RGFP966Specific HDAC3 inhibitor CAS# 1357389-11-7 |
- Entinostat (MS-275,SNDX-275)
Catalog No.:BCC3595
CAS No.:209783-80-2
- Scriptaid
Catalog No.:BCC2163
CAS No.:287383-59-9
- SBHA
Catalog No.:BCC2425
CAS No.:38937-66-5
- Resminostat (RAS2410)
Catalog No.:BCC2165
CAS No.:864814-88-0
- JNJ-26481585
Catalog No.:BCC2147
CAS No.:875320-29-9
- TC-H 106
Catalog No.:BCC2426
CAS No.:937039-45-7
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

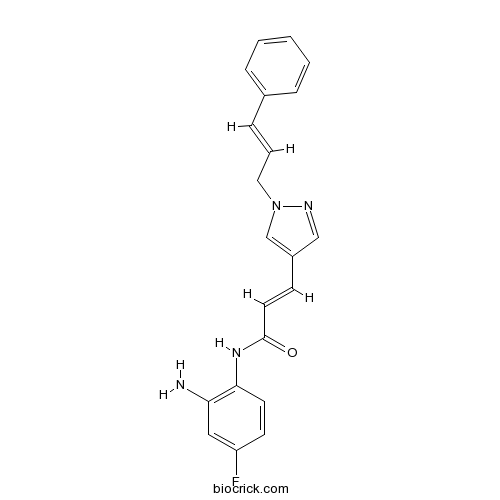
| Cas No. | 1357389-11-7 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 56650312 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C21H19FN4O | M.Wt | 362.4 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Synonyms | 1396841-57-8 | ||
| Solubility | DMSO : 50 mg/mL (137.97 mM; Need ultrasonic) H2O : < 0.1 mg/mL (insoluble) | ||
| Chemical Name | (E)-N-(2-amino-4-fluorophenyl)-3-[1-[(E)-3-phenylprop-2-enyl]pyrazol-4-yl]prop-2-enamide | ||
| SMILES | C1=CC=C(C=C1)C=CCN2C=C(C=N2)C=CC(=O)NC3=C(C=C(C=C3)F)N | ||
| Standard InChIKey | BLVQHYHDYFTPDV-VCABWLAWSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C21H19FN4O/c22-18-9-10-20(19(23)13-18)25-21(27)11-8-17-14-24-26(15-17)12-4-7-16-5-2-1-3-6-16/h1-11,13-15H,12,23H2,(H,25,27)/b7-4+,11-8+ | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | RGFP966 is a specific inhibitor of HDAC3 with an IC50 value of 0.08 μM. | |||||
| Targets | HDAC3 | |||||
| IC50 | 0.08 μM | |||||

RGFP966 Dilution Calculator

RGFP966 Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.7594 mL | 13.7969 mL | 27.5938 mL | 55.1876 mL | 68.9845 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.5519 mL | 2.7594 mL | 5.5188 mL | 11.0375 mL | 13.7969 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.2759 mL | 1.3797 mL | 2.7594 mL | 5.5188 mL | 6.8985 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0552 mL | 0.2759 mL | 0.5519 mL | 1.1038 mL | 1.3797 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0276 mL | 0.138 mL | 0.2759 mL | 0.5519 mL | 0.6898 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
RGFP966 is a selective inhibitor of HDAC3 with IC50 value of 80 nM [1].
HDAC3 (histone deacetylase 3) is an isoform of HDACs family and plays an important role in DNA transcriptional regulation. It has been shown that HDACs involves in a variety of biologic processes, like DNA repair, replication, transcription and chromatin structure. Many studies have shown that HDACs is the most highly expressed class I HDAC in the brain and involves in learning and memory process negatively [2].
RGFP966 is a potent HDAC3 inhibitor and has no inhibition on other HDACs at the concentration up to 15 μM. Using a substrate-dependent biochemical assay to investigate RGFP966 inhibition of HDACs, and results showed that it inhibited HDAC3 with IC50 value of 80 nM while had no effective inhibition on other HDACs [1]. When tested with cutaneous T cell lymphoma (CTCL) cell lines with RGFP966, the cell growth were significantly decreased by inhibiting HDAC3 which increased cell apoptosis [3].
In male C57BL/6J mice model, trained them in object recognition (ORM) and location-dependent object recognition (OLM) with a subthreshold period after administration of RGFP966 significantly increased the novel object preference and enhanced enhanced long-term OLM in a dose-dependent manner [1].
References:
[1]. Malvaez, M., et al., HDAC3-selective inhibitor enhances extinction of cocaine-seeking behavior in a persistent manner. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A, 2013. 110(7): p. 2647-52.
[2]. Rogge, G.A., et al., HDAC3 is a negative regulator of cocaine-context-associated memory formation. J Neurosci, 2013. 33(15): p. 6623-32.
[3]. Wells, C.E., et al., Inhibition of histone deacetylase 3 causes replication stress in cutaneous T cell lymphoma. PLoS One, 2013. 8(7): p. e68915.
- Nonin A
Catalog No.:BCN7149
CAS No.:1357351-29-1
- OG-L002
Catalog No.:BCC4549
CAS No.:1357302-64-7
- Taxinine M
Catalog No.:BCN6942
CAS No.:135730-55-1
- Palonosetron hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCN2171
CAS No.:135729-62-3
- Palonosetron
Catalog No.:BCC1834
CAS No.:135729-61-2
- MDL 29,913
Catalog No.:BCC5729
CAS No.:135721-56-1
- ML 228
Catalog No.:BCC2435
CAS No.:1357171-62-0
- c-Met inhibitor 1
Catalog No.:BCC1488
CAS No.:1357072-61-7
- N-Acetylglycyl-D-glutamic acid
Catalog No.:BCC6634
CAS No.:135701-69-8
- HG-14-10-04
Catalog No.:BCC5392
CAS No.:1356962-34-9
- AZD-3463
Catalog No.:BCC3907
CAS No.:1356962-20-3
- ent-3-Oxokaurane-16,17-diol
Catalog No.:BCN6188
CAS No.:135683-73-7
- Boc-Glu(OBzl)-OH
Catalog No.:BCC3389
CAS No.:13574-13-5
- Isoforsythiaside
Catalog No.:BCN5413
CAS No.:1357910-26-9
- Koumine
Catalog No.:BCN6190
CAS No.:1358-76-5
- erythro-Guaiacylglycerol beta-dihydroconiferyl ether
Catalog No.:BCN7025
CAS No.:135820-77-8
- Blumenol C glucoside
Catalog No.:BCN6189
CAS No.:135820-80-3
- H-D-Asp(OtBu)-OtBu.HCl
Catalog No.:BCC2898
CAS No.:135904-71-1
- Lupinol C
Catalog No.:BCN4809
CAS No.:135905-53-2
- RP 67580
Catalog No.:BCC7134
CAS No.:135911-02-3
- SR 2211
Catalog No.:BCC6310
CAS No.:1359164-11-6
- Caulophylline B
Catalog No.:BCN7499
CAS No.:1359978-55-4
- Phenazopyridine HCl
Catalog No.:BCC4698
CAS No.:136-40-3
- Tetracaine HCl
Catalog No.:BCC4399
CAS No.:136-47-0
HDAC 3-selective inhibitor RGFP966 demonstrates anti-inflammatory properties in RAW 264.7 macrophages and mouse precision-cut lung slices by attenuating NF-kappaB p65 transcriptional activity.[Pubmed:26993378]
Biochem Pharmacol. 2016 May 15;108:58-74.
The increasing number of patients suffering from chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) represents a major and increasing health problem. Therefore, novel therapeutic approaches are needed. Class I HDACs 1, 2 and 3 play key roles in the regulation of inflammatory gene expression with a particular pro-inflammatory role for HDAC 3. HDAC 3 has been reported to be an important player in inflammation by deacetylating NF-kappaB p65, which has been implicated in the pathology of COPD. Here, we applied the pharmacological HDAC 3-selective inhibitor RGFP966, which attenuated pro-inflammatory gene expression in models for inflammatory lung diseases. Consistent with this, a robust decrease of the transcriptional activity of NF-kappaB p65 was observed. HDAC 3 inhibition affected neither the acetylation status of NF-kappaB p65 nor histone H3 or histone H4. This indicates that HDAC 3 inhibition does not inhibit NF-kappaB p65 transcriptional activity by affecting its deacetylation but rather by inhibiting enzymatic activity of HDAC 3. Taken together, our findings indicate that pharmacological HDAC 3-selective inhibition by inhibitors such as RGFP966 may provide a novel and effective approach toward development of therapeutics for inflammatory lung diseases.
Histone Deacetylase Inhibition via RGFP966 Releases the Brakes on Sensory Cortical Plasticity and the Specificity of Memory Formation.[Pubmed:26400942]
J Neurosci. 2015 Sep 23;35(38):13124-32.
Research over the past decade indicates a novel role for epigenetic mechanisms in memory formation. Of particular interest is chromatin modification by histone deacetylases (HDACs), which, in general, negatively regulate transcription. HDAC deletion or inhibition facilitates transcription during memory consolidation and enhances long-lasting forms of synaptic plasticity and long-term memory. A key open question remains: How does blocking HDAC activity lead to memory enhancements? To address this question, we tested whether a normal function of HDACs is to gate information processing during memory formation. We used a class I HDAC inhibitor, RGFP966 (C21H19FN4O), to test the role of HDAC inhibition for information processing in an auditory memory model of learning-induced cortical plasticity. HDAC inhibition may act beyond memory enhancement per se to instead regulate information in ways that lead to encoding more vivid sensory details into memory. Indeed, we found that RGFP966 controls memory induction for acoustic details of sound-to-reward learning. Rats treated with RGFP966 while learning to associate sound with reward had stronger memory and additional information encoded into memory for highly specific features of sounds associated with reward. Moreover, behavioral effects occurred with unusually specific plasticity in primary auditory cortex (A1). Class I HDAC inhibition appears to engage A1 plasticity that enables additional acoustic features to become encoded in memory. Thus, epigenetic mechanisms act to regulate sensory cortical plasticity, which offers an information processing mechanism for gating what and how much is encoded to produce exceptionally persistent and vivid memories. Significance statement: Here we provide evidence of an epigenetic mechanism for information processing. The study reveals that a class I HDAC inhibitor (Malvaez et al., 2013; Rumbaugh et al., 2015; RGFP966, chemical formula C21H19FN4O) alters the formation of auditory memory by enabling more acoustic information to become encoded into memory. Moreover, RGFP966 appears to affect cortical plasticity: the primary auditory cortex reorganized in a manner that was unusually "tuned-in" to the specific sound cues and acoustic features that were related to reward and subsequently remembered. We propose that HDACs control "informational capture" at a systems level for what and how much information is encoded by gating sensory cortical plasticity that underlies the sensory richness of newly formed memories.


