TrachelanthamineCAS# 14140-18-2 |
- Cynaustraline
Catalog No.:BCN2048
CAS No.:17958-37-1
- Lindelofine
Catalog No.:BCN2043
CAS No.:487-99-0
- Viridiflorine
Catalog No.:BCN2045
CAS No.:551-57-5
- Heliovicine
Catalog No.:BCN2047
CAS No.:68473-85-8
- Coromandaline
Catalog No.:BCN2044
CAS No.:68473-86-9
- Heliocoromandaline
Catalog No.:BCN2046
CAS No.:82354-33-4
- Heliocurassavicine
Catalog No.:BCN2049
CAS No.:82354-34-5
- Heliocurassavinine
Catalog No.:BCN2050
CAS No.:82374-02-5
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 14140-18-2 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 26477 | Appearance | Cryst. |
| Formula | C15H27NO4 | M.Wt | 285.38 |
| Type of Compound | Alkaloids | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | Soluble in Chloroform,Dichloromethane,Ethyl Acetate,DMSO,Acetone,etc. | ||
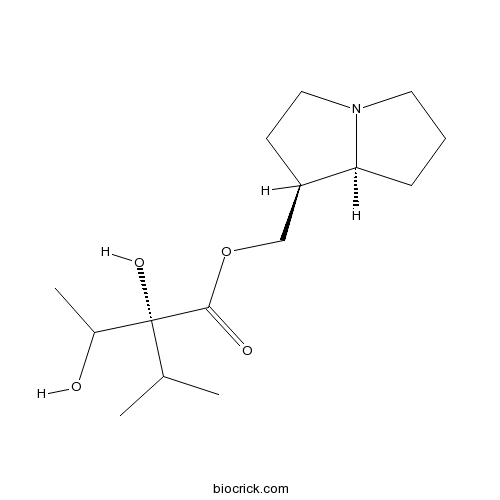
| Chemical Name | [(1S,8S)-2,3,5,6,7,8-hexahydro-1H-pyrrolizin-1-yl]methyl (2R)-2-hydroxy-2-(1-hydroxyethyl)-3-methylbutanoate | ||
| SMILES | CC(C)C(C(C)O)(C(=O)OCC1CCN2C1CCC2)O | ||
| Standard InChIKey | BWQSLRZZOVFVHJ-VYHDIPPYSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C15H27NO4/c1-10(2)15(19,11(3)17)14(18)20-9-12-6-8-16-7-4-5-13(12)16/h10-13,17,19H,4-9H2,1-3H3/t11?,12-,13+,15-/m1/s1 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Trachelanthamine is a natural product from Eupatorium fortunei. |
| Structure Identification | Phytochemistry, 2007,68(7):1026-37.Tissue distribution, core biosynthesis and diversification of pyrrolizidine alkaloids of the lycopsamine type in three Boraginaceae species.[Pubmed: 17320124]
|

Trachelanthamine Dilution Calculator

Trachelanthamine Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 3.5041 mL | 17.5205 mL | 35.041 mL | 70.082 mL | 87.6025 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.7008 mL | 3.5041 mL | 7.0082 mL | 14.0164 mL | 17.5205 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.3504 mL | 1.752 mL | 3.5041 mL | 7.0082 mL | 8.7602 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0701 mL | 0.3504 mL | 0.7008 mL | 1.4016 mL | 1.752 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.035 mL | 0.1752 mL | 0.3504 mL | 0.7008 mL | 0.876 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
- Orobanchyl acetate
Catalog No.:BCN7779
CAS No.:1413843-71-6
- PEPA
Catalog No.:BCC5951
CAS No.:141286-78-4
- QS-21
Catalog No.:BCC8243
CAS No.:141256-04-4
- Asenapine hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC1371
CAS No.:1412458-61-7
- Btk inhibitor 1
Catalog No.:BCC4238
CAS No.:1412418-47-3
- 2-(Dimethylaminomethyl)-2-propanol
Catalog No.:BCN1774
CAS No.:14123-48-9
- Epiguajadial B
Catalog No.:BCN4075
CAS No.:1411629-26-9
- TRAP-6
Catalog No.:BCC3957
CAS No.:141136-83-6
- 12-Hydroxydodecanoic Acid
Catalog No.:BCN8405
CAS No.:505-95-3
- JNK-IN-8
Catalog No.:BCC1673
CAS No.:1410880-22-6
- Xanomeline oxalate
Catalog No.:BCC4146
CAS No.:141064-23-5
- 1-Hydroxy-2,3,4,7-tetramethoxyxanthone
Catalog No.:BCN6506
CAS No.:14103-09-4
- PX 12
Catalog No.:BCC2436
CAS No.:141400-58-0
- MRS 2219
Catalog No.:BCC6966
CAS No.:14141-47-0
- ABT-751 (E7010)
Catalog No.:BCC1085
CAS No.:141430-65-1
- Diosgenin glucoside
Catalog No.:BCN1250
CAS No.:14144-06-0
- Guajadial B
Catalog No.:BCN3972
CAS No.:1414455-03-0
- Rauvoyunine A
Catalog No.:BCN7002
CAS No.:1414883-81-0
- Rauvoyunine B
Catalog No.:BCN6995
CAS No.:1414883-82-1
- Aloin A
Catalog No.:BCN1042
CAS No.:1415-73-2
- Levosimendan
Catalog No.:BCC4793
CAS No.:141505-33-1
- 5S rRNA modificator
Catalog No.:BCC5442
CAS No.:1415238-77-5
- Pelandjauic acid
Catalog No.:BCN3752
CAS No.:141545-69-9
- LY 231617
Catalog No.:BCC7005
CAS No.:141545-89-3
Tissue distribution, core biosynthesis and diversification of pyrrolizidine alkaloids of the lycopsamine type in three Boraginaceae species.[Pubmed:17320124]
Phytochemistry. 2007 Apr;68(7):1026-37.
Three species of the Boraginaceae were studied: greenhouse-grown plants of Heliotropium indicum and Agrobacterium rhizogenes transformed roots cultures (hairy roots) of Cynoglossum officinale and Symphytum officinale. The species-specific pyrrolizidine alkaloid (PA) profiles of the three systems were established by GC-MS. All PAs are genuinely present as N-oxides. In H. indicum the tissue-specific PA distribution revealed the presence of PAs in all tissues with the highest levels in the inflorescences which in a flowering plant may account for more than 70% of total plant alkaloid. The sites of PA biosynthesis vary among species. In H. indicum PAs are synthesized in the shoot but not roots whereas they are only made in shoots for C. officinale and in roots of S. officinale. Classical tracer studies with radioactively labelled precursor amines (e.g., putrescine, spermidine and homospermidine) and various necine bases (trachelanthamidine, supinidine, retronecine, heliotridine) and potential ester alkaloid intermediates (e.g., Trachelanthamine, supinine) were performed to evaluate the biosynthetic sequences. It was relevant to perform these comparative studies since the key enzyme of the core pathway, homospermidine synthase, evolved independently in the Boraginaceae and, for instance, in the Asteraceae [Reimann, A., Nurhayati, N., Backenkohler, A., Ober, D., 2004. Repeated evolution of the pyrrolizidine alkaloid-mediated defense system in separate angiosperm lineages. Plant Cell 16, 2772-2784.]. These studies showed that the core pathway for the formation of trachelanthamidine from putrescine and spermidine via homospermidine is common to the pathway in Senecio ssp. (Asteraceae). In both pathways homospermidine is further processed by a beta-hydroxyethylhydrazine sensitive diamine oxidase. Further steps of PA biosynthesis starting with trachelanthamidine as common precursor occur in two successive stages. Firstly, the necine bases are structurally modified and either before or after this modification are converted into their O(9)-esters by esterification with one of the stereoisomers of 2,3-dihydroxy-2-isopropylbutyric acid, the unique necic acid of PAs of the lycopsamine type. Secondly, the necine O(9)-esters may be further diversified by O(7)- and/or O(3')-acylation.


