Orobanchyl acetateCAS# 1413843-71-6 |
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 1413843-71-6 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 24796587 | Appearance | Powder |
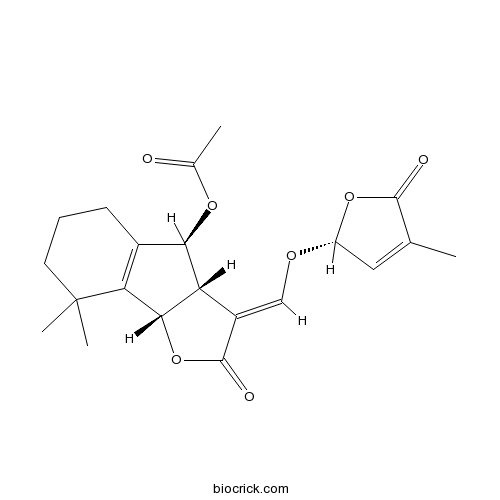
| Formula | C21H24O7 | M.Wt | 388.41 |
| Type of Compound | Sesquiterpenoids | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | Soluble in Chloroform,Dichloromethane,Ethyl Acetate,DMSO,Acetone,etc. | ||
| Chemical Name | [(3E,3aS,4S,8bS)-8,8-dimethyl-3-[[(2R)-4-methyl-5-oxo-2H-furan-2-yl]oxymethylidene]-2-oxo-3a,4,5,6,7,8b-hexahydroindeno[1,2-b]furan-4-yl] acetate | ||
| SMILES | CC1=CC(OC1=O)OC=C2C3C(C4=C(C3OC(=O)C)CCCC4(C)C)OC2=O | ||
| Standard InChIKey | DLRIUVHQJRZTMZ-CQMYTRALSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C21H24O7/c1-10-8-14(27-19(10)23)25-9-13-15-17(26-11(2)22)12-6-5-7-21(3,4)16(12)18(15)28-20(13)24/h8-9,14-15,17-18H,5-7H2,1-4H3/b13-9+/t14-,15+,17-,18+/m1/s1 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | 1. Orobanchyl acetate is a germination stimulant for root parasitic plants. |

Orobanchyl acetate Dilution Calculator

Orobanchyl acetate Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.5746 mL | 12.873 mL | 25.746 mL | 51.492 mL | 64.365 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.5149 mL | 2.5746 mL | 5.1492 mL | 10.2984 mL | 12.873 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.2575 mL | 1.2873 mL | 2.5746 mL | 5.1492 mL | 6.4365 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0515 mL | 0.2575 mL | 0.5149 mL | 1.0298 mL | 1.2873 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0257 mL | 0.1287 mL | 0.2575 mL | 0.5149 mL | 0.6436 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
- PEPA
Catalog No.:BCC5951
CAS No.:141286-78-4
- QS-21
Catalog No.:BCC8243
CAS No.:141256-04-4
- Asenapine hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC1371
CAS No.:1412458-61-7
- Btk inhibitor 1
Catalog No.:BCC4238
CAS No.:1412418-47-3
- 2-(Dimethylaminomethyl)-2-propanol
Catalog No.:BCN1774
CAS No.:14123-48-9
- Epiguajadial B
Catalog No.:BCN4075
CAS No.:1411629-26-9
- TRAP-6
Catalog No.:BCC3957
CAS No.:141136-83-6
- 12-Hydroxydodecanoic Acid
Catalog No.:BCN8405
CAS No.:505-95-3
- JNK-IN-8
Catalog No.:BCC1673
CAS No.:1410880-22-6
- Xanomeline oxalate
Catalog No.:BCC4146
CAS No.:141064-23-5
- 1-Hydroxy-2,3,4,7-tetramethoxyxanthone
Catalog No.:BCN6506
CAS No.:14103-09-4
- PACOCF3
Catalog No.:BCC7074
CAS No.:141022-99-3
- Trachelanthamine
Catalog No.:BCN2041
CAS No.:14140-18-2
- PX 12
Catalog No.:BCC2436
CAS No.:141400-58-0
- MRS 2219
Catalog No.:BCC6966
CAS No.:14141-47-0
- ABT-751 (E7010)
Catalog No.:BCC1085
CAS No.:141430-65-1
- Diosgenin glucoside
Catalog No.:BCN1250
CAS No.:14144-06-0
- Guajadial B
Catalog No.:BCN3972
CAS No.:1414455-03-0
- Rauvoyunine A
Catalog No.:BCN7002
CAS No.:1414883-81-0
- Rauvoyunine B
Catalog No.:BCN6995
CAS No.:1414883-82-1
- Aloin A
Catalog No.:BCN1042
CAS No.:1415-73-2
- Levosimendan
Catalog No.:BCC4793
CAS No.:141505-33-1
- 5S rRNA modificator
Catalog No.:BCC5442
CAS No.:1415238-77-5
- Pelandjauic acid
Catalog No.:BCN3752
CAS No.:141545-69-9
Strigolactones, host recognition signals for root parasitic plants and arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi, from Fabaceae plants.[Pubmed:19086293]
New Phytol. 2008 Jul;179(2):484-94.
Both root parasitic plants and arbuscular mycorrhizal (AM) fungi take advantage of strigolactones, released from plant roots as signal molecules in the initial communication with host plants, in order to commence parasitism and mutualism, respectively. In this study, strigolactones in root exudates from 12 Fabaceae plants, including hydroponically grown white lupin (Lupinus albus), a nonhost of AM fungi, were characterized by comparing retention times of germination stimulants on reverse-phase high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) with those of standards and by using tandem mass spectrometry (LC/MS/MS). All the plant species examined were found to exude known strigolactones, such as orobanchol, Orobanchyl acetate, and 5-deoxystrigol, suggesting that these strigolactones are widely distributed in the Fabaceae. It should be noted that even the nonmycotrophic L. albus exuded orobanchol, Orobanchyl acetate, 5-deoxystrigol, and novel germination stimulants. By contrast to the mycotrophic Fabaceae plant Trifolium pratense, in which phosphorus deficiency promoted strigolactone exudation, neither phosphorus nor nitrogen deficiency increased exudation of these strigolactones in L. albus. Therefore, the regulation of strigolactone production and/or exudation seems to be closely related to the nutrient acquisition strategy of the plants.
Isolation and identification of alectrol as (+)-orobanchyl acetate, a germination stimulant for root parasitic plants.[Pubmed:17822727]
Phytochemistry. 2008 Jan;69(2):427-31.
Alectrol, a germination stimulant for root parasitic plants, was purified from root exudates of red clover (Trifolium pratense L.) and identified as a strigolactone, (+)-Orobanchyl acetate [(3aS,4S,8bS,E)-8,8-dimethyl-3-(((R)-4-methyl-5-oxo-2,5-dihydrofuran-2-yloxy)meth ylene)-2-oxo-3,3a,4,5,6,7,8,8b-octahydro-2H-indeno[1,2-b]furan-4-yl acetate], by 1D and 2D NMR spectroscopy and ESI- and EI-MS spectrometry. Orobanchyl acetate afforded an [M-42](+) ion in EI-MS and thus had been recognized as an isomer of strigol. Orobanchyl acetate was detected in root exudates of soybean (Glycine max L.) and cowpea (Vigina unguiculata L.) along with orobanchol.


