IWP 4CAS# 686772-17-8 |
- FH535
Catalog No.:BCC1573
CAS No.:108409-83-2
- CHIR-99021 (CT99021)
Catalog No.:BCC1275
CAS No.:252917-06-9
- XAV-939
Catalog No.:BCC1120
CAS No.:284028-89-3
- Salinomycin
Catalog No.:BCC1916
CAS No.:53003-10-4
- Salinomycin sodium salt
Catalog No.:BCC1917
CAS No.:55721-31-8
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 686772-17-8 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 2155264 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C23H20N4O3S3 | M.Wt | 496.62 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | DMSO : 5 mg/mL (10.07 mM; Need ultrasonic and warming) | ||
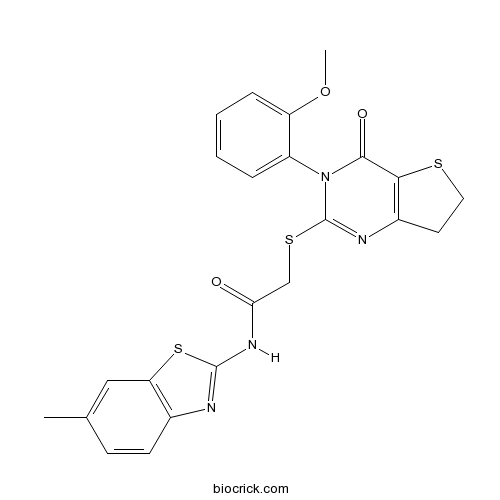
| Chemical Name | 2-[[3-(2-methoxyphenyl)-4-oxo-6,7-dihydrothieno[3,2-d]pyrimidin-2-yl]sulfanyl]-N-(6-methyl-1,3-benzothiazol-2-yl)acetamide | ||
| SMILES | CC1=CC2=C(C=C1)N=C(S2)NC(=O)CSC3=NC4=C(C(=O)N3C5=CC=CC=C5OC)SCC4 | ||
| Standard InChIKey | RHUJMHOIQBDFQR-UHFFFAOYSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C23H20N4O3S3/c1-13-7-8-14-18(11-13)33-22(24-14)26-19(28)12-32-23-25-15-9-10-31-20(15)21(29)27(23)16-5-3-4-6-17(16)30-2/h3-8,11H,9-10,12H2,1-2H3,(H,24,26,28) | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Potent inhibitor of Wnt/β-catenin signaling (IC50 = 25 nM). Has minimal effect on Notch and Hedgehog signaling pathways. Induces differentiation of cardiomyocytes from human ESCs and iPSCs. |

IWP 4 Dilution Calculator

IWP 4 Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.0136 mL | 10.0681 mL | 20.1361 mL | 40.2722 mL | 50.3403 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.4027 mL | 2.0136 mL | 4.0272 mL | 8.0544 mL | 10.0681 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.2014 mL | 1.0068 mL | 2.0136 mL | 4.0272 mL | 5.034 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0403 mL | 0.2014 mL | 0.4027 mL | 0.8054 mL | 1.0068 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0201 mL | 0.1007 mL | 0.2014 mL | 0.4027 mL | 0.5034 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
- BC 11-38
Catalog No.:BCC7940
CAS No.:686770-80-9
- IWP-2
Catalog No.:BCC1665
CAS No.:686770-61-6
- (±)-Palmitoylcarnitine chloride
Catalog No.:BCC6718
CAS No.:6865-14-1
- BOP-Cl
Catalog No.:BCC2808
CAS No.:68641-49-6
- CP-945598 HCl
Catalog No.:BCC1082
CAS No.:686347-12-6
- Otenabant
Catalog No.:BCC1828
CAS No.:686344-29-6
- Procerine
Catalog No.:BCN2017
CAS No.:68622-81-1
- Xylobiose
Catalog No.:BCN8424
CAS No.:6860-47-5
- Isorhynchophylline
Catalog No.:BCN6458
CAS No.:6859-1-4
- Isorhyncophylline
Catalog No.:BCN3466
CAS No.:6859-01-4
- PX-478 2HCl
Catalog No.:BCC6502
CAS No.:685898-44-6
- Prometaphanine
Catalog No.:BCN4244
CAS No.:6858-85-1
- Qianhucoumarin G
Catalog No.:BCN3704
CAS No.:68692-61-5
- Retronecine N-oxide
Catalog No.:BCN2035
CAS No.:6870-33-3
- Jacobine
Catalog No.:BCN2087
CAS No.:6870-67-3
- 11β,17α-Dihydroxy-6α-methylpregna-1,4-diene-3,20-dione
Catalog No.:BCC8434
CAS No.:6870-94-6
- 13,18-Dehydroglaucarubinone
Catalog No.:BCN7957
CAS No.:68703-94-6
- Asimilobine
Catalog No.:BCN7076
CAS No.:6871-21-2
- Echitamine
Catalog No.:BCN4245
CAS No.:6871-44-9
- (-)-Lotusine
Catalog No.:BCN8443
CAS No.:6871-67-6
- Arteanoflavone
Catalog No.:BCN6824
CAS No.:68710-17-8
- Xanthoplanine
Catalog No.:BCN4246
CAS No.:6872-88-4
- Epiberberine
Catalog No.:BCN5387
CAS No.:6873-09-2
- Phellodendrine
Catalog No.:BCN5933
CAS No.:6873-13-8
Differentiation of human epidermal neural crest stem cells (hEPI-NCSC) into virtually homogenous populations of dopaminergic neurons.[Pubmed:24399192]
Stem Cell Rev. 2014 Apr;10(2):316-26.
Here we provide a protocol for the directed differentiation of hEPI-NCSC into midbrain dopaminergic neurons, which degenerate in Parkinson's disease. hEPI-NCSC are neural crest-derived multipotent stem cells that persist into adulthood in the bulge of hair follicles. The experimental design is distinctly different from conventional protocols for embryonic stem cells and induced pluripotent stem (iPS) cells. It includes pre-differentiation of the multipotent hEPI-NCSC into neural stem cell-like cells, followed by ventralizing, patterning, continued exposure to the TGFbeta receptor inhibitor, SB431542, and at later stages of differentiation the presence of the WNT inhibitor, IWP-4. All cells expressed A9 midbrain dopaminergic neuron progenitor markers with gene expression levels comparable to those in normal human substantia nigra. The current study shows for the first time that virtually homogeneous populations of dopaminergic neurons can be derived ex vivo from somatic stem cells without the need for purification, with useful timeliness and high efficacy. This novel development is an important first step towards the establishment of fully functional dopaminergic neurons from an ontologically relevant stem cell type, hEPI-NCSC.
Small molecule-mediated disruption of Wnt-dependent signaling in tissue regeneration and cancer.[Pubmed:19125156]
Nat Chem Biol. 2009 Feb;5(2):100-7.
The pervasive influence of secreted Wnt signaling proteins in tissue homeostasis and tumorigenesis has galvanized efforts to identify small molecules that target Wnt-mediated cellular responses. By screening a diverse synthetic chemical library, we have discovered two new classes of small molecules that disrupt Wnt pathway responses; whereas one class inhibits the activity of Porcupine, a membrane-bound acyltransferase that is essential to the production of Wnt proteins, the other abrogates destruction of Axin proteins, which are suppressors of Wnt/beta-catenin pathway activity. With these small molecules, we establish a chemical genetic approach for studying Wnt pathway responses and stem cell function in adult tissue. We achieve transient, reversible suppression of Wnt/beta-catenin pathway response in vivo, and we establish a mechanism-based approach to target cancerous cell growth. The signal transduction mechanisms shown here to be chemically tractable additionally contribute to Wnt-independent signal transduction pathways and thus could be broadly exploited for chemical genetics and therapeutic goals.
Robust cardiomyocyte differentiation from human pluripotent stem cells via temporal modulation of canonical Wnt signaling.[Pubmed:22645348]
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2012 Jul 3;109(27):E1848-57.
Human pluripotent stem cells (hPSCs) offer the potential to generate large numbers of functional cardiomyocytes from clonal and patient-specific cell sources. Here we show that temporal modulation of Wnt signaling is both essential and sufficient for efficient cardiac induction in hPSCs under defined, growth factor-free conditions. shRNA knockdown of beta-catenin during the initial stage of hPSC differentiation fully blocked cardiomyocyte specification, whereas glycogen synthase kinase 3 inhibition at this point enhanced cardiomyocyte generation. Furthermore, sequential treatment of hPSCs with glycogen synthase kinase 3 inhibitors followed by inducible expression of beta-catenin shRNA or chemical inhibitors of Wnt signaling produced a high yield of virtually (up to 98%) pure functional human cardiomyocytes from multiple hPSC lines. The robust ability to generate functional cardiomyocytes under defined, growth factor-free conditions solely by genetic or chemically mediated manipulation of a single developmental pathway should facilitate scalable production of cardiac cells suitable for research and regenerative applications.


