahydrocyclopenta[a]phenanthren-17-yl]-2-methyl-4-oxoheptanoic acid | ||
| SMILES | CC(CC(=O)CC(C)C(=O)O)C1CC(=O)C2(C1(CC(=O)C3=C2C(CC4C3(CCC(=O)C4(C)C)C)O)C)C | ||
| Standard InChIKey | YTVGSCZIHGRVAV-FTRKVESOSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C30H42O7/c1-15(10-17(31)11-16(2)26(36)37)18-12-23(35)30(7)25-19(32)13-21-27(3,4)22(34)8-9-28(21,5)24(25)20(33)14-29(18,30)6/h15-16,18-19,21,32H,8-14H2,1-7H3,(H,36,37)/t15-,16?,18-,19+,21?,28+,29-,30+/m1/s1 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Ganoderic acid D treatment for 48h inhibits the proliferation of HeLa human cervical carcinoma cells with an IC(50) value of 17.3 +/- 0.3 microM. |
| In vitro | Proteomics characterization of the cytotoxicity mechanism of ganoderic acid D and computer-automated estimation of the possible drug target network.[Pubmed: 18166740]Mol Cell Proteomics. 2008 May;7(5):949-61.Triterpenes isolated from Ganoderma lucidum could inhibit the growth of numerous cancer cell lines and were thought to be the basis of the anticancer effects of G. lucidum. Ganoderic acid D (GAD) is one of the major components in Ganoderma triterpenes. GAD treatment for 48 h inhibited the proliferation of HeLa human cervical carcinoma cells with an IC(50) value of 17.3 +/- 0.3 microM. Flow cytometric analysis and DNA fragmentation analysis indicated that Ganoderic acid D induced G(2)/M cell cycle arrest and apoptosis. |
| In vivo | Identification of metabolites of ganoderic acid D by ultra-performance liquid chromatography/quadrupole time-of-flight mass spectrometry.[Pubmed: 22942320]Drug Metab Dispos. 2012 Dec;40(12):2307-14.Ganoderic acid D (GD) is the major active triterpenoid in Ganoderma lucidum, a medicinal fungus used daily. However, the metabolic fate of Ganoderic acid D remains unknown. To know whether Ganoderic acid D is extensively metabolized, we first investigated the metabolism of Ganoderic acid D in vitro and in vivo.
|

Ganoderic acid D Dilution Calculator

Ganoderic acid D Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 1.943 mL | 9.7152 mL | 19.4303 mL | 38.8606 mL | 48.5758 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.3886 mL | 1.943 mL | 3.8861 mL | 7.7721 mL | 9.7152 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.1943 mL | 0.9715 mL | 1.943 mL | 3.8861 mL | 4.8576 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0389 mL | 0.1943 mL | 0.3886 mL | 0.7772 mL | 0.9715 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0194 mL | 0.0972 mL | 0.1943 mL | 0.3886 mL | 0.4858 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
- Geneticin, G-418 Sulfate
Catalog No.:BCC1202
CAS No.:108321-42-2
- Fmoc-D-Asn-OH
Catalog No.:BCC3083
CAS No.:108321-39-7
- 1,7-Bis(4-hydroxyphenyl)hept-1-en-3-one
Catalog No.:BCN1629
CAS No.:1083200-79-6
- 1,7-Bis(4-hydroxyphenyl)hept-6-en-3-ol
Catalog No.:BCN1630
CAS No.:1083195-05-4
- Cariprazine hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC1454
CAS No.:1083076-69-0
- A 987306
Catalog No.:BCC7732
CAS No.:1082954-71-9
- LY2584702
Catalog No.:BCC6369
CAS No.:1082949-67-4
- PF-04447943
Catalog No.:BCC1850
CAS No.:1082744-20-4
- PDE-9 inhibitor
Catalog No.:BCC1842
CAS No.:1082743-70-1
- TC-S 7005
Catalog No.:BCC6189
CAS No.:1082739-92-1
- TUG 424
Catalog No.:BCC7776
CAS No.:1082058-99-8
- SKF 83566 hydrobromide
Catalog No.:BCC7121
CAS No.:108179-91-5
- Noradrenaline bitartrate monohydrate
Catalog No.:BCC4810
CAS No.:108341-18-0
- Fuligorubin A
Catalog No.:BCN1837
CAS No.:108343-55-1
- FH535
Catalog No.:BCC1573
CAS No.:108409-83-2
- [D-Phe12]-Bombesin
Catalog No.:BCC5844
CAS No.:108437-87-2
- [D-Phe12,Leu14]-Bombesin
Catalog No.:BCC6020
CAS No.:108437-88-3
- Ilexsaponin A
Catalog No.:BCN7867
CAS No.:108524-93-2
- Ilexgenin A
Catalog No.:BCC9233
CAS No.:108524-94-3
- Eupahualin C
Catalog No.:BCN7234
CAS No.:108525-39-9
- 23S-hydroxy-11,15-dioxo-ganoderic acid DM
Catalog No.:BCN8131
CAS No.:1085273-49-9
- Pyridostatin
Catalog No.:BCC1875
CAS No.:1085412-37-8
- Lumichrome
Catalog No.:BCN7083
CAS No.:1086-80-2
-
4-Hydroxy-Teriflunomide
Catalog No.:BCC4734
CAS No.:
Identification of metabolites of ganoderic acid D by ultra-performance liquid chromatography/quadrupole time-of-flight mass spectrometry.[Pubmed:22942320]
Drug Metab Dispos. 2012 Dec;40(12):2307-14.
Ganoderic acid D (GD) is the major active triterpenoid in Ganoderma lucidum, a medicinal fungus used daily. However, the metabolic fate of GD remains unknown. To know whether GD is extensively metabolized, we first investigated the metabolism of GD in vitro and in vivo. The metabolic profiles of the bile samples obtained from rats in vivo were almost the same as those obtained in vitro. Using ultra-performance liquid chromatography/quadrupole time-of-flight mass spectrometry, a total of 25 metabolites were identified from the bile sample. Few metabolites were found in the urine samples. These results indicated that biliary rather than renal clearance was the major route of excretion. The major metabolites were identified by comparison with the standard reference compounds. Metabolites at low concentrations were identified by interpreting the mass spectra. Both phase I and phase II metabolites were observed. The metabolic transformation included reduction, monohydroxylation, dihydroxylation, trihydroxylation, oxidation, desaturation, sulfation, and glucuronidation. The main metabolic soft spots in the chemical structure of GD were the 3-carbonyl group, angular methyl groups, the 7-hydroxy group, and the 26-carboxylic acid moiety. Overall, this study gives us an insight into the metabolism of GD, an active oxygenated tetracyclic triterpenoid.
Proteomics characterization of the cytotoxicity mechanism of ganoderic acid D and computer-automated estimation of the possible drug target network.[Pubmed:18166740]
Mol Cell Proteomics. 2008 May;7(5):949-61.
Triterpenes isolated from Ganoderma lucidum could inhibit the growth of numerous cancer cell lines and were thought to be the basis of the anticancer effects of G. lucidum. Ganoderic acid D (GAD) is one of the major components in Ganoderma triterpenes. GAD treatment for 48 h inhibited the proliferation of HeLa human cervical carcinoma cells with an IC(50) value of 17.3 +/- 0.3 microM. Flow cytometric analysis and DNA fragmentation analysis indicated that GAD induced G(2)/M cell cycle arrest and apoptosis. To identify the cellular targets of GAD, two-dimensional gel electrophoresis was performed, and proteins altered in expressional level after GAD exposure of cells were identified by MALDI-TOF MS/MS. The regulation of proteins was also confirmed by Western blotting. The cytotoxic effect of GAD was associated with regulated expression of 21 proteins. Furthermore these possible GAD target-related proteins were evaluated by an in silico drug target searching program, INVDOCK. The INVDOCK analysis results suggested that GAD could bind six isoforms of 14-3-3 protein family, annexin A5, and aminopeptidase B. The direct binding affinity of GAD toward 14-3-3 zeta was confirmed in vitro using surface plasmon resonance biosensor analysis. In addition, the intensive study of functional association among these 21 proteins revealed that 14 of them were closely related in the protein-protein interaction network. They had been found to either interact with each other directly or associate with each other via only one intermediate protein from previous protein-protein interaction experimental results. When the network was expanded to a further interaction outward, all 21 proteins could be included into one network. In this way, the possible network associated with GAD target-related proteins was constructed, and the possible contribution of these proteins to the cytotoxicity of GAD is discussed in this report.


