MuscimolGABAA receptor agonist, potent CAS# 2763-96-4 |
- PSI-7977
Catalog No.:BCC1871
CAS No.:1190307-88-0
- Trovafloxacin mesylate
Catalog No.:BCC3931
CAS No.:147059-75-4
- Capecitabine
Catalog No.:BCN2168
CAS No.:154361-50-9
- Viomycin
Catalog No.:BCC3930
CAS No.:32988-50-4
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 2763-96-4 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 4266 | Appearance | Beige powder |
| Formula | C4H6N2O2 | M.Wt | 114.1 |
| Type of Compound | Nitrogen-containing Compounds | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Synonyms | Agarine; Pantherine | ||
| Solubility | Soluble to 100 mM in water | ||
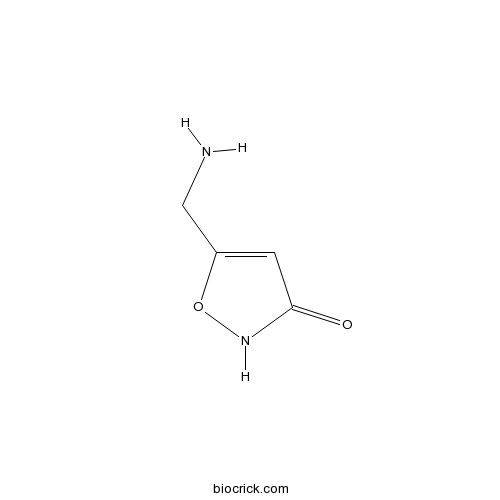
| Chemical Name | 5-(aminomethyl)-1,2-oxazol-3-one | ||
| SMILES | C1=C(ONC1=O)CN | ||
| Standard InChIKey | ZJQHPWUVQPJPQT-UHFFFAOYSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C4H6N2O2/c5-2-3-1-4(7)6-8-3/h1H,2,5H2,(H,6,7) | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Potent GABAA receptor agonist and partial GABAA-ρ receptor agonist. Inhibits memory retention and attenuates airway constriction in vivo. |

Muscimol Dilution Calculator

Muscimol Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 8.7642 mL | 43.8212 mL | 87.6424 mL | 175.2848 mL | 219.106 mL |
| 5 mM | 1.7528 mL | 8.7642 mL | 17.5285 mL | 35.057 mL | 43.8212 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.8764 mL | 4.3821 mL | 8.7642 mL | 17.5285 mL | 21.9106 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.1753 mL | 0.8764 mL | 1.7528 mL | 3.5057 mL | 4.3821 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0876 mL | 0.4382 mL | 0.8764 mL | 1.7528 mL | 2.1911 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
Muscimol is a potent agonist of GABAA receptor [1].
The GABAA receptor is a ligand-gated ion channel and activated by γ-aminobutyric acid (GABA). The GABAA receptor selectively permits Cl- through its pore and results in hyperpolarization of the neuron, which causes an inhibitory effect on neurotransmission.
Muscimol is a potent GABAA receptor agonist. In immortalized GT1-7 neurons, muscimol increased pulsatile GnRH release with EC50 value of 0.47 μM in a concentration-dependent way. The increased GnRH pulsatility by muscimol (5 μM) was blocked by bicuculline, a GABAA receptor antagonist. Muscimol increased GnRH pulse amplitude during exposure to muscimol [1]. With hippocampi slices of rat stimulated with a frequency of 0.01 Hz, muscimol induced long-term depression (LTD) of the amplitude of orthodromic potentials in a concentration- and time-dependent way [2].
In guinea pigs, intravenous muscimol inhibited intravenous acetylcholine-, intravenous histamine- or vagal nerve-stimulated airway constriction through activating GABAA channel [3].
References:
[1]. King TS, Potter D, Kang IS, et al. Concentration-dependent effects of muscimol to enhance pulsatile GnRH release from GT1-7 neurons in vitro. Brain Res, 1999, 824(1): 56-62.
[2]. Akhondzadeh S, Stone TW. Induction of a novel form of hippocampal long-term depression by muscimol: involvement of GABAA but not glutamate receptors. Br J Pharmacol, 1995, 115(3): 527-533.
[3]. Gleason NR, Gallos G, Zhang Y, et al. The GABAA agonist muscimol attenuates induced airway constriction in guinea pigs in vivo. J Appl Physiol (1985). 2009, 106(4): 1257-1263.
- Rhodexin B
Catalog No.:BCC8246
CAS No.:2763-20-4
- Danaidal
Catalog No.:BCN1965
CAS No.:27628-46-2
- Communic acid
Catalog No.:BCN5166
CAS No.:2761-77-5
- MMF
Catalog No.:BCC7941
CAS No.:2756-87-8
- Baccatin III
Catalog No.:BCN5165
CAS No.:27548-93-2
- MS 245 oxalate
Catalog No.:BCC6127
CAS No.:275363-58-1
- H-Gly-OtBu.HCl
Catalog No.:BCC2952
CAS No.:27532-96-3
- Feretoside
Catalog No.:BCN5164
CAS No.:27530-67-2
- Gedunin
Catalog No.:BCC7676
CAS No.:2753-30-2
- H-Cha-OH
Catalog No.:BCC2663
CAS No.:27527-05-5
- Gambogic acid
Catalog No.:BCN2318
CAS No.:2752-65-0
- Mesaconitine
Catalog No.:BCN5987
CAS No.:2752-64-9
- 15-Nonacosanol
Catalog No.:BCC8439
CAS No.:2764-81-0
- 5-Isoquinolinesulfonic acid
Catalog No.:BCC8749
CAS No.:27655-40-9
- Boc-Ser-OMe
Catalog No.:BCC3441
CAS No.:2766-43-0
- Cyanidin-3-O-galactoside chloride
Catalog No.:BCN3022
CAS No.:27661-36-5
- Leucoside
Catalog No.:BCN5167
CAS No.:27661-51-4
- Akt/SKG Substrate Peptide
Catalog No.:BCC5748
CAS No.:276680-69-4
- WAY 161503 hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC7179
CAS No.:276695-22-8
- Cryptomoscatone D2
Catalog No.:BCN7203
CAS No.:276856-55-4
- 7-Megastigmene-3,5,6,9-tetraol
Catalog No.:BCN5168
CAS No.:276870-26-9
- 2,4-Bis(α,α-dimethylbenzyl)phenol
Catalog No.:BCC8498
CAS No.:2772-45-4
- Scutellarin
Catalog No.:BCN5902
CAS No.:27740-01-8
- Erysotrine
Catalog No.:BCN5170
CAS No.:27740-43-8
Multivariate optimization of the hollow fibre liquid phase microextraction of muscimol in human urine samples.[Pubmed:27631575]
J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci. 2016 Oct 15;1033-1034:372-381.
A liquid phase microextraction based on hollow fibre followed by liquid chromatographic determination was developed for the extraction and quantitation of the hallucinogenic Muscimol from urine samples. Method applicability on polar hallucinogens was also tested on two alkaloids, a psychedelic hallucinogen, tryptamine and a polar amino acid, tryptophan which exists in its charged state in the entire pH range. A multivariate design of experiments was used in which a half fractional factorial approach was applied to screen six factors (donor phase pH, acceptor phase HCl concentration, carrier composition, stirring rate, extraction time and salt content) for their extent of vitality in carrier mediated liquid microextractions. Four factors were deemed essential for the effective extraction of each analyte. The vital factors were further optimized for the extraction of single-spiked analyte solutions using a central composite design. When the simultaneous extraction of analytes was performed under universal factor conditions biased towards maximizing the enrichment of Muscimol, a good composite desirability value of 0.687 was obtained. The method was finally applied on spiked urine samples with acceptable enrichments of 4.1, 19.7 and 24.1 obtained for Muscimol, tryptophan and tryptamine respectively. Matrix-based calibration curves were used to address matrix effects. The r(2) values of the matrix-based linear regression prediction models ranged from 0.9933 to 0.9986. The linearity of the regression line of the matrix-based calibration curves for each analyte was directly linked to the analyte enrichment repeatability which ranged from an RSD value of 8.3-13.1%. Limits of detection for the developed method were 5.12, 3.10 and 0.21ngmL(-1) for Muscimol, tryptophan and tryptamine respectively. The developed method has proven to offer a viable alternative for the quantitation of Muscimol in human urine samples.
The GABAA receptor agonist muscimol induces an age- and region-dependent form of long-term depression in the mouse striatum.[Pubmed:27531838]
Learn Mem. 2016 Aug 16;23(9):479-85.
Several forms of long-term depression (LTD) of glutamatergic synaptic transmission have been identified in the dorsal striatum and in the nucleus accumbens (NAc). Such experience-dependent synaptic plasticity might play important roles in reward-related learning. The GABAA receptor agonist Muscimol was recently found to trigger a long-lasting depression of glutamatergic synaptic transmission in the NAc of adolescent mice, but the mechanisms that underlie this novel form of LTD were not studied. Here we examined the effect of Muscimol applied in the perfusion solution on the amplitude of field excitatory postsynaptic potentials/population spikes (fEPSP/PSs) in mouse brain slices. We found that Muscimol depressed the fEPSP/PS in the NAc of adolescent mice but not adult mice, through both postsynaptic and presynaptic mechanisms. Indeed, Muscimol altered the fEPSP/PS paired-pulse ratio, depolarized the membrane of projection neurons, and decreased the frequency, but not amplitude, of spontaneous excitatory postsynaptic currents in the NAc of adolescent mice. The LTD induced by Muscimol likely involved endocannabinoids, metabotropic glutamate receptors (mGluRs), but not TRPV1 receptors. Muscimol-LTD was occluded by prior induction of LTD through low-frequency stimulation (LFS) of the slice, demonstrating a common pathway in the induction of LFS-LTD and Muscimol-LTD. We also found that Muscimol induced a form of LTD in the dorsolateral striatum of adult but not adolescent mice. This LTD was mediated by endocannabinoids but did not involve mGluRs or TRPV1 receptors. These results identify a novel form of synaptic plasticity, and its mechanisms of induction, which is age and region dependent. These findings may contribute to a better understanding of the increased susceptibility of the adolescent brain to long-term synaptic changes in regions associated with reward mechanisms.
The lesion of dorsolateral funiculus changes the antiallodynic effect of the intrathecal muscimol and baclofen in distinct phases of neuropathic pain induced by spinal nerve ligation in rats.[Pubmed:27063286]
Brain Res Bull. 2016 Jun;124:103-15.
The abnormal firing of damaged primary afferents and the changes in the central nervous system (CNS) play important role in the initiation and maintenance phases of neuropathic pain. These phases of neuropathic pain involve changes in the GABAergic control of descending pathways that travel through the dorsolateral funiculus (DLF). The present study shows that unilateral DLF lesion increased the antiallodynic effect of Muscimol (0.2mug/5muL) (a GABAA receptor agonist) in the initiation, but not maintenance phase of the mechanical allodynia induced by a spinal nerve ligation (SNL) of the ipsilateral hindpaw of rats. The unilateral DLF lesion increased the antiallodynic effect of baclofen (0.8mug/5muL) (a GABAB receptor agonist) in the initiation phase and reduced your effect in the maintenance phase of the mechanical allodynia induced by a spinal nerve ligation (SNL) of the ipsilateral paw of rats. The unilateral DLF lesion significantly reduced the proallodynic effect of an intrathecal injection of phaclofen (30mug/5muL) (a GABAB receptor antagonist), but not bicuculline (0.3mug/5muL) (a GABAA receptor antagonist). The effect of DLF lesion on the proallodynic effect of phaclofen was observed in the maintenance, but not in the initiation phase of the mechanical allodynia induced by SNL. We than conclude that the spinal GABAergic neurotransmission is negatively modulated by DLF using GABAA and GABAB receptors, in the initiation phase of mechanical allodynia induced by SNL. In addition, the integrity of DLF is necessary for the effectiveness of GABAergic transmission that occurs via spinal GABAB, but not GABAA receptors, in the maintenance phase of mechanical allodynia induced by SNL.
Additive effect of harmane and muscimol for memory consolidation impairment in inhibitory avoidance task.[Pubmed:27725215]
Neuroscience. 2016 Dec 17;339:287-295.
In the current study, we examined the effect of bilateral intra-dorsal hippocampal (intra-CA1) microinjections of GABAA receptor agents on amnesia induced by a beta-carboline alkaloid, harmane in mice. We used a single-trial step-down passive avoidance task to assess memory retention and then, open-field test to assess locomotor activity. The results indicated that post-training intra-CA1 injections of bicuculline - a GABAA receptor antagonist - had no significant effect, while Muscimol (0.01 and 0.1mug/mouse) - a GABAA receptor agonist - impaired memory consolidation. Post-training intra-peritoneal (i.p.) infusion of harmane (3 and 5mg/kg) decreased memory consolidation. Furthermore, post-training intra-CA1 administration of sub-threshold dose of bicuculline (0.001mug/mouse) restored, whereas Muscimol (0.001mug/mouse) potentiated impairment of memory consolidation induced by harmane. The isobologram analysis revealed that there is an additive effect between harmane and Muscimol on impairment of memory consolidation. Moreover, all above doses of drugs did not alter locomotor activity. These findings suggest that GABAA receptors of the CA1 area, at least partly, play a role in modulating the effect of harmane on memory consolidation.
The GABAA agonist muscimol attenuates induced airway constriction in guinea pigs in vivo.[Pubmed:19213928]
J Appl Physiol (1985). 2009 Apr;106(4):1257-63.
GABA(A) channels are ubiquitously expressed on neuronal cells and act via an inward chloride current to hyperpolarize the cell membrane of mature neurons. Expression and function of GABA(A) channels on airway smooth muscle cells has been demonstrated in vitro. Airway smooth muscle cell membrane hyperpolarization contributes to relaxation. We hypothesized that Muscimol, a selective GABA(A) agonist, could act on endogenous GABA(A) channels expressed on airway smooth muscle to attenuate induced increases in airway pressures in anesthetized guinea pigs in vivo. In an effort to localize Muscimol's effect to GABA(A) channels expressed on airway smooth muscle, we pretreated guinea pigs with a selective GABA(A) antagonist (gabazine) or eliminated lung neural control from central parasympathetic, sympathetic, and nonadrenergic, noncholinergic (NANC) nerves before Muscimol treatment. Pretreatment with intravenous Muscimol alone attenuated intravenous histamine-, intravenous acetylcholine-, or vagal nerve-stimulated increases in peak pulmonary inflation pressure. Pretreatment with the GABA(A) antagonist gabazine blocked Muscimol's effect. After the elimination of neural input to airway tone by central parasympathetic nerves, peripheral sympathetic nerves, and NANC nerves, intravenous Muscimol retained its ability to block intravenous acetylcholine-induced increases in peak pulmonary inflation pressures. These findings demonstrate that the GABA(A) agonist Muscimol acting specifically via GABA(A) channel activation attenuates airway constriction independently of neural contributions. These findings suggest that therapeutics directed at the airway smooth muscle GABA(A) channel may be a novel therapy for airway constriction following airway irritation and possibly more broadly in diseases such as asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease.
Muscimol state-dependent memory: involvement of dorsal hippocampal mu-opioid receptors.[Pubmed:19447274]
Behav Brain Res. 2009 Aug 24;202(1):5-10.
In the present study, the effects of subcutaneous (s.c.) injections of morphine, a mu-opioid receptor agonist and intra-dorsal hippocampal (intra-CA1) injections of naloxone, a mu-opioid receptor antagonist on Muscimol state-dependent memory were examined in mice. A single-trial step-down passive avoidance task was used for the assessment of memory retention in adult male NMRI mice. Pre-training intra-CA1 administration of a GABAA receptor agonist, Muscimol (0.025, 0.05, 0.1 and 0.2 microg/mouse) dose dependently induced impairment of memory retention. Pre-test injection of Muscimol (0.05, 0.1 and 0.2 microg/mouse, intra-CA1) induced state-dependent retrieval of the memory acquired under pre-training Muscimol (0.1 microg/mouse, intra-CA1) influence. Pre-test injection of morphine (0.5 and 1 mg/kg, s.c.) 30 min before the administration of Muscimol (0.1 microg/mouse, intra-CA1) dose dependently inhibited Muscimol state-dependent memory. Pre-test intra-CA1 injection of naloxone (0.1 and 0.2 microg/mouse, intra-CA1) improved pre-training Muscimol (0.1 microg/mouse)-induced retrieval impairment. Moreover, pre-test administration of naloxone (0.1 and 0.2 microg/mouse, intra-CA1) with an ineffective dose of Muscimol (0.025 microg/mouse) significantly restored the retrieval and induced Muscimol state-dependent memory. These findings implicate the involvement of a dorsal hippocampal mu-opioid receptor mechanism in Muscimol state-dependent memory.
GABAc receptors: relatively simple transmitter -gated ion channels?[Pubmed:8885697]
Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1996 Sep;17(9):319-23.
The inhibitory neurotransmitter, GABA, activates a variety of receptors in all areas of the CNS. Two major subtypes of GABA receptors are well known: (1) GABAA receptors are ligand-gated Cl- channels that consist of a heteromeric mixture of protein subunits forming a pentameric structure, and (2) GABAB receptors couple to Ca2+ and K+ channels via G proteins and second messengers. Here, Graham Johnston discusses evidence for a third major subclass of GABA receptors. GABAC receptors appear to be relatively simple ligand-gated Cl- channels with a distinctive pharmacology, in that they are not blocked by bicuculline and not modulated by barbiturates, benzodiazepines or neuroactive steroids. Compared with GABAA receptors, GABAC receptors are activated at lower concentrations of GABA and are less liable to desensitization. In addition, their channels open for a longer time. The pharmacology of these novel subtypes of GABA receptors may yield important therapeutic agents.
Induction of a novel form of hippocampal long-term depression by muscimol: involvement of GABAA but not glutamate receptors.[Pubmed:7582468]
Br J Pharmacol. 1995 Jun;115(3):527-33.
1. Unlike long-term potentiation, long-term depression (LTD) in the central nervous system remains poorly understood. The present study was undertaken to investigate the role of GABAA receptors in LTD and synaptic plasticity. 2. Extracellular recordings were made in the CA1 pyramidal cell layer of rat hippocampal slices following orthodromic stimulation of Schaffer collateral fibres in stratum radiatum (0.01 Hz). 3. Muscimol induced a time- and concentration-dependent LTD of the amplitude of orthodromic potentials. Increasing the stimulation frequency from 0.01 Hz to 1 Hz for 10 s reversed the LTD induced by Muscimol. Muscimol also induced LTD in the absence of electrical stimulation. 4. Adenosine decreased the spike size in a concentration-dependent manner, but failed to induce LTD. 5. Alphaxalone and 5 alpha-pregnan-3 alpha-ol-20-one at concentrations that did not have any effect themselves on the population spike (0.5 and 1 microM), potentiated the inhibitory effect of Muscimol on the population spike size, including concentrations which were not effective by themselves. Both steroids were able to potentiate the ability of Muscimol to induce LTD. 6. Bicuculline, 5 microM, reversed the LTD induced by Muscimol, 10 microM. 7. The NMDA receptor antagonist (+/-)-2-amino-5-phosphonopentanoic acid (2-AP5), the NMDA/metabotropic antagonist 2-AP3 and selective metabotropic antagonist L-(+)-2-amino-3-phosphonopropionic acid (L(+)-AP3) failed to modify the LTD. Similarly, quisqualic acid and (1S, 3R)-aminocyclopentane dicarboxylic acid (ACPD) a selective agonist at metabotropic receptors did not induce LTD or short-term depression, whereas kynurenic acid prevented the reversal of the LTD obtained at 1 Hz. 8. It is concluded that LTD can be induced by the selective activation of GABAA receptors. The lack of involvement of glutamate receptors in our protocol confirms the unique nature of the LTD described here. The phenomenon of GABA-induced LTD and its reversal by 1 Hz stimulation may represent a novel type of long-lasting depression by which inhibitory interneurones can modulate pyramidal cell excitability in a frequency-dependent manner.


