YC 1inhibitor of HIF-1α CAS# 170632-47-0 |
- Hydroxyfasudil
Catalog No.:BCC1635
CAS No.:105628-72-6
- chroman 1
Catalog No.:BCC1480
CAS No.:1273579-40-0
- Y-27632 dihydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC1273
CAS No.:129830-38-2
- H-1152
Catalog No.:BCC1615
CAS No.:451462-58-1
- H-1152 dihydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC1616
CAS No.:871543-07-6
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 170632-47-0 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 5712 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C19H16N2O2 | M.Wt | 304.34 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Synonyms | Yc-1; Lificiguat; Y 33075;Y33075 | ||
| Solubility | DMSO : ≥ 100 mg/mL (328.58 mM) H2O : < 0.1 mg/mL (insoluble) *"≥" means soluble, but saturation unknown. | ||
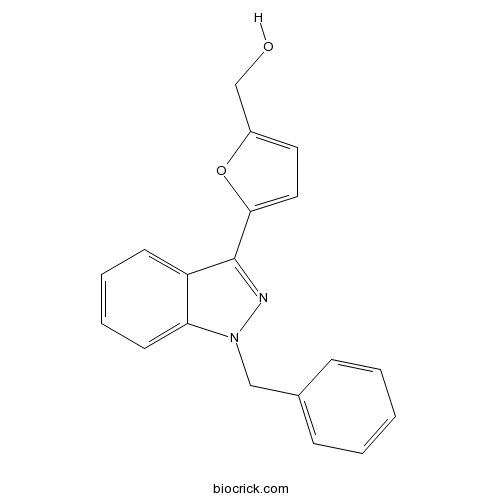
| Chemical Name | [5-(1-benzylindazol-3-yl)furan-2-yl]methanol | ||
| SMILES | C1=CC=C(C=C1)CN2C3=CC=CC=C3C(=N2)C4=CC=C(O4)CO | ||
| Standard InChIKey | OQQVFCKUDYMWGV-UHFFFAOYSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C19H16N2O2/c22-13-15-10-11-18(23-15)19-16-8-4-5-9-17(16)21(20-19)12-14-6-2-1-3-7-14/h1-11,22H,12-13H2 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Nitric oxide-independent activator of soluble guanylyl cyclase (sGC). Significantly elevates cGMP levels and inhibits collagen-stimulated aggregation of washed rabbit platelets (IC50 = 14.6 μM); induces relaxation in denuded phenylephrine-contracted rabbit aortic rings (EC50 = 1.9 μM). Also displays antiproliferative activity in vitro and in vivo by inducing G1 cell cycle arrest in two human hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) cell lines, and in HCC xenografts in athymic SCID mice. Exhibits low cytotoxicity in non-malignant cells. |

YC 1 Dilution Calculator

YC 1 Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 3.2858 mL | 16.429 mL | 32.858 mL | 65.716 mL | 82.145 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.6572 mL | 3.2858 mL | 6.5716 mL | 13.1432 mL | 16.429 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.3286 mL | 1.6429 mL | 3.2858 mL | 6.5716 mL | 8.2145 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0657 mL | 0.3286 mL | 0.6572 mL | 1.3143 mL | 1.6429 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0329 mL | 0.1643 mL | 0.3286 mL | 0.6572 mL | 0.8214 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
IC50: 1.2 M for hypoxia-induced HIF-1 transcriptional activity
YC-1 is a novel anticancer drug initially developed as an inhibitor of HIF-1α. Hypoxia-inducible factor-1α (HIF-1α) is a basic helix-loop-helix transcription factor regulating expression of VEGF and other genes which modulate survival, growth and metastasis of tumor cells under conditions of hypoxia.
In vitro: YC-1 could inhibit platelet aggregation and vascular contraction via activating soluble guanylyl cyclase and was originally developed as a potential therapeutic agent for circulation disorders. YC-1 completely inhibited HIF-1α expression at the post-transcriptional level and consequently blocked the transcription factor activity of HIF-1 in hepatoma cells under hypoxic conditions, indicating that such effects of YC-1 were likely to be associated with the oxygen-sensing pathway but not with the soluble guanylyl cyclase activation [1].
In vivo: Compared with tumors from vehicle-treated mice, tumors from YC-1-treated group were found to be statistically smaller and less vascularized. In addition, tumors from YC-1-treated group expressed lower levels of HIF-1α as well as HIF-1-inducible genes, regardless of tumor type [1].
Clinical trial: N/A
Reference:
[1] Yeo EJ,Chun YS,Cho YS,Kim J,Lee JC,Kim MS,Park JW. YC-1: a potential anticancer drug targeting hypoxia-inducible factor 1. J Natl Cancer Inst.2003 Apr 2;95(7):516-25.
- Oteromycin
Catalog No.:BCN1849
CAS No.:170591-45-4
- SC 236
Catalog No.:BCC7809
CAS No.:170569-86-5
- Isohyperectine
Catalog No.:BCN3405
CAS No.:170384-75-5
- 1,4-Epidioxybisabola-2,10-dien-9-one
Catalog No.:BCN7532
CAS No.:170380-69-5
- 4-(6-Methyl-4-oxohept-5-en-2-yl)cyclohex-2-en-1-one
Catalog No.:BCN7528
CAS No.:170380-68-4
- Enzastaurin (LY317615)
Catalog No.:BCC1100
CAS No.:170364-57-5
- CD 2665
Catalog No.:BCC7778
CAS No.:170355-78-9
- CD 2314
Catalog No.:BCC6071
CAS No.:170355-37-0
- 24-Methylenecycloartane-3beta,26-diol
Catalog No.:BCN1530
CAS No.:17020-27-8
- Bauerenol acetate
Catalog No.:BCN1106
CAS No.:17020-04-1
- 11-Keto-beta-boswellic acid
Catalog No.:BCN2298
CAS No.:17019-92-0
- Nepicastat (SYN-117) HCl
Catalog No.:BCC2286
CAS No.:170151-24-3
- Fmoc-D-Abu-OH
Catalog No.:BCC3203
CAS No.:170642-27-0
- α-Conotoxin EI
Catalog No.:BCC5979
CAS No.:170663-33-9
- D-Mannitol diacetonide
Catalog No.:BCC8951
CAS No.:1707-77-3
- Bindone
Catalog No.:BCC8877
CAS No.:1707-95-5
- 6beta-Hydroxyhispanone
Catalog No.:BCN7453
CAS No.:170711-93-0
- Nociceptin
Catalog No.:BCC5686
CAS No.:170713-75-4
- 11-Deoxymogroside V
Catalog No.:BCN8143
CAS No.:1707161-17-8
- Aprepitant
Catalog No.:BCC1101
CAS No.:170729-80-3
- Trityl candesartan cilexetil
Catalog No.:BCC9188
CAS No.:170791-09-0
- Astressin
Catalog No.:BCC5790
CAS No.:170809-51-5
- CHPG
Catalog No.:BCC6910
CAS No.:170846-74-9
- E4CPG
Catalog No.:BCC6888
CAS No.:170846-89-6
YC-1 reduces placental sFlt-1 and soluble endoglin production and decreases endothelial dysfunction: A possible therapeutic for preeclampsia.[Pubmed:26159901]
Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2015 Sep 15;413:202-8.
Preeclampsia is a serious complication of pregnancy with no medical treatment. It is caused by intermittent placental hypoxia and release of sFlt-1 and soluble endoglin, leading to wide spread maternal endothelial dysfunction and multisystem organ injury. YC-1 is a guanylyl cyclase activator and HIF1alpha inhibitor developed for use in hypertension and atherosclerosis. We examined whether YC-1 reduces sFlt-1 and sENG secretion and reverses endothelial dysfunction in primary human tissues. YC-1 significantly reduced sFlt-1 and sENG secretion from human umbilical vein endothelial cells, purified primary trophoblast cells and placental explants taken from patients with preterm preeclampsia. This was concordant with reduced HIF1alpha expression. YC-1 also reversed TNFalpha induced endothelial dysfunction, including reduced vascular cell adhesion molecule 1 expression and monocyte adhesion to primary endothelial cells. We conclude YC-1 decreases placental production of sFlt-1 and sENG and decreases endothelial dysfunction. It is a novel therapeutic candidate for preeclampsia.
[Potentiation of activation of soluble guanylate cyclase by YC-1, NO-donors and increase of the synergistic effect of YC-1 on NO-dependent activation of the enzyme by 1,2,3-triazolyl-1,2,5-oxadiazole derivatives].[Pubmed:26716741]
Biomed Khim. 2015 Nov-Dec;61(6):705-11.
The influence of (1H-1,2,3-triazol-1-yl)-1,2,5-oxadiazole derivatives: 4-amino-3-(5-methyl-4- ethoxycarbonyl-(1H-1,2,3-triazol-1-yl)-1,2,5-oxadiazole (TF4CH3) and 4,4'-bis(5-methel-4-ethoxycarbonyl-1H- 1,2,3-triazol-1-yl)-3,3'-azo-1,2,5-oxadiazole (2TF4CH3) on stimulation of human platelet soluble guanylate cyclase by YC-1, NO-donors (sodium nitroprusside, SNP, and spermine NONO) and on a synergistic increase of NO-dependent enzyme activation in the presence of YC-1 has been investigated. Both compounds increased guanylate cyclase activation by YC-1, potentiated guanylate cyclase stimulation by NO-donors and increased the synergistic effect of YC-1 on NO-dependent activation of soluble guanylate cyclase. The similarity in the properties of the examined TF4CH3 and 2TF4CH3 with that of YC-1 and the possible mechanism underlying the revealed properties of compounds used are discussed.
YC-1 induces lipid droplet formation in RAW 264.7 macrophages.[Pubmed:26767504]
J Biomed Sci. 2016 Jan 15;23:2.
BACKGROUND: 3-(5'-Hydroxymethyl-2'-furyl)-1-benzylindazole (YC-1) is a potential anticancer drug that may activate soluble guanylyl cyclase (sGC) and increase the level of cyclic guanosine monophosphate (cGMP). The aim of this study was to explore the effects of YC-1 on lipid droplet accumulation and foam cell formation in macrophages. RESULTS: Human-oxidized low density lipoprotein (ox-LDL) was used to induce accumulation of lipid droplets in a murine macrophage cell line, RAW 264.7. Oil red O staining showed that treatment with 20 muM YC-1 for 24 h increased the area of intracellular lipid droplets in macrophages. The results of high content screening (HCS) with the AdipoRed assay further revealed that YC-1 enhanced ox-LDL-induced foam cell formation. This was evidenced by an increase in the total area of lipid droplets and the mean fluorescence intensity per cell. Inhibition of cGMP-dependent protein kinase (PKG) using KT5823 significantly reduced YC-1-enhanced lipid droplet formation in ox-LDL-induced macrophage foam cells. CONCLUSION: YC-1 induces lipid droplet formation in macrophages, possibly through the sGC/cGMP/PKG signaling pathway. This chemical should be tested with caution in future clinical trials.
Potent ameliorating effect of Hypoxia-inducible factor 1alpha (HIF-1alpha) antagonist YC-1 on combined allergic rhinitis and asthma syndrome (CARAS) in Rats.[Pubmed:27498367]
Eur J Pharmacol. 2016 Oct 5;788:343-350.
Recent studies have implicated that Hypoxia-inducible factor 1alpha (HIF-1alpha) plays an integral role in the pathogenesis of allergic rhinitis and asthma. In the present study, we showed that HIF-1alpha antagonist YC-1, 3-(5-hydroxymethyl-2-furyl)-1-benzylindazole, elicited a potent allergy-ameliorating effect in a rat model of ovalbumin (OVA)-sensitized combined allergic rhinitis and asthma syndrome (CARAS). We revealed that YC-1 administration markedly impaired the total number and percentage of eosinophil in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid (BAL Fluid) of the rats, suggesting that YC-1 might attenuate lung and nasal mucosal inflammation in OVA-sensitized rats. Moreover, histological examination found that OVA-induced pathological alterations were evidently attenuated following YC-1 administration. In addition, immunohistochemistrial analysis indicated that YC-1 treatment decreased the expression of HIF-1alpha in rat lungs and nasal mucosa. Notably, Nuclear factor kappa B (NF-kappaB) p65 and Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor alpha (PPARalpha), two important regulators of inflammatory responses, were also significantly down-regulated following YC-1 administration. Real-time PCR analysis confirmed that YC-1 impaired the expression of HIF-1alpha, NF-kappaB and PPARalpha in CARAS model. These findings together indicated that YC-1 exerted remarkable anti-allergic effects through the modulation of inflammatory pathways, implying that YC-1 may potentially serve as a novel anti-CARAS medicine in clinical patients.
Molecular mechanisms underlying rat mesenteric artery vasorelaxation induced by the nitric oxide-independent soluble guanylyl cyclase stimulators BAY 41-2272 [5-cyclopropyl-2-[1-(2-fluorobenzyl)-1H-pyrazolo[3,4-b]pyridin-3-yl]pyrimidin-4-y lamine] and YC-1 [3-(5'-hydroxymethyl-2'-furyl)-1-benzyl Indazole].[Pubmed:16352702]
J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2006 Apr;317(1):258-66.
The aim of this study was to investigate the mechanisms of relaxation to the nitric oxide (NO)-independent soluble guanylyl cyclase (sGC) stimulators 5-cyclopropyl-2-[1-(2-fluorobenzyl)-1H-pyrazolo[3,4-b]pyridin-3-yl]pyrimidin-4-yl amine (BAY 41-2272) and 3-(5'-hydroxymethyl-2'-furyl)-1-benzyl indazole (YC-1) in the rat mesenteric artery. In endothelium-intact rings, BAY 41-2272 (0.0001-1 microM) and YC-1 (0.001-30 microM) caused concentration-dependent relaxations (pEC(50) values of 8.21 +/- 0.05 and 6.75 +/- 0.06, respectively), which were shifted to the right by 6-fold in denuded rings. The sGC inhibitor H-[1,2,4]oxadiazolo [4,3,-a]quinoxalin-1-one (ODQ) (10 microM) partially attenuated the maximal responses to BAY 41-2272 and YC-1 and displaced their curves to the right by 9- to 10-fold in intact and 3-fold in denuded vessels. The NO synthesis inhibitor N(omega)-nitro-L-arginine methyl ester (100 microM) and the NO scavenger 2-(4-carboxyphenyl)-4,4,5,5-tetramethylimidazoline-1-oxyl-3-oxide (100 microM) reduced BAY 41-2272 and YC-1 relaxations, whereas the phosphodiesterase type 5 inhibitor sildenafil (0.1 microM) potentiated these responses. The phosphatase inhibitor calyculin A (50 nM) reduced the relaxant responses, and high concentrations of BAY 41-2272 (1 micorM) and YC-1 (10 microM) inhibited Ca(2+)-induced contractions in K(+)-depolarized rings. BAY 41-2272 (0.1 microM) and YC-1 (1 microM) markedly elevated cGMP levels in an ODQ-sensitive manner. Coincubation of BAY 41-2272 or YC-1 with a NO donor resulted in a synergistic inhibition of phenylephrine-induced contractions paralleled by marked increases in cGMP levels. In conclusion, BAY 41-2272 and YC-1 relax the mesenteric artery through cGMP-dependent and -independent mechanisms, including blockade of Ca(2+) influx. The synergistic responses probably reflect the direct effects of NO and NO-independent sGC stimulators on the enzyme, thus representing a potential therapeutic effect by permitting reductions of nitrovasodilator dose.
YC-1 [3-(5'-Hydroxymethyl-2'-furyl)-1-benzyl Indazole] exhibits a novel antiproliferative effect and arrests the cell cycle in G0-G1 in human hepatocellular carcinoma cells.[Pubmed:15525795]
J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2005 Mar;312(3):917-25.
This study delineates the antiproliferative activities and in vivo efficacy of YC-1 [3-(5'-hydroxymethyl-2'-furyl)-1-benzyl indazole] in human hepatocellular carcinoma cells. YC-1 inhibited the growth of HA22T and Hep3B cells in a concentration-dependent manner without significant cytotoxicity. YC-1 induced G(1) phase arrest in the cell cycle, as detected by an increase in the proportion of cells in the G(1) phase using FAC-Scan flow cytometric analysis. It was further shown that cGMP, p42/p44 mitogen-activated protein kinase, or AKT kinase-mediated signaling pathways did not contribute to the YC-1-induced effect. Of note, YC-1 induced a dramatic increase in the expression of cyclin-dependent kinase (CDK)-inhibitory protein, p21(CIP1/WAP1), and a modest increase in p27(KIP1). The association of p21(CIP1/WAP1) with CDK2 was markedly increased in cells responsive to YC-1. YC-1 did not modify the expression of cyclin D1, cyclin E, CDK2, or CDK4. In a corollary in vivo study, YC-1 induced dose-dependent inhibition of tumor growth in mice inoculated with HA22T cells. Immunohistochemical analysis revealed an inverse relationship between the staining of p21(CIP1/WAF) and the staining of Ki-67, a cell proliferation marker. Based on the results reported herein, we suggest that YC-1 induces cell cycle arrest and inhibits tumor growth both in vitro and in vivo via the up-regulation of p21(CIP1/WAP1) expression in HA22T cells. Because of this, YC-1 is a potential antitumor agent worthy of further investigation.
YC-1 activation of human soluble guanylyl cyclase has both heme-dependent and heme-independent components.[Pubmed:11687640]
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2001 Nov 6;98(23):12938-42.
YC-1 [3-(5'-hydroxymethyl-2'furyl)-1-benzyl indazole] is an allosteric activator of soluble guanylyl cyclase (sGC). YC-1 increases the catalytic rate of the enzyme and sensitizes the enzyme toward its gaseous activators nitric oxide or carbon monoxide. In other studies the administration of YC-1 to experimental animals resulted in the inhibition of the platelet-rich thrombosis and a decrease of the mean arterial pressure, which correlated with increased cGMP levels. However, details of YC-1 interaction with sGC and enzyme activation are incomplete. Although evidence in the literature indicates that YC-1 activation of sGC is strictly heme-dependent, this report presents evidence for both heme-dependent and heme-independent activation of sGC by YC-1. The oxidation of the sGC heme by 1H-(1,2,4)oxadiazole(4,3-a)quinoxalin-1-one completely inhibited the response to NO, but only partially attenuated activation by YC-1. We also observed activation by YC-1 of a mutant sGC, which lacks heme. These findings indicate that YC-1 activation of sGC can occur independently of heme, but that activation is substantially increased when the heme moiety is present in the enzyme.
YC-1, a novel activator of platelet guanylate cyclase.[Pubmed:7527671]
Blood. 1994 Dec 15;84(12):4226-33.
YC-1 [3-(5'-hydroxymethyl-2'-furyl)-1-benzylindazole] inhibited the aggregation of and ATP release from washed rabbit platelets induced by arachidonic acid (AA), collagen, U46619, platelet-activating factor (PAF), and thrombin in a concentration-dependent manner. YC-1 also disaggregated the clumped platelets caused by these inducers. The thromboxane B2 formation caused by collagen, PAF, and thrombin was inhibited by concentrations of YC-1 that did not affect formation of thromboxane B2 and prostaglandin D2 caused by AA. YC-1 suppressed the increase of intracellular Ca2+ concentration and generation of inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate caused by these five aggregation inducers. Both the cAMP and cGMP contents of platelets were increased by YC-1 in a concentration- and time-dependent manner. Like sodium nitroprusside, YC-1 potentiated formation of cAMP caused by prostaglandin E1 but not that by 3-isobutyl-1-methylxanthine. Adenylate cyclase and cAMP phosphodiesterase activities were not altered by YC-1. Activity of cGMP phosphodiesterase was unaffected by YC-1. Activities of guanylate cyclase in platelet homogenate and cytosolic fraction were activated by YC-1, whereas particulate guanylate cyclase activity was unaffected. The antiplatelet effect of sodium nitroprusside but not that of YC-1 was blocked by hemoglobin and potentiated by superoxide dismutase. After intraperitoneal administration for 30 minutes, YC-1 prolonged the tail bleeding time of conscious mice. These data indicate that YC-1 is a direct soluble guanylate cyclase activator in rabbit platelets. It may also possess antithrombotic potential in vivo.


