PSB 11 hydrochloridePotent, selective hA3 receptor antagonist/inverse agonist CAS# 453591-58-7 |
- PSI
Catalog No.:BCC1124
CAS No.:158442-41-2
- Salinosporamide A (NPI-0052, Marizomib)
Catalog No.:BCC2094
CAS No.:437742-34-2
- Aclacinomycin A
Catalog No.:BCC1232
CAS No.:57576-44-0
- E-64
Catalog No.:BCC1222
CAS No.:66701-25-5
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 453591-58-7 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 73324725 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C16H17ClN5O+ | M.Wt | 330.8 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | Soluble to 20 mM in DMSO with gentle warming | ||
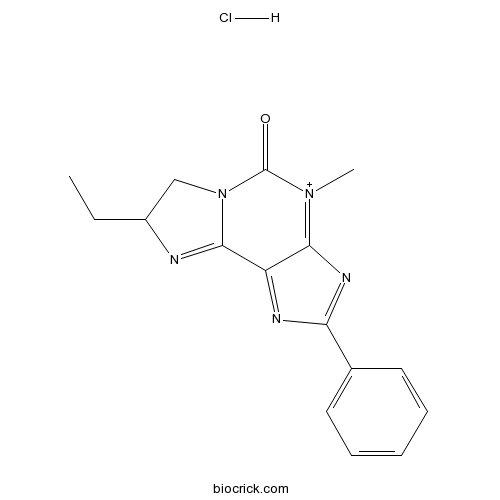
| Chemical Name | 8-ethyl-4-methyl-2-phenyl-7,8-dihydroimidazo[2,1-f]purin-4-ium-5-one;hydrochloride | ||
| SMILES | CCC1CN2C(=N1)C3=NC(=NC3=[N+](C2=O)C)C4=CC=CC=C4.Cl | ||
| Standard InChIKey | HNDXRUPGLQZLJT-UHFFFAOYSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C16H16N5O.ClH/c1-3-11-9-21-15(17-11)12-14(20(2)16(21)22)19-13(18-12)10-7-5-4-6-8-10;/h4-8,11H,3,9H2,1-2H3;1H/q+1; | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Potent and selective antagonist for the human adenosine A3 receptor, with low affinity for the rat A3 receptor (Ki values are 2.3 and > 10000 nM respectively). Displays > 1000-fold selectivity over human A1 and A2A receptors (Ki values are 4.1 and 3.3 μM respectively) and > 180-fold selectivity over rat A1, rat A2A and mouse A2B receptors. Acts as an inverse agonist in the [35S]GTPγS binding assay in hA3-CHO cells (IC50 = 36 nM). |

PSB 11 hydrochloride Dilution Calculator

PSB 11 hydrochloride Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 3.023 mL | 15.1149 mL | 30.2297 mL | 60.4595 mL | 75.5744 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.6046 mL | 3.023 mL | 6.0459 mL | 12.0919 mL | 15.1149 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.3023 mL | 1.5115 mL | 3.023 mL | 6.0459 mL | 7.5574 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0605 mL | 0.3023 mL | 0.6046 mL | 1.2092 mL | 1.5115 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0302 mL | 0.1511 mL | 0.3023 mL | 0.6046 mL | 0.7557 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
- Motesanib
Catalog No.:BCC1776
CAS No.:453562-69-1
- Saprirearine
Catalog No.:BCN3980
CAS No.:453518-30-4
- Boc-Gly-OH
Catalog No.:BCC3396
CAS No.:4530-20-5
- Boc-DL-Phe-OH
Catalog No.:BCC3434
CAS No.:4530-18-1
- GW788388
Catalog No.:BCC3666
CAS No.:452342-67-5
- SU14813 double bond Z
Catalog No.:BCC1972
CAS No.:452105-23-6
- Boc-N-Me-Val-OH
Catalog No.:BCC3357
CAS No.:45170-31-8
- AV-412
Catalog No.:BCC5119
CAS No.:451493-31-5
- AV-412 free base
Catalog No.:BCC5120
CAS No.:451492-95-8
- 10-Hydroxydihydroperaksine
Catalog No.:BCN5502
CAS No.:451478-47-0
- H-1152
Catalog No.:BCC1615
CAS No.:451462-58-1
- H-D-Glu(OtBu)-OH
Catalog No.:BCC2942
CAS No.:45125-00-6
- Nudifloside D
Catalog No.:BCN7005
CAS No.:454212-54-5
- kobe2602
Catalog No.:BCC5291
CAS No.:454453-49-7
- Acetophenone tosylhydrazone
Catalog No.:BCC8804
CAS No.:4545-21-5
- Corosolic acid
Catalog No.:BCN5503
CAS No.:4547-24-4
- Grossamide K
Catalog No.:BCC4547
CAS No.:
- 4-Benzoyl-3-methyl-1-phenyl-5-pyrazolone
Catalog No.:BCC8695
CAS No.:4551-69-3
- Isovouacapenol C
Catalog No.:BCN6557
CAS No.:455255-15-9
- Zaurategrast
Catalog No.:BCC2070
CAS No.:455264-31-0
- H-Glu(OBzl)-OBzl.HCl
Catalog No.:BCC2927
CAS No.:4561-10-8
- Neocnidilide
Catalog No.:BCN8174
CAS No.:4567-33-3
- 3-Benzyl-5-(2-hydroxyethyl)-4-methylthiazolium chloride
Catalog No.:BCC8625
CAS No.:4568-71-2
- 5-O-Methylgenistein
Catalog No.:BCN7714
CAS No.:4569-98-6
Medicinal chemistry of adenosine A3 receptor ligands.[Pubmed:12570761]
Curr Top Med Chem. 2003;3(4):445-62.
A(3) Adenosine receptors (ARs) exhibit large species differences. Potent, selective agonists for rat (e.g. Cl-IB-MECA, 5) and human A(3) ARs (e.g. PENECA, 17, and analogs) have been developed during the past years. Potent, selective antagonists for human A(3) ARs include the imidazopurinones PSB-10 (28) and PSB-11 (29), the pyrazolotriazolopyrimidines MRE-3005F20 (38) and analogs, and the dihydropyridines (e.g. MRS-1334, 50). For rat A(3) ARs only moderately potent antagonists have been identified, such as the pyridine derivative MRS-1523 (51) and the flavonoid MRS-1067 (52), both of which exhibit only a low degree of selectivity versus the other AR subtypes. Selective antagonist radioligands for the human A(3) receptor, [(3)H]MRE-3008F20 and [(3)H]PSB-11, have been prepared, while A(3)-selective agonist radioligands are still lacking. Recent developments also include allosteric modulators, irreversibly binding antagonists, fluorescence-labelled agonists, partial agonists and inverse agonists for A(3)ARs. Site-directed mutagenesis and molecular modeling studies have been performed in order to obtain information about the ligand binding site and the process of receptor activation. A(3)Adenosine receptors have recently attracted considerable interest as novel drug targets. A(3) Agonists may have potential as cardioprotective and cerebroprotective agents, for the treatment of asthma, as antiinflammatory and immunosuppressive agents, and in cancer therapy as cytostatics and chemoprotective compounds. A(3) AR antagonists might be therapeutically useful for the acute treatment of stroke, for glaucoma, and also as antiasthmatic and antiallergic drugs, since A(3)receptors cannot only mediate antiinflammatory, but also proinflammatory responses. The future development of further pharmacological tools, including potent, selective antagonists for rat A(3) receptors and selective agonist radioligands for rat and human receptors will facilitate the evaluation of the (patho)physiological roles of A(3) receptors and the pharmacological potential of their ligands.
2-Phenylimidazo[2,1-i]purin-5-ones: structure-activity relationships and characterization of potent and selective inverse agonists at Human A3 adenosine receptors.[Pubmed:12517430]
Bioorg Med Chem. 2003 Feb 6;11(3):347-56.
Structure-activity relationships of 2-phenyl-imidazo[2,1-i]purin-5-ones as ligands for human A(3) adenosine receptors (ARs) were investigated. An ethyl group in the 8-position of the imidazoline ring of 4-methyl-2-phenyl-imidazopurinone leading to chiral compounds was found to increase affinity for human A(3) ARs by several thousand-fold. Propyl substitution instead of methyl at N4 decreased A(3) affinity but increased A(1) affinity leading to potent A(1)-selective AR antagonists. The most potent A(1) antagonist of the present series was (S)-8-ethyl-2-phenyl-4-propyl-4,5,7,8-tetrahydro-1H-imidazo[2,1-i]purin-5-one (S-3) exhibiting a K(i) value of 7.4 nM at rat A(1) ARs and greater than 100-fold selectivity versus rat A(2A) and human A(3) ARs. At human A(1) ARs 2-phenylimidazo[2,1-i]purin-5-ones were generally less potent and therefore less A(1)-selective (S-3: K(i)=98 nM). 2-, 3-, or 4-Mono-chlorination of the 2-phenyl ring reduced A(3) affinity but led to an increase in affinity for A(1) ARs, whereas di- (3,4-dichloro) or polychlorination (2,3,5-trichloro) increased A(3) affinity. The most potent and selective A(3) antagonist of the present series was the trichlorophenyl derivative (R)-8-ethyl-4-methyl-2-(2,3,5-trichlorophenyl)-4,5,7,8-tetrahydro-1H-imidazo[2,1- i]purin-5-one (R-8) exhibiting a subnanomolar K(i) value at human A(3) ARs and greater than 800-fold selectivity versus the other AR subtypes. Methylation of 4-alkyl-2-phenyl-substituted imidazo[2,1-i]purin-5-ones led exclusively to the N9-methyl derivatives, which exhibited largely reduced AR affinities as compared to the unmethylated compounds. [35S]GTP gamma S binding studies of the most potent 2-phenyl-imidazo[2,1-i]purin-5-ones at membranes of Chinese hamster ovary cells expressing the human A(3) AR revealed that the compounds were inverse agonists at A(3) receptors under standard test conditions. Due to their high A(3) affinity, selectivity, and relatively high water-solubility, 2-phenyl-imidazo[2,1-i]purin-5-ones may become useful research tools.
Imidazo[2,1-i]purin-5-ones and related tricyclic water-soluble purine derivatives: potent A(2A)- and A(3)-adenosine receptor antagonists.[Pubmed:12139454]
J Med Chem. 2002 Aug 1;45(16):3440-50.
A series of tricyclic imidazo[2,1-i]purinones and ring-enlarged analogues derived from xanthine derivatives have been prepared as adenosine receptor (AR) antagonists. In comparison with xanthines, the tricyclic compounds exhibit increased water solubility due to a basic nitrogen atom, which can be protonated under physiological conditions. Substituents were introduced that confer high affinity for A(2A) or A(3) ARs, respectively. A new capillary electrophoresis method was developed for the determination of the enantiomeric purity of selected chiral products using native and modified beta-cyclodextrins as chiral discriminators. The compounds were investigated in radioligand binding assays at rat brain A(1) and A(2A) ARs. Selected compounds were additionally investigated in radioligand binding assays at human recombinant A(3) ARs and in functional studies (adenylate cyclase assays) at A(1) ARs of rat fat cell membranes, A(2A) ARs of rat PC 12 cell membranes, and mouse A(2B) ARs of NIH 3T3 cell membranes. Structure-activity relationships were similar to those of corresponding xanthine derivatives. The 2-styrylimidazopurinones were less potent at A(2A) ARs as compared to 8-styrylxanthine derivatives. The most potent compound at A(2A) ARs was (S)-1,4-dimethyl-8-ethyl-2-styryl-imidazo[2,1-i]purinone (S-25) exhibiting a K(i) value of 424 nM at rat A(2A) ARs. The compound was highly selective for A(2A) receptors vs A(1) and A(3) ARs. Selectivity vs A(2B) ARs, however, was low. Among the 1-unsubstituted 2-phenyl-imidazo[2,1-i]purin-5-one derivatives, very potent and highly selective antagonists for human A(3) ARs were identified. The most potent A(3) antagonist of the present series was (R)-4-methyl-8-ethyl-2-phenyl-imidazo[2,1-i]purin-5-one (R-24) exhibiting a K(i) value of 2.3 nM and high selectivity for A(3) receptors vs all other AR subtypes.


