NS 1619Activator of BKCa (KCa1.1) channels CAS# 153587-01-0 |
- Melphalan
Catalog No.:BCC2403
CAS No.:148-82-3
- GRI 977143
Catalog No.:BCC2401
CAS No.:325850-81-5
- Mdivi 1
Catalog No.:BCC2402
CAS No.:338967-87-6
- DAPK Substrate Peptide
Catalog No.:BCC2400
CAS No.:386769-53-5
- Cesium chloride
Catalog No.:BCC2399
CAS No.:7647-17-8
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 153587-01-0 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 4552 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C15H8F6N2O2 | M.Wt | 362.23 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | DMSO : ≥ 31 mg/mL (85.58 mM) *"≥" means soluble, but saturation unknown. | ||
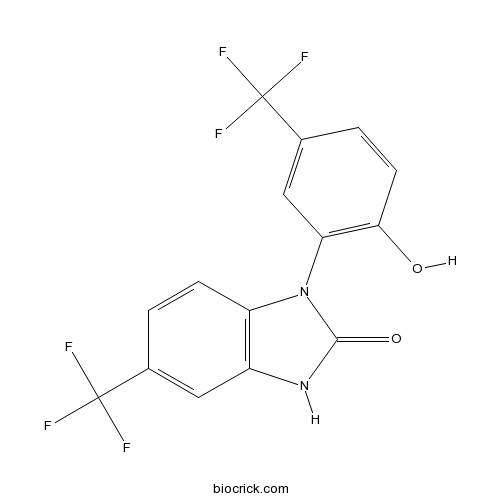
| Chemical Name | 3-[2-hydroxy-5-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]-6-(trifluoromethyl)-1H-benzimidazol-2-one | ||
| SMILES | C1=CC2=C(C=C1C(F)(F)F)NC(=O)N2C3=C(C=CC(=C3)C(F)(F)F)O | ||
| Standard InChIKey | YLFMCMWKHSDUCT-UHFFFAOYSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C15H8F6N2O2/c16-14(17,18)7-1-3-10-9(5-7)22-13(25)23(10)11-6-8(15(19,20)21)2-4-12(11)24/h1-6,24H,(H,22,25) | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Large-conductance Ca2+-activated potassium (BKCa, KCa1.1) channel activator. Induces a concentration-dependent decrease in mitochondrial membrane potential (EC50 = 3.6 μM). |

NS 1619 Dilution Calculator

NS 1619 Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.7607 mL | 13.8034 mL | 27.6068 mL | 55.2135 mL | 69.0169 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.5521 mL | 2.7607 mL | 5.5214 mL | 11.0427 mL | 13.8034 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.2761 mL | 1.3803 mL | 2.7607 mL | 5.5214 mL | 6.9017 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0552 mL | 0.2761 mL | 0.5521 mL | 1.1043 mL | 1.3803 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0276 mL | 0.138 mL | 0.2761 mL | 0.5521 mL | 0.6902 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
- 13-Hydroxylupanine
Catalog No.:BCN3204
CAS No.:15358-48-2
- DL-Menthol
Catalog No.:BCN5950
CAS No.:15356-70-4
- D-Menthol
Catalog No.:BCN4973
CAS No.:15356-60-2
- Bexarotene
Catalog No.:BCC3737
CAS No.:153559-49-0
- [D-Trp34]-Neuropeptide Y
Catalog No.:BCC7690
CAS No.:153549-84-9
- Cevimeline hydrochloride hemihydrate
Catalog No.:BCC1471
CAS No.:153504-70-2
- Xanthinin
Catalog No.:BCN1686
CAS No.:153483-31-9
- Carbazeran citrate
Catalog No.:BCC6173
CAS No.:153473-94-0
- Desmethoxy yangonin
Catalog No.:BCN2295
CAS No.:15345-89-8
- Fexofenadine HCl
Catalog No.:BCC4542
CAS No.:153439-40-8
- WHI-P180 hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC4243
CAS No.:153437-55-9
- PD153035 hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC3617
CAS No.:153436-54-5
- GNE-9605
Catalog No.:BCC5458
CAS No.:1536200-31-3
- Dofequidar fumarate
Catalog No.:BCC4177
CAS No.:153653-30-6
- H-Ile-OEt.HCl
Catalog No.:BCC2961
CAS No.:15366-32-3
- 9,10-Bis(3,5-dihydroxyphenyl)anthracene
Catalog No.:BCC8793
CAS No.:153715-08-3
- Eriodictyol-8-glucoside
Catalog No.:BCN8029
CAS No.:153733-96-1
- Dioxopromethazine hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC8946
CAS No.:15374-15-9
- Fmoc-Trp-ol
Catalog No.:BCC2573
CAS No.:153815-60-2
- BLU9931
Catalog No.:BCC3979
CAS No.:1538604-68-0
- Boc-Gln-ONp
Catalog No.:BCC3383
CAS No.:15387-45-8
- NBOH-2C-CN hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC8025
CAS No.:1539266-32-4
- p-Hydroxyphenethyl vanillate
Catalog No.:BCN7555
CAS No.:1539303-03-1
- ANQ 11125
Catalog No.:BCC6359
CAS No.:153966-48-4
The mitochondrial Ca2+-activated K+ channel activator, NS 1619 inhibits L-type Ca2+ channels in rat ventricular myocytes.[Pubmed:17698036]
Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2007 Oct 12;362(1):31-36.
We examined the effects of the mitochondrial Ca(2+)-activated K(+) (mitoBK(Ca)) channel activator NS 1619 on L-type Ca(2+) channels in rat ventricular myocytes. NS 1619 inhibited the Ca(2+) current in a dose-dependent manner. NS 1619 shifted the activation curve to more positive potentials, but did not have a significant effect on the inactivation curve. Pretreatment with inhibitors of membrane BK(Ca) channel, mitoBK(Ca) channel, protein kinase C, protein kinase A, and protein kinase G had little effect on the Ca(2+) current and did not alter the inhibitory effect of NS 1619 significantly. The application of additional NS 1619 in the presence of isoproterenol, a selective beta-adrenoreceptor agonist, reduced the Ca(2+) current to approximately the same level as a single application of NS 1619. In conclusion, our results suggest that NS 1619 inhibits the Ca(2+) current independent of the mitoBK(Ca) channel and protein kinases. Since NS 1619 is widely used to study mitoBK(Ca) channel function, it is essential to verify these unexpected effects of NS 1619 before experimental data can be interpreted accurately.
Functional contribution of the endothelial component to the vasorelaxing effect of resveratrol and NS 1619, activators of the large-conductance calcium-activated potassium channels.[Pubmed:17203288]
Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2007 Mar;375(1):73-80.
Large-conductance calcium-activated potassium channels (BK) of smooth muscle play a role in the relevant modulation of vascular tone, due to their calcium- and voltage-dependent mechanisms of activation. A potential role of endothelial BK channels has also been suggested by approaches on endothelial cell cultures. However, no functional study, aimed at evaluating the contribution of endothelial BK channels to the effect of BK-openers, has been reported. Resveratrol and NS 1619, BK-openers, have been tested on endothelium-intact and -denuded aortic rings. Furthermore, the effects of high depolarisation of potassium channel blockers TEA (Tetraethylammonium), 4-AP ( 4-Aminopyridine) and IbTX (Iberiotoxin) and of inhibitors of NO-pathway (L-NAME and ODQ) have been evaluated. The presence of endothelium increased the vasorelaxing potency of BK-openers. This potentiation was eliminated by L-NAME and ODQ. TEA, 4-AP, IbTX and high depolarisation had modest or no antagonist influence on resveratrol in endothelium-denuded aortic rings. The effects of NS 1619 on endothelium-denuded aortic rings were not affected by IbTX, and were modestly antagonised by TEA, 4-AP and high depolarisation. In intact endothelium vessels, TEA, IbTX and 4-AP antagonised the vasorelaxing effect of the two BK-activators. A BK-mediated release of endothelial NO seems a very important factor, determining a strong influence on vasodilator profile of BK-openers. Therefore, an eventual therapy with a BK-opener could promote a series of cardiovascular impacts not confined to the only direct vasorelaxing effects, but also due to a significant contribution of endothelial NO.
Inhibition of guinea pig detrusor contraction by NS-1619 is associated with activation of BKCa and inhibition of calcium currents.[Pubmed:9399993]
J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1997 Dec;283(3):1193-200.
The effects of NS-1619 on bladder contractile function and on transmembrane currents were evaluated in vitro on isolated guinea pig detrusor strips and isolated detrusor myocytes, respectively. In the isolated bladder strip, NS-1619 inhibited KCl-induced contractions in a concentration-dependent manner (IC50 = 12.2 +/- 3. 2 microM). Isolated detrusor myocytes were quiescent and had resting membrane potentials that averaged -45.3 +/- 2.7 mV. With patch-clamp techniques we demonstrated that exposure to 10 to 100 microM NS-1619 increased an iberiotoxin-sensitive current consistent with the activation of the large conductance calcium-dependent potassium channel (BKCa). Single-channel analysis confirmed that NS-1619 increased the open probability of BKCa channels. NS-1619 also appeared to decrease inward calcium current (ICa). After exposure to 30 microM NS-1619, peak current amplitude significantly decreased by approximately 50%. Analysis of the current voltage relationship revealed a significant decrease in maximal conductance from 10.5 +/- 4 to 6.2 +/- 3 nS. The voltage dependence of calcium current activation and inactivation was well fit by a Boltzmann relationship. Besides the decrease in conductance, there was a small, but significant shift in the half-inactivation voltage, which suggests that NS-1619 preferentially blocks the open state of the channel. Steady-state (window) calcium current was also decreased. Analysis of the theoretical window current revealed a 71% decrease in this noninactivating current. These data indicate that NS-1619 inhibits detrusor smooth muscle contraction in a concentration-dependent manner and that the underlying mechanism of action for this effect involves inhibition of calcium current, and may also include activation of the BKCa channel. Compounds with this profile may be useful in the treatment of bladder instability.
BK channel activation by NS-1619 is partially mediated by intracellular Ca2+ release in smooth muscle cells of porcine coronary artery.[Pubmed:11181423]
Br J Pharmacol. 2001 Feb;132(4):828-34.
1. Effects of NS-1619, an opener of large conductance Ca2+-activated K+ (BK) channel, on intracellular Ca2+ concentration ([Ca2+]i) and membrane potential were examined in single myocytes freshly isolated from porcine coronary artery. 2. Under current clamp mode, the application of 1-30 microM NS-1619 hyperpolarized the membrane in concentration-dependent manner. The NS-1619-induced hyperpolarization was abolished by the presence of 100 nM iberiotoxin. 3. Application of 1-10 microM NS-1619 hyperpolarized the membrane by approximately 6 mV or less but did not change significantly the [Ca2+]i. When membrane hyperpolarization of 12 mV or so was caused by 30 microM NS-1619, [Ca2+]i was unexpectedly increased by approximately 200 nM. This increase in [Ca2+]i and the concomitant outward current activation were also observed under voltage-clamp at holding potential of -40 mV. 4. The increase in [Ca2+]i by 30 microM NS-1619 occurred mainly in peripheral regions than in the centre of the myocytes. The removal of extracellular Ca2+ affected neither the membrane hyperpolarization nor the increase in [Ca2+]i. 5. In the presence of 10 mM caffeine and 10 microM ryanodine, the increase in [Ca2+]i by 30 microM NS-1619 was not observed and the membrane hyperpolarization was reduced to approximately 67% of the control. 6. These results indicate that the opening of BK channels by NS-1619 at 30 microM, which is the most frequently used concentration of this agent, is partly due to Ca2+ release from caffeine/ryanodine-sensitive intracellular storage sites but is mainly due to the direct activation of the channels.
Large-conductance K+ channel openers NS1619 and NS004 as inhibitors of mitochondrial function in glioma cells.[Pubmed:12781334]
Biochem Pharmacol. 2003 Jun 1;65(11):1827-34.
Recently, it has been reported that large-conductance Ca(2+)-activated potassium channels, also known as BK(Ca)-type potassium channels, are present in the inner mitochondrial membrane of the human glioma LN229 cell line. Hence, in the present study, we have investigated whether BK(Ca)-channel openers (BK(Ca)COs), such as the benzimidazolone derivatives NS004 (5-trifluoromethyl-1-(5-chloro-2-hydroxyphenyl)-1,3-dihydro-2H-benzimidazole-2-on e) and NS1619 (1,3-dihydro-1-[2-hydroxy-5-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]-5-(trifluoromethyl)-2H-benzi midazol-2-one), affect the functioning of LN229 glioma cell mitochondria in situ. We examined the effect of BK(Ca)COs on mitochondrial membrane potential, mitochondrial respiration and plasma membrane potassium current in human glioma cell line LN229. We found that BK(Ca)COs decrease the mitochondrial membrane potential with an EC(50) value of 3.6+/-0.4 microM for NS1619 and 5.4+/-0.8 microM for NS004. This mitochondrial depolarization was accompanied by an inhibition of the mitochondrial respiratory chain. Both BK(Ca)COs induced whole-cell potassium current blocked by charybdotoxin, as measured by the patch-clamp technique. The BK(Ca)COs had no effect on membrane bilayer conductance. Moreover, the inhibition of mitochondrial function by NS004 and NS1619 was without effect on cell survival, as measured by lactate dehydrogenase release from the cells.
Selective activation of Ca(2+)-dependent K+ channels by novel benzimidazolone.[Pubmed:8137869]
Eur J Pharmacol. 1994 Jan 4;251(1):53-9.
Activators and blockers of specific ion channels are important pharmacological tools for characterizing ion channels and their influence on cell function. The large-conductance Ca(2+)-dependent K+ channel (BK channel) is blocked by peptides such as charybdotoxin and iberiotoxin, but no selective activator of the channel has been described. Here we report single-channel and whole-cell patch-clamp experiments on the specific activation of BK channels in aortic smooth muscle cells with a new heterocyclic molecule, NS 1619 (1-(2'-hydroxy-5'-trifluoromethylphenyl)-5-trifluoromethyl- 2(3H)benzimidazolone). The effect of NS 1619 on the BK channel was dose-dependent, resulting in a shift of the activation curve by up to -50 mV towards negative membrane potentials. The effect was fully reversible and was antagonized by charybdotoxin as well as by tetraethylammonium ions. The compound hyperpolarized the smooth muscle cells. NS 1619 is a selective and new type of K+ channel activator, which may significantly modulate cell excitability.


