Nepicastat (SYN-117) HClDopamine-β-hydroxylase inhibitor CAS# 170151-24-3 |
- (R)-Nepicastat HCl
Catalog No.:BCC4315
CAS No.:195881-94-8
- Isotretinoin
Catalog No.:BCC2284
CAS No.:4759-48-2
- Mildronate
Catalog No.:BCC2289
CAS No.:76144-81-5
- Disulfiram
Catalog No.:BCC2098
CAS No.:97-77-8
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 170151-24-3 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 9840545 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C14H16ClF2N3S | M.Wt | 331.81 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Synonyms | SYN-117 hydrochloride; RS-25560-197 hydrochloride | ||
| Solubility | DMSO : 6 mg/mL (18.08 mM; Need ultrasonic) H2O : 2 mg/mL (6.03 mM; Need ultrasonic and warming) | ||
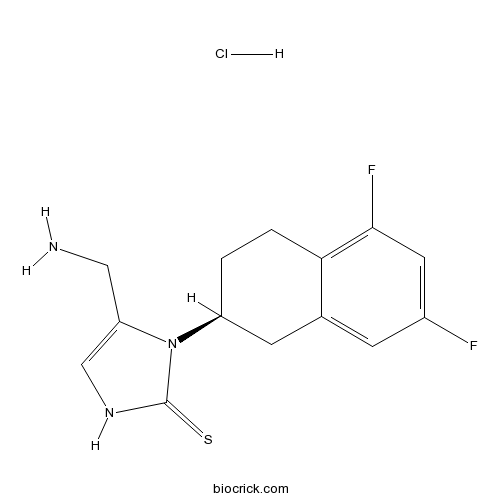
| Chemical Name | 4-(aminomethyl)-3-[(2S)-5,7-difluoro-1,2,3,4-tetrahydronaphthalen-2-yl]-1H-imidazole-2-thione;hydrochloride | ||
| SMILES | C1CC2=C(C=C(C=C2CC1N3C(=CNC3=S)CN)F)F.Cl | ||
| Standard InChIKey | DIPDUAJWNBEVOY-PPHPATTJSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C14H15F2N3S.ClH/c15-9-3-8-4-10(1-2-12(8)13(16)5-9)19-11(6-17)7-18-14(19)20;/h3,5,7,10H,1-2,4,6,17H2,(H,18,20);1H/t10-;/m0./s1 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Potent and selective dopamine β-hydroxylase (DBH) inhibitor (IC50 = 9 nM) . Selective for DBH over 12 other enzymes. Decreases noradrenaline and increases dopamine levels in tissues and plasma in hypertensive rats. Prevents progressive left ventricular dysfunction in an in vivo heart failure model. Also potentiates the stimulus effects of cocaine without producing cocaine-like effects in rats. Orally bioavailable. |

Nepicastat (SYN-117) HCl Dilution Calculator

Nepicastat (SYN-117) HCl Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 3.0138 mL | 15.0689 mL | 30.1377 mL | 60.2755 mL | 75.3443 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.6028 mL | 3.0138 mL | 6.0275 mL | 12.0551 mL | 15.0689 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.3014 mL | 1.5069 mL | 3.0138 mL | 6.0275 mL | 7.5344 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0603 mL | 0.3014 mL | 0.6028 mL | 1.2055 mL | 1.5069 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0301 mL | 0.1507 mL | 0.3014 mL | 0.6028 mL | 0.7534 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
Nepicastat (SYN-117) HCl is a potent and selective inhibitor of dopamine-β-hydroxylase with IC50 values of 8.5 and 9.0 nM in bovine and human, respectively [1].
Dopamine-β-hydroxylase is an enzyme involved in the synthesis of small-molecule membrane-bound neurotransmitters. Dopamine-β-hydroxylase catalyses the synthesis of noradrenaline [1].
Nepicastat (SYN-117) HCl is a potent and selective dopamine-β-hydroxylase inhibitor. (R)-Nepicastat exhibited 2-3 fold less potent than nepicastat [1].
In beagle dogs and spontaneously hypertensive rats, nepicastat reduced noradrenaline in a dose-dependent way and increased dopamine and dopamine/noradrenaline ratio in cerebral cortex, left ventricle and the artery. In beagle dogs, nepicastat (2 mg/kg) significantly reduced noradrenaline by 52% and increased dopamine by 646% and dopamine/noradrenaline ratio in plasma [1]. In pithed spontaneously hypertensive rats, nepicastat inhibited the pressor and positive chronotropic due to preganglionic sympathetic nerve stimulation. In spontaneously hypertensive rats, nepicastat (3 mg/kg) exhibited antihypertensive effects and reduced renal vascular resistance by 38% [2]. In rats, nepicastat significantly increased extracellular dopamine accumulation induced by cocaine and amphetamine in the medial prefrontal cortex [3].
References:
[1]. Stanley WC, Li B, Bonhaus DW, et al. Catecholamine modulatory effects of nepicastat (RS-25560-197), a novel, potent and selective inhibitor of dopamine-beta-hydroxylase. Br J Pharmacol, 1997, 121(8): 1803-1809.
[2]. Stanley WC, Lee K, Johnson LG, et al. Cardiovascular effects of nepicastat (RS-25560-197), a novel dopamine beta-hydroxylase inhibitor. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol, 1998, 31(6): 963-970.
[3]. Devoto P, Flore G, Saba P, et al. The dopamine beta-hydroxylase inhibitor nepicastat increases dopamine release and potentiates psychostimulant-induced dopamine release in the prefrontal cortex. Addict Biol, 2014, 19(4): 612-622.
- Curcolone
Catalog No.:BCN3559
CAS No.:17015-43-9
- Alvimopan dihydrate
Catalog No.:BCC1348
CAS No.:170098-38-1
- Pseudobufarenogin
Catalog No.:BCN8234
CAS No.:17008-69-4
- Bufarenogin
Catalog No.:BCN2297
CAS No.:17008-65-0
- Reserpine hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC4279
CAS No.:16994-56-2
- LY 333531 hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC7969
CAS No.:169939-93-9
- Iso-cuparenal
Catalog No.:BCN7350
CAS No.:16982-01-7
- Mesuol
Catalog No.:BCN6583
CAS No.:16981-20-7
- Dibutyryl-cAMP, sodium salt
Catalog No.:BCC8079
CAS No.:16980-89-5
- Angelol K
Catalog No.:BCN8142
CAS No.:169736-93-0
- Ro 60-0175 fumarate
Catalog No.:BCC7196
CAS No.:169675-09-6
- Z-Thr(tBu)-OH.DCHA
Catalog No.:BCC2565
CAS No.:16966-07-7
- 11-Keto-beta-boswellic acid
Catalog No.:BCN2298
CAS No.:17019-92-0
- Bauerenol acetate
Catalog No.:BCN1106
CAS No.:17020-04-1
- 24-Methylenecycloartane-3beta,26-diol
Catalog No.:BCN1530
CAS No.:17020-27-8
- CD 2314
Catalog No.:BCC6071
CAS No.:170355-37-0
- CD 2665
Catalog No.:BCC7778
CAS No.:170355-78-9
- Enzastaurin (LY317615)
Catalog No.:BCC1100
CAS No.:170364-57-5
- 4-(6-Methyl-4-oxohept-5-en-2-yl)cyclohex-2-en-1-one
Catalog No.:BCN7528
CAS No.:170380-68-4
- 1,4-Epidioxybisabola-2,10-dien-9-one
Catalog No.:BCN7532
CAS No.:170380-69-5
- Isohyperectine
Catalog No.:BCN3405
CAS No.:170384-75-5
- SC 236
Catalog No.:BCC7809
CAS No.:170569-86-5
- Oteromycin
Catalog No.:BCN1849
CAS No.:170591-45-4
- YC 1
Catalog No.:BCC7912
CAS No.:170632-47-0
Dopamine beta-hydroxylase inhibitors enhance the discriminative stimulus effects of cocaine in rats.[Pubmed:24068832]
J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2013 Dec;347(3):564-73.
Inhibitors of dopamine beta-hydroxylase (DBH), the enzyme that converts dopamine (DA) to norepinephrine (NE) in noradrenergic cells, have shown promise for the treatment of cocaine abuse disorders. However, the mechanisms underlying the beneficial effects of these compounds have not been fully elucidated. We used the drug discrimination paradigm to determine the impact of DBH inhibitors on the interoceptive stimulus properties of cocaine. Sprague-Dawley rats were trained to discriminate cocaine (5.6 mg/kg) from saline using a multicomponent, food-reinforced discrimination procedure. On test days, subjects were pretreated with the nonselective DBH inhibitor disulfiram (0-100.0 mg/kg i.p.) or the selective DBH inhibitor nepicastat (0-56.0 mg/kg i.p.) 2 hours prior to a test session either alone or in combination with cumulatively administered cocaine (0-5.6 mg/kg i.p.). Neither disulfiram nor nepicastat substituted for the cocaine stimulus when tested up to doses that nonspecifically reduced responding. However, in combination studies, pretreatment with either disulfiram or nepicastat produced leftward shifts in the cocaine dose-response function and also conferred cocaine-like stimulus effects to the selective NE transporter inhibitor, reboxetine (0.3-5.6 mg/kg i.p.). These results indicate that pharmacological inhibition of DBH does not produce cocaine-like interoceptive stimulus effects alone, but functionally enhances the interoceptive stimulus effects of cocaine, possibly due to facilitated increases in DA released from noradrenergic terminals. These findings suggest that DBH inhibitors have low abuse liability and provide support to clinical reports that some subjective effects produced by cocaine, particularly aversive effects, are enhanced after DBH inhibition.
Effects of dopamine beta-hydroxylase inhibition with nepicastat on the progression of left ventricular dysfunction and remodeling in dogs with chronic heart failure.[Pubmed:11034950]
Circulation. 2000 Oct 17;102(16):1990-5.
BACKGROUND: Inhibition of dopamine beta-hydroxylase (DBH) results in a decrease in norepinephrine synthesis. The present study was a randomized, blinded, placebo-controlled investigation of the long-term effects of therapy with the DBH inhibitor nepicastat (NCT) on the progression of left ventricular (LV) dysfunction and remodeling in dogs with chronic heart failure (HF). METHODS AND RESULTS: Moderate HF (LV ejection fraction [LVEF] 30% to 40%) was produced in 30 dogs by intracoronary microembolization. Dogs were randomized to low-dose NCT (0.5 mg/kg twice daily, n=7) (L-NCT), high-dose NCT (2 mg/kg twice daily, n=7) (H-NCT), L-NCT plus enalapril (10 mg twice daily, n=8) (L-NCT+ENA), or placebo (PL, n=8). Transmyocardial (coronary sinus-arterial) plasma norepinephrine (tNEPI), LVEF, end-systolic volume, and end-diastolic volume were measured before and 3 months after initiating therapy. tNEPI levels were higher in PL compared with NL (86+/-20 versus 13+/-14 pg/mL, P:<0.01). L-NCT alone and L-NCT+ENA reduced tNEPI toward normal (28+/-4 and 39+/-17 pg/mL respectively), whereas HD-NCT reduced tNEPI to below normal levels (3+/-10 pg/mL). In PL dogs, LVEF decreased but was unchanged with L-NCT and increased with L-NCT+ENA. L-NCT and L-NCT+ENA prevented progressive LV remodeling, as evidenced by lack of ongoing increase in end-diastolic volume and end-systolic volume, whereas H-NCT did not CONCLUSIONS: In dogs with HF, therapy with L-NCT prevented progressive LV dysfunction and remodeling. The addition of ENA to L-NCT afforded a greater increase in LV systolic function. NCT at doses that normalize tNEPI may be useful in the treatment of chronic HF.
Catecholamine modulatory effects of nepicastat (RS-25560-197), a novel, potent and selective inhibitor of dopamine-beta-hydroxylase.[Pubmed:9283721]
Br J Pharmacol. 1997 Aug;121(8):1803-9.
1. Inhibitory modulation of sympathetic nerve function may have a favourable impact on the progression of congestive heart failure. Nepicastat is a novel inhibitor of dopamine-beta-hydroxylase, the enzyme which catalyses the conversion of dopamine to noradrenaline in sympathetic nerves. The in vitro pharmacology and in vivo catecholamine modulatory effects of nepicastat were investigated in the present study. 2. Nepicastat produced concentration-dependent inhibition of bovine (IC50 = 8.5 +/- 0.8 nM) and human (IC50 = 9.0 +/- 0.8 nM) dopamine-beta-hydroxylase. The corresponding R-enantiomer (RS-25560-198) was approximately 2-3 fold less potent than nepicastat. Nepicastat had negligible affinity (> 10 microM) for twelve other enzymes and thirteen neurotransmitter receptors. 3. Administration of nepicastat to spontaneously hypertensive rats (SHRs) (three consecutive doses of either 3, 10, 30 or 100 mg kg-1, p.o.; 12 h apart) or beagle dogs (0.05, 0.5, 1.5 or 5 mg kg-1, p.o.; b.i.d., for 5 days) produced dose-dependent decreases in noradrenaline content, increases in dopamine content and increases in dopamine/noradrenaline ratio in the artery (mesenteric or renal), left ventricle and cerebral cortex. At the highest dose studied, the decreases in tissue noadrenaline were 47%, 35% and 42% (in SHRs) and 88%, 91% and 96% (in dogs) in the artery, left ventricle and cerebral cortex, respectively. When tested at 30 mg kg-1, p.o., in SHRs, nepicastat produced significantly greater changes in noradrenaline and dopamine content, as compared to the R-enantiomer (RS-25560-198), in the mesenteric artery and left ventricle. 4. Administration of nepicastat (2 mg kg-1, b.i.d, p.o.) to beagle dogs for 15 days produced significant decreases in plasma concentrations of noradrenaline and increases in plasma concentrations of dopamine and dopamine/noradrenaline ratio. The peak reduction (52%) in plasma concentration of noradrenaline and the peak increase (646%) in plasma concentration of dopamine were observed on day-6 and day-7 of dosing, respectively. 5. The findings of this study suggest that nepicastat is a potent, selective and orally active inhibitor of dopamine-beta-hydroxylase which produces gradual modulation of the sympathetic nervous system by inhibiting the biosynthesis of noradrenaline. This drug may, therefore, be of value in the treatment of cardiovascular disorders associated with over-activation of the sympathetic nervous system, such as congestive heart failure.


