DAPTAChemokine receptor 5 (CCR5) antagonist CAS# 106362-34-9 |
- BMS-708163 (Avagacestat)
Catalog No.:BCC2104
CAS No.:1146699-66-2
- YO-01027 (Dibenzazepine, DBZ)
Catalog No.:BCC2100
CAS No.:209984-56-5
- LY-900009
Catalog No.:BCC2103
CAS No.:209984-68-9
- Flurizan
Catalog No.:BCC2342
CAS No.:51543-40-9
- Begacestat
Catalog No.:BCC2346
CAS No.:769169-27-9
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 106362-34-9 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 184644 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C35H56N10O15 | M.Wt | 856.89 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Synonyms | D-Ala-peptide T-amide | ||
| Solubility | H2O : 50 mg/mL (58.35 mM; Need ultrasonic) | ||
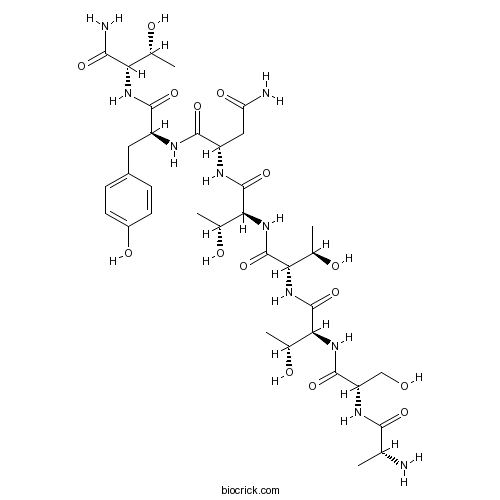
| Sequence | ASTTTNYT (Modifications: Ala-1 = D-Ala, Thr-8 = C-terminal amide) | ||
| Chemical Name | (2S)-N-[(2S)-1-[[(2S,3R)-1-amino-3-hydroxy-1-oxobutan-2-yl]amino]-3-(4-hydroxyphenyl)-1-oxopropan-2-yl]-2-[[(2S,3R)-2-[[(2S,3R)-2-[[(2S,3R)-2-[[(2S)-2-[[(2R)-2-aminopropanoyl]amino]-3-hydroxypropanoyl]amino]-3-hydroxybutanoyl]amino]-3-hydroxybutanoyl]amino]-3-hydroxybutanoyl]amino]butanediamide | ||
| SMILES | CC(C(C(=O)N)NC(=O)C(CC1=CC=C(C=C1)O)NC(=O)C(CC(=O)N)NC(=O)C(C(C)O)NC(=O)C(C(C)O)NC(=O)C(C(C)O)NC(=O)C(CO)NC(=O)C(C)N)O | ||
| Standard InChIKey | AKWRNBWMGFUAMF-ZESMOPTKSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C35H56N10O15/c1-13(36)29(54)41-22(12-46)32(57)43-26(16(4)49)34(59)45-27(17(5)50)35(60)44-25(15(3)48)33(58)40-21(11-23(37)52)30(55)39-20(10-18-6-8-19(51)9-7-18)31(56)42-24(14(2)47)28(38)53/h6-9,13-17,20-22,24-27,46-51H,10-12,36H2,1-5H3,(H2,37,52)(H2,38,53)(H,39,55)(H,40,58)(H,41,54)(H,42,56)(H,43,57)(H,44,60)(H,45,59)/t13-,14-,15-,16-,17-,20+,21+,22+,24+,25+,26+,27+/m1/s1 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Chemokine receptor 5 (CCR5) antagonist. Acts as a selective viral entry inhibitor for R5 tropic HIV-1 strains. Blocks CCR5-mediated monocyte chemotaxis and reduces microglia and astrocyte activation in a neuroinflammatory rat model of Alzheimer's disease. |

DAPTA Dilution Calculator

DAPTA Molarity Calculator

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
DAPTA is a synthetic peptide, functions as a viral entry inhibitor by targeting selectively CCR5, and shows potent anti-HIV activities. Sequence: Ala-Ser-Thr-Thr-Thr-Asn-Tyr-Thr-NH2 .
In Vitro:DAPTA (1 nM) inhibits HIV-1 replication in monocytes/macrophages (M/M) by >90%. DAPTA blocks HIV entry and prevents HIV-1 infection. DAPTA reduces CCR5 mAb binding in human primary macrophages. DAPTA potently blocks R5 gp120-mediated neuronal apoptosis. DAPTA is even more potent in preventing neuronal apoptosis than the CCR5 antagonist TAK-779[1]. DAPTA potently inhibits specific CD4-dependent binding of gp120 Bal (IC50 = 0.06 nM) and CM235 (IC50 = 0.32 nM) to CCR5. DAPTA (1 nM) blocks formation of the gp120/sCD4 complex with CCR5. DAPTA inhibits the binding of gp120BaL/sCD4 to CCR5 (Cf2Th/synR5) cells with IC50 of 55 ± 0.08 pM[2].
References:
[1]. Pollicita M, et al. Profound anti-HIV-1 activity of DAPTA in monocytes/macrophages and inhibition of CCR5-mediated apoptosis in neuronal cells. Antivir Chem Chemother. 2007;18(5):285-95.
[2]. Polianova MT, et al. Chemokine receptor-5 (CCR5) is a receptor for the HIV entry inhibitor peptide T (DAPTA). Antiviral Res. 2005 Aug;67(2):83-92.
- Rufinamide
Catalog No.:BCC5078
CAS No.:106308-44-5
- Nomilin
Catalog No.:BCN1034
CAS No.:1063-77-0
- Sikokianin A
Catalog No.:BCN3133
CAS No.:106293-99-6
- Risperidone
Catalog No.:BCC3850
CAS No.:106266-06-2
- 4-[(4-Methylpiperazin-1-yl) methyl]benzoic acid dihydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC8669
CAS No.:106261-49-8
- Thioperamide
Catalog No.:BCC6734
CAS No.:106243-16-7
- LDN193189 Hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC1695
CAS No.:1062368-62-0
- ML347
Catalog No.:BCC5331
CAS No.:1062368-49-3
- LDN-193189
Catalog No.:BCC3687
CAS No.:1062368-24-4
- Ro3280
Catalog No.:BCC3962
CAS No.:1062243-51-9
- WYE-354
Catalog No.:BCC1059
CAS No.:1062169-56-5
- WYE-687
Catalog No.:BCC4604
CAS No.:1062161-90-3
- ω-Conotoxin GVIA
Catalog No.:BCC5700
CAS No.:106375-28-4
- Boc-D-Alaninol
Catalog No.:BCC2727
CAS No.:106391-86-0
- Boc-D-Valinol
Catalog No.:BCC2692
CAS No.:106391-87-1
- Deoxymorellin
Catalog No.:BCN3067
CAS No.:1064-34-2
- Acid Black 1
Catalog No.:BCC8806
CAS No.:1064-48-8
- Korepimedoside A
Catalog No.:BCN7887
CAS No.:106441-31-0
- Boc-D-Phenylalaninol
Catalog No.:BCC2714
CAS No.:106454-69-7
- Boldenone cyclopentanepropionate
Catalog No.:BCC8894
CAS No.:106505-90-2
- Ganoderiol A
Catalog No.:BCN8158
CAS No.:106518-61-0
- Ganodermanontriol
Catalog No.:BCN5872
CAS No.:106518-63-2
- Dafadine-A
Catalog No.:BCC5406
CAS No.:1065506-69-5
- SMND-309
Catalog No.:BCC1956
CAS No.:1065559-56-9
trans-thionate derivatives of Pt(II) and Pd(II) with water-soluble phosphane PTA and DAPTA ligands: antiproliferative activity against human ovarian cancer cell lines.[Pubmed:23692403]
Inorg Chem. 2013 Jun 3;52(11):6635-47.
A series of PTA and DAPTA platinum(II) and palladium(II) thionate complexes of the type trans-[M(SN)2P2] were prepared from the reaction of cis-[MCl2P2] [M = Pt, Pd; P = PTA (1,3,5-triaza-7-phosphaadamantane), DAPTA (3,7-diacetyl-1,3,7-triaza-5-phosphabicyclo[3.3.1]nonane)] with the in situ generated sodium salts of the heterocyclic thiones S-m-methylpyrimidine-2-thione, S-4,6-dimethylpyrimidine-2-thione, S-4,6-dihydroxypyrimidine-2-thione, benzothiazole-2-thione, benzoxazole-2-thione, S-1,3,4,-thiadiazole-2-thione, S-4,5-H-thiazolan-2-thione, and S-pyrimidine-4(1H)-one-2-thione. The X-ray structures of six of the compounds confirm the trans disposition and, only in the case of [Pd2Cl2(S-pyrimidine-4(1H)-one-2-thionate)2(PTA)2], a dinuclear structure with a Pd-Pd distance of 3.0265(14)A was observed. In vitro cytotoxicities against human ovarian cancer cell lines A2780 and A2780cisR were evaluated for ten complexes showing a high inhibition of cellular growth with a comparable inhibitory potency (IC50) against A2780 cells to that of cisplatin. Notably, the compounds also show significant (up to 7-fold higher) activity in cisplatin-resistant A2780cisR cell lines.
Chemokine receptor-5 (CCR5) is a receptor for the HIV entry inhibitor peptide T (DAPTA).[Pubmed:16002156]
Antiviral Res. 2005 Aug;67(2):83-92.
The chemokine receptor CCR5 plays a crucial role in transmission of HIV isolates, which predominate in the early and middle stages of infection, as well as those, which populate the brain and cause neuro-AIDS. CCR5 is therefore an attractive therapeutic target for design of entry inhibitors. Specific rapid filtration binding assays have been useful for almost 30 years both for drug discovery and understanding molecular mechanisms of drug action. Reported in 1986, prior to discovery of chemokine co-receptors and so thought to act at CD4, peptide T (DAPTA) appears to greatly reduce cellular viral reservoirs in both HAART experienced and treatment naive patients, without toxicities. We here report that DAPTA potently inhibits specific CD4-dependent binding of gp120 Bal (IC50=0.06 nM) and CM235 (IC50=0.32 nM) to CCR5. In co-immunoprecipitation studies, DAPTA (1 nM) blocks formation of the gp120/sCD4 complex with CCR5. Confocal microscopic studies of direct FITC-DAPTA binding to CCR5+, but not CCR5-, cells show that CCR5 is a DAPTA receptor. The capability of DAPTA to potently block gp120-CD4 binding to the major co-receptor CCR5 explains its molecular and therapeutic mechanism of action as a selective antiviral entry inhibitor for R5 tropic HIV-1 isolates.
Profound anti-HIV-1 activity of DAPTA in monocytes/macrophages and inhibition of CCR5-mediated apoptosis in neuronal cells.[Pubmed:18046961]
Antivir Chem Chemother. 2007;18(5):285-95.
Monocytes/macrophages (M/M) are strategic reservoirs of HIV-1, spreading the virus to other cells and inducing apoptosis in T-lymphocytes, astrocytes and neurons. M/M are commonly infected by R5 HIV-1 strains, which use the chemokine receptor CCR5. D-Ala-peptide T-amide (DAPTA), or Peptide T, named for its high threonine content (ASTTTNYT), is a synthetic peptide comprised of eight amino acids (185-192) of the gp120 V2 region and functions as a viral entry inhibitor by targeting selectively CCR5. The anti-HIV-1 activity of DAPTA was evaluated in M/M infected with R5 HIV-1 strains. DAPTA at 10(-9) M inhibited HIV-1 replication in M/M by > 90%. PCR analysis of viral cDNA in M/M showed that DAPTA blocks HIV entry and in this way prevents HIV-1 infection. Moreover, DAPTA acts as a strong inhibitor and was more active than the non-peptidic CCR5 antagonist TAK-779 in inhibiting apoptosis (mediated by RS HIV-1 strains produced and released by infected M/M) on a neuroblastoma cell line. Our results suggest that antiviral compounds which interfere with receptor mechanisms such as CCR5 could be important, either alone or in combination with other antiretroviral treatments, in preventing HIV infection in the central nervous system and the consequential neuronal damage that leads to neuronal AIDS.
Synthesis, characterization, and in vitro cytotoxicity of some gold(I) and trans platinum(II) thionate complexes containing water-soluble PTA and DAPTA ligands. X-ray crystal structures of [Au(SC4H3N2)(PTA)], trans-[Pt(SC4H3N2)2(PTA)2], trans-[Pt(SC5H4N)2(PTA)2], and trans-[Pt(SC5H4N)2(DAPTA)2].[Pubmed:18447334]
Inorg Chem. 2008 Jul 7;47(13):5641-8.
A series of gold(I) and platinum(II) complexes of the type [Au(SR)(P)] and trans-[Pt(SR) 2(P) 2] [SR = 2-thiopyridine (SPy), 2-thiopyrimidine (SPyrim); P = 1,3,5-triaza-7-phosphaadamantane (PTA), 3,7-diacetyl-1,3,7-triaza-5-phosphabicyclo[3.3.1]nonane (DAPTA)] were prepared and characterized, and their in vitro cytotoxicities against a panel of seven human cancer cell lines were evaluated. The highly water soluble gold(I) complexes [Au(SR)(P)] [P = PTA and SR = SPy ( 1), SPyrim ( 2); P = DAPTA and SR = SPy ( 3), SPyrim ( 4)] showed low cytotoxicity, while the platinum(II) complexes trans-[Pt(SR) 2(P) 2] [P = PTA and SR = SPyrim ( 5), SPy ( 6); P = DAPTA and SR = SPyrim ( 7), SPy ( 8)] demonstrated potent cytotoxicity for ovarian, colon, renal, and melanoma cancer cell lines on the basis of a comparison with ID 50 values for some established cytotoxic drugs. Single crystals of 2, 5, 6, and 8 suitable for X-ray structural characterization were obtained, and the study revealed the trans configuration for 5, 6, and 8 in their solid states.
Chemokine receptor 5 antagonist D-Ala-peptide T-amide reduces microglia and astrocyte activation within the hippocampus in a neuroinflammatory rat model of Alzheimer's disease.[Pubmed:15979806]
Neuroscience. 2005;134(2):671-6.
Chronic neuroinflammation plays a prominent role in the progression of Alzheimer's disease. Reactive microglia and astrocytes are observed within the hippocampus during the early stages of the disease. Epidemiological findings suggest that anti-inflammatory therapies may slow the onset of Alzheimer's disease. Chemokine receptor 5 (CCR5) up-regulation may influence the recruitment and accumulation of glia near senile plaques; activated microglia express CCR5 and reactive astrocytes express chemokines. We have previously shown that neuroinflammation induced by chronic infusion of lipopolysaccharide into the 4th ventricle reproduces many of the behavioral, neurochemical, electrophysiological and neuropathological changes associated with Alzheimer's disease. The current study investigated the ability of D-Ala-peptide T-amide (DAPTA), a chemokine receptor 5 chemokine receptor antagonist of monocyte chemotaxis, to influence the consequences of chronic infusion of lipopolysaccharide. DAPTA (0.01 mg/kg, s.c., for 14 days) dramatically reduced the number of activated microglia and astrocytes, as compared with lipopolysaccharide-infused rats treated with vehicle. DAPTA treatment also reduced the number of immunoreactive cells expressing nuclear factor kappa binding protein, a prominent component of the proinflammatory cytokine signaling pathway. The present study suggests that DAPTA and other CCR5 antagonists may attenuate critical aspects of the neuroinflammation associated with Alzheimer's disease.
Update on D-ala-peptide T-amide (DAPTA): a viral entry inhibitor that blocks CCR5 chemokine receptors.[Pubmed:15043212]
Curr HIV Res. 2003 Jan;1(1):51-67.
Peptide T, named for its high threonine content (ASTTTNYT), was derived by a database search which assumed that a relevant receptor binding epitope within env (gp120) would have sequence homology to a known signaling peptide. Binding of radiolabeled gp120 to brain membranes was displaced by peptide T and three octapeptide analogs (including "DAPTA", Dala1-peptide T-amide, the protease-resistant analog now in Phase II clinical trials) with the same potency that these four octapeptides blocked infectivity of an early passage patient isolate. This 1986 report was controversial due to a number of laboratories' failure to find peptide T antiviral effects; we now know that peptide T is a potent HIV entry inhibitor selectively targeting CCR5 receptors with minimal effects on the X4 tropic lab adapted virus exclusively in use at that time. Early clinical trials, which demonstrated lack of toxicity and focused on neurological and neurocognitive benefits, are reviewed and data from a small ongoing Phase II trial--the first to assess peptide T's antiviral effects--are presented. Studies using infectivity, receptor binding, chemotaxis, and blockade of gp120-induced neurotoxicity in vitro and in vivo are reviewed, discussed and presented here. Peptide T and analogs of its core pentapeptide, present near the V2 stem of numerous gp120 isolates, are potent ligands for CCR5. Clinical data showing peptide T's immunomodulation of plasma cytokine levels and increases in the percentage of IFNgamma secreting CD8+ T cells in patients with HIV disease are presented and suggests additional therapeutic mechanisms via regulation of specific immunity.


