SMND-309Novel derivative of salvianolic acid B CAS# 1065559-56-9 |
- 3,3'-Diindolylmethane
Catalog No.:BCC1306
CAS No.:1968-05-4
- BAM7
Catalog No.:BCC1397
CAS No.:331244-89-4
- Bendamustine HCl
Catalog No.:BCC1153
CAS No.:3543-75-7
- Betulinic acid
Catalog No.:BCN5524
CAS No.:472-15-1
- Brassinolide
Catalog No.:BCC1438
CAS No.:72962-43-7
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 1065559-56-9 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 45138954 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C18H14O8 | M.Wt | 358.3 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | DMSO : ≥ 3.7 mg/mL (10.33 mM) *"≥" means soluble, but saturation unknown. | ||
| Chemical Name | (E)-2-[6-[(E)-2-carboxyethenyl]-2,3-dihydroxyphenyl]-3-(3,4-dihydroxyphenyl)prop-2-enoic acid | ||
| SMILES | C1=CC(=C(C=C1C=C(C2=C(C=CC(=C2O)O)C=CC(=O)O)C(=O)O)O)O | ||
| Standard InChIKey | OAHRXWZJURTMHG-ACIWFXKJSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C18H14O8/c19-12-4-1-9(8-14(12)21)7-11(18(25)26)16-10(3-6-15(22)23)2-5-13(20)17(16)24/h1-8,19-21,24H,(H,22,23)(H,25,26)/b6-3+,11-7+ | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
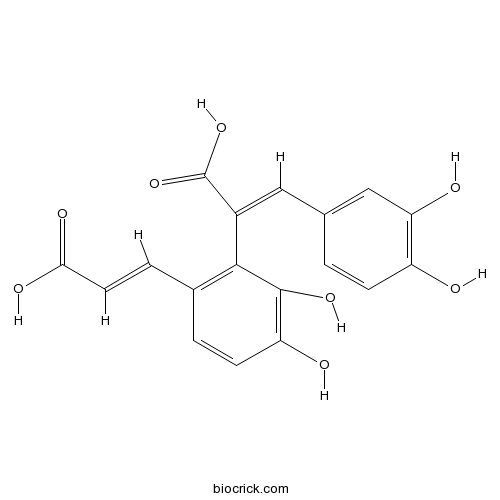
| Description | SMND-309 is a novel derivative of salvianolic acid B, and has shown protective effects against rat cortical neuron damage in vitro and in vivo.
IC50 value:
Target:
SMND-309 mitigated the effects of ischemia and reperfusion injury on brain by decreasing the infract volume, improving neurological function, increasing the survival of neurons and promoting angiogenesis by increasing the levels of erythropoietin (EPO), erythropoietin receptor (EPOR), phosphorylated JAK2 (P-JAK2), phosphorylated STAT3 (P-STAT3), VEGF and VEGF receptor 2 (Flk-1) in the brain. References: | |||||

SMND-309 Dilution Calculator

SMND-309 Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.791 mL | 13.9548 mL | 27.9096 mL | 55.8191 mL | 69.7739 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.5582 mL | 2.791 mL | 5.5819 mL | 11.1638 mL | 13.9548 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.2791 mL | 1.3955 mL | 2.791 mL | 5.5819 mL | 6.9774 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0558 mL | 0.2791 mL | 0.5582 mL | 1.1164 mL | 1.3955 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0279 mL | 0.1395 mL | 0.2791 mL | 0.5582 mL | 0.6977 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
SMND-309 is a novel derivative of salvianolic acid B, and has shown protective effects against rat cortical neuron damage in vitro and in vivo.
- Dafadine-A
Catalog No.:BCC5406
CAS No.:1065506-69-5
- Ganodermanontriol
Catalog No.:BCN5872
CAS No.:106518-63-2
- Ganoderiol A
Catalog No.:BCN8158
CAS No.:106518-61-0
- Boldenone cyclopentanepropionate
Catalog No.:BCC8894
CAS No.:106505-90-2
- Boc-D-Phenylalaninol
Catalog No.:BCC2714
CAS No.:106454-69-7
- Korepimedoside A
Catalog No.:BCN7887
CAS No.:106441-31-0
- Acid Black 1
Catalog No.:BCC8806
CAS No.:1064-48-8
- Deoxymorellin
Catalog No.:BCN3067
CAS No.:1064-34-2
- Boc-D-Valinol
Catalog No.:BCC2692
CAS No.:106391-87-1
- Boc-D-Alaninol
Catalog No.:BCC2727
CAS No.:106391-86-0
- ω-Conotoxin GVIA
Catalog No.:BCC5700
CAS No.:106375-28-4
- DAPTA
Catalog No.:BCC5909
CAS No.:106362-34-9
- 7-Amino-4-methylcoumarin-3-acetic acid
Catalog No.:BCN2562
CAS No.:106562-32-7
- Parstatin (human)
Catalog No.:BCC6041
CAS No.:1065755-99-8
- Parstatin (mouse)
Catalog No.:BCC6042
CAS No.:1065756-01-5
- Hederacolchiside A1
Catalog No.:BCN6553
CAS No.:106577-39-3
- 3,10-Dihydroxy-5,11-dielmenthadiene-4,9-dione
Catalog No.:BCN1633
CAS No.:106623-23-8
- Qingyangshengenin A
Catalog No.:BCN8126
CAS No.:106644-33-1
- Trachelosiaside
Catalog No.:BCN7743
CAS No.:106647-12-5
- Matairesinol 4'-O-beta-gentiobioside
Catalog No.:BCN2848
CAS No.:106647-14-7
- Boc-D-Lys-OH
Catalog No.:BCC3420
CAS No.:106719-44-2
- Olprinone
Catalog No.:BCC1820
CAS No.:106730-54-5
- GYY 4137 morpholine salt
Catalog No.:BCC7739
CAS No.:106740-09-4
- 24-Deacetylalisol O
Catalog No.:BCN3365
CAS No.:1067510-31-9
Therapeutic effects of SMND-309, a new metabolite of salvianolic acid B, on experimental liver fibrosis.[Pubmed:20969856]
Eur J Pharmacol. 2011 Jan 10;650(1):390-5.
(2E)-2-{6-[(E)-2-carboxylvinyl]-2,3-dihydroxyphenyl}-3-(3,4-dihydroxyphenyl) propenoic acid, a novel compound designated SMND-309, is a new metabolite of salvianolic acid B. The present study was carried out to investigate the effects of SMND-309 on experimental liver fibrosis in rats induced by subcutaneous injection of carbon tetrachloride and explore its possible mechanisms on the basis of biochemical, histopathologic and immunohistochemical studies. The results showed that intragastrical treatment with SMND-309 ameliorated liver function and decreased the elevation of serum hyaluronic acid, laminin, procollagen type III levels and hydroxyproline content in liver tissue. It also decreased the elevation in the malondialdehyde level and restored the decrease in superoxide dismutase and glutathione peroxidase activities. Upon histopathologic examination, the SMND-309-treated rats reduced the liver damage and the liver fibrosis grade. Moreover, the results of immunohistochemical examination showed that SMND-309 powerfully down-regulated the expression of connective tissue growth factor (CTGF) rather than transforming growth factor-beta1 (TGF-beta1) in serum and liver. Meanwhile, SMND-309 exhibits significantly higher potency compared with salvianolic acid B (Sal B) at the same dose. The antifibrotic mechanisms of SMND-309 might be associated with its ability to suppress the expression of CTGF as well as scavenge lipid peroxidation products and increase endogenous antioxidant enzyme activity.
SMND-309, a novel derivative of salvianolic acid B, protects rat brains ischemia and reperfusion injury by targeting the JAK2/STAT3 pathway.[Pubmed:23764464]
Eur J Pharmacol. 2013 Aug 15;714(1-3):23-31.
SMND-309 is a novel derivative of salvianolic acid B, and has shown protective effects against rat cortical neuron damage in vitro and in vivo. However the molecular mechanisms through which SMND-309 affords this protection are unclear. The present study aimed to investigate the mechanisms associated with the protective activities of SMND-309 in a cerebral ischemia and reperfusion injury rat model. In this study, we used AG490, a specific inhibitor of the signaling pathway involving the Janus Kinase 2 (JAK2)/Signal Transducers and Activators of Transcription 3 (STAT3) signaling molecules and suramin, a potent inhibitor of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF), to investigate the mechanisms of SMND-309. The cerebral ischemia and reperfusion injury model was induced by performing middle cerebral artery occlusion (MCAO) in the rats. SMND-309 mitigated the effects of ischemia and reperfusion injury on brain by decreasing the infract volume, improving neurological function, increasing the survival of neurons and promoting angiogenesis by increasing the levels of erythropoietin (EPO), erythropoietin receptor (EPOR), phosphorylated JAK2 (P-JAK2), phosphorylated STAT3 (P-STAT3), VEGF and VEGF receptor 2 (Flk-1) in the brain. Our results suggest that SMND-309 provides significant neuroprotective effects against cerebral ischemia and reperfusion injury. The mechanisms of this protection may be attributed to the increased VEGF expression occurring from the JAK2/STAT3 pathway, activated by the increased EPO/EPOR expression in the brain.
SMND-309 promotes angiogenesis in human umbilical vein endothelial cells through activating erythropoietin receptor/STAT3/VEGF pathways.[Pubmed:23276662]
Eur J Pharmacol. 2013 Jan 30;700(1-3):173-80.
The aim of the study is to investigate the direct angiogenic activities of SMND-309, a novel metabolite of salvianolic acid B, on human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVEC) in vitro and its potential molecular mechanisms. Effects of SMND-309 on proliferation and adhesion of HUVEC were measured using sulforhodamine B assay and cell adhesion assay kit, respectively. Effects of SMND-309 on migration and differentiation of HUVEC were examined through wound-healing assay and tube formation on matrigel method, respectively. Expressions of erythropoietin (EPO), EPO receptor, phosphorylated EPO receptor, signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 (STAT3), phosphorylated STAT3 and vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) were detected by Western blot. Knocking down EPO receptor gene and blocking the epidermal growth factor (EGF) receptor/Janus kinase 2 (JAK2) pathways were used to explore the potential mechanisms in SMND-309 induced angiogenesis. SMND-309 strongly induced the proliferation of HUVEC in a concentration-dependent manner within the concentrations of 1-30 mug/ml and significantly promoted the adhesion of HUVEC to different extracellular matrix at 30mug/ml. SMND-309 at doses of 3, 10, 30 mug/ml significantly enhanced the migration, capillary-like structure formation, and the levels of VEGF, phosphorylated EPO receptor and phosphorylated STAT3. Results from further experiments using HUVEC(EPO receptor-) and AG-490 showed that SMND-309 activated EPO receptor first, and then stimulated JAK2/STAT3, which up-regulated the expression of VEGF, and resulted in the angiogenesis. These results clearly show that SMND-309 has powerful angiogenic activity on HUVEC, which is mostly correlated with the up-regulation of VEGF through EPO receptor/STAT3 signal pathways.
SMND-309 promotes neuron survival through the activation of the PI3K/Akt/CREB-signalling pathway.[Pubmed:26911316]
Pharm Biol. 2016 Oct;54(10):1982-90.
Context In clinical practice, the promotion of neuron survival is necessary to recover neurological functions after the onset of stroke. Objective This study aimed to investigate the post-ischaemic neuroprotective effect of SMND-309, a novel metabolite of salvianolic acid, on differentiated SH-SY5Y cells. Materials and methods SH-SY5Y cells were differentiated by pre-treating with 5 muM all-trans-retinoic acid for 6 d. The differentiated SH-SY5Y cells were exposed to oxygen-glucose deprivation (OGD) for 2 h and reperfusion (R) for 24 h to induce OGD/R injury. After OGD injury, differentiated SH-SY5Y cells were treated with or without SMND-309 (5, 10, 20 muM) for another 24 h. Cell viability was detected through Cell counting kit-8 assay and lactate dehydrogenase leakage assay. Apoptosis was evaluated through flow cytometry, caspase-3 activity assay. Changes in protein levels were assessed through Western blot. Results SMND-309 ameliorated the degree of injury in the differentiated SH-SY5Y cells by increasing cell viabilities (5 muM, 65.4% +/- 4.1%; 10 muM, 69.8% +/- 3.7%; 20 muM, 75.3% +/- 5.1%) and by reducing LDH activity (20 muM, 2.5 fold) upon OGD/R stimulation. Annexin V-fluorescein isothiocyanate/propidium iodide staining results suggested that apoptotic rate of differentiated SH-SY5Y cells decreased from 43.8% induced by OGD/R injury to 19.2% when the cells were treated with 20 muM SMND-309. SMND-309 significantly increased the Bcl-2 level of the injured differentiated SH-SY5Y cells but decreased the caspase-3 activity of these cells by 1.6-fold. In contrast, SMND-309 did not affect the Bax level of these cells. SMND-309 evidently increased the protein expression of BDNF when Akt and CREB were activated. This function was antagonized by the addition of LY294002. Conclusion SMND-309 can prevent neuronal cell death in vitro. This process may be related to the activation of the PI3K/Akt/CREB-signalling pathway.


