Sodium DichloroacetateMitochondrial pyruvate dehydrogenase kinase (PDK) inhibitor CAS# 2156-56-1 |
- Batimastat (BB-94)
Catalog No.:BCC1223
CAS No.:130370-60-4
- CTS-1027
Catalog No.:BCC1502
CAS No.:193022-04-7
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 2156-56-1 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 517326 | Appearance | Powder |
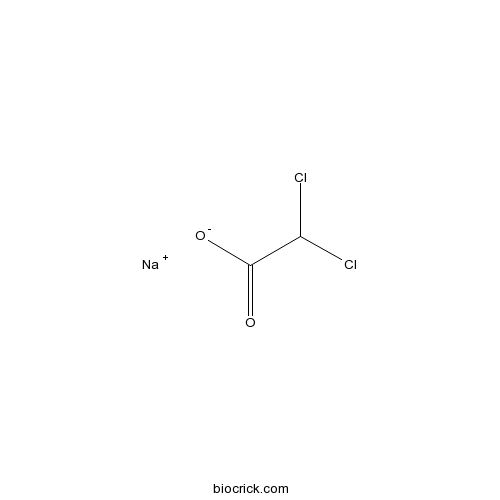
| Formula | C2HCl2NaO2 | M.Wt | 150.9 |
| Type of Compound | Miscellaneous | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | DMSO : ≥ 250 mg/mL (1656.51 mM) *"≥" means soluble, but saturation unknown. | ||
| Chemical Name | sodium;2,2-dichloroacetate | ||
| SMILES | C(C(=O)[O-])(Cl)Cl.[Na+] | ||
| Standard InChIKey | LUPNKHXLFSSUGS-UHFFFAOYSA-M | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C2H2Cl2O2.Na/c3-1(4)2(5)6;/h1H,(H,5,6);/q;+1/p-1 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Sodium dichloroacetate is a drug with potential for treating patients with stroke and head injury. Sodium dichloroacetate exhibits anti-leukemic activity in B-chronic lymphocytic leukemia (B-CLL) and synergizes with the p53 activator Nutlin-3; it is cytoprotective to some colorectal cancer cells under hypoxic conditions. |
| Targets | p53 | Mdm2 | p21 |
| In vitro | Sodium dichloroacetate (DCA) reduces apoptosis in colorectal tumor hypoxia.[Pubmed: 20537792 ]Cancer Lett. 2010 Nov 1;297(1):75-83.
Sodium dichloroacetate exhibits anti-leukemic activity in B-chronic lymphocytic leukemia (B-CLL) and synergizes with the p53 activator Nutlin-3[Pubmed: 24962518 ]Oncotarget. 2014 Jun; 5(12): 4347–4360.
|
| In vivo | Absence of mutagenic effects of sodium dichloroacetate.[Pubmed: 8812237]Fundam Appl Toxicol. 1996 Jul;32(1):87-95.Sodium Dichloroacetate (DCA) is a drug with potential for treating patients with stroke and head injury. Conflicting evidence has been published on the mutagenic potential of DCA. |

Sodium Dichloroacetate Dilution Calculator

Sodium Dichloroacetate Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 6.6269 mL | 33.1345 mL | 66.2691 mL | 132.5381 mL | 165.6726 mL |
| 5 mM | 1.3254 mL | 6.6269 mL | 13.2538 mL | 26.5076 mL | 33.1345 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.6627 mL | 3.3135 mL | 6.6269 mL | 13.2538 mL | 16.5673 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.1325 mL | 0.6627 mL | 1.3254 mL | 2.6508 mL | 3.3135 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0663 mL | 0.3313 mL | 0.6627 mL | 1.3254 mL | 1.6567 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
- SU 5402
Catalog No.:BCC1970
CAS No.:215543-92-3
- Mianserin HCl
Catalog No.:BCC1114
CAS No.:21535-47-7
- Senampeline F
Catalog No.:BCN7804
CAS No.:71075-43-9
- BMS 753
Catalog No.:BCC6031
CAS No.:215307-86-1
- Betamethasone Valerate
Catalog No.:BCC3736
CAS No.:2152-44-5
- Pemoline
Catalog No.:BCC5967
CAS No.:2152-34-3
- BMS 493
Catalog No.:BCC7697
CAS No.:215030-90-3
- Methyl 2,6-dihydroxybenzoate
Catalog No.:BCN3563
CAS No.:2150-45-0
- Protocatechuic acid methyl ester
Catalog No.:BCN3542
CAS No.:2150-43-8
- 7,3',4'-Trihydroxyflavone
Catalog No.:BCN4674
CAS No.:2150-11-0
- Bruceine D
Catalog No.:BCN2894
CAS No.:21499-66-1
- Agrimonolide
Catalog No.:BCN4925
CAS No.:21499-24-1
- 23-deoxojessic acid
Catalog No.:BCN4926
CAS No.:215609-93-1
- Cyclocephaloside II
Catalog No.:BCC8310
CAS No.:215776-78-6
- SB269652
Catalog No.:BCC8052
CAS No.:215802-15-6
- SB-277011
Catalog No.:BCC1928
CAS No.:215803-78-4
- Bruceine E
Catalog No.:BCN7619
CAS No.:21586-90-3
- CX 546
Catalog No.:BCC7532
CAS No.:215923-54-9
- 7-Hydroxy-beta-carboline-1-propionic acid
Catalog No.:BCN1492
CAS No.:215934-15-9
- 15,16-Epoxy-12S-hydroxylabda-8(17),13(16),14-triene
Catalog No.:BCN1491
CAS No.:216011-55-1
- 1-Methyl-3-nitrophthalate
Catalog No.:BCC8468
CAS No.:21606-04-2
- β-Pompilidotoxin
Catalog No.:BCC1048
CAS No.:216064-36-7
- Bis(2,6-diisopropylphenyl)carbodiimide
Catalog No.:BCC8879
CAS No.:2162-74-5
- 1alpha, 25-Dihydroxy VD2-D6
Catalog No.:BCC1299
CAS No.:216244-04-1
Absence of mutagenic effects of sodium dichloroacetate.[Pubmed:8812237]
Fundam Appl Toxicol. 1996 Jul;32(1):87-95.
Sodium Dichloroacetate (DCA) is a drug with potential for treating patients with stroke and head injury. Conflicting evidence has been published on the mutagenic potential of DCA. A series of genetic tests for mutagenicity and clastogenicity was carried out on pharmaceutical grade DCA. Four types of mutagenicity test were included, with and without metabolic activation where appropriate. These studies included: (i) Salmonella and Escherichia coli mutation (Ames) test, (ii) thymidine kinase locus forward mutation in L5178Y mouse lymphoma cells, (iii) tests for chromosomal aberrations in Chinese hamster ovary cells, and (iv) and in vivo rat bone marrow erythroid micronucleus test. In each study, there was no evidence of mutagenic activity attributable to DCA. It is possible that the present test material, of pharmaceutical grade, has fewer impurities than materials studied in previous reports. These data extend, and in some cases contradict, previous published reports on DCA.
Sodium dichloroacetate (DCA) reduces apoptosis in colorectal tumor hypoxia.[Pubmed:20537792]
Cancer Lett. 2010 Nov 1;297(1):75-83.
We examined the effect of hypoxia on apoptosis of human colorectal cancer (CRC) cells in vitro and in vivo. All cell lines tested were susceptible to hypoxia-induced apoptosis. DCA treatment caused significant apoptosis under normoxia in SW480 and Caco-2 cells, but these cells displayed decreased apoptosis when treated with DCA combined with hypoxia, possibly through HIF-1alpha dependent pathways. DCA treatment also induced significantly increased growth of SW480 tumor xenografts, and a decrease in TUNEL positive nuclei in hypoxic but not normoxic regions of treated tumors. Thus DCA is cytoprotective to some CRC cells under hypoxic conditions, highlighting the need for further investigation before DCA can be used as a reliable apoptosis-inducing agent in cancer therapy.
Sodium dichloroacetate exhibits anti-leukemic activity in B-chronic lymphocytic leukemia (B-CLL) and synergizes with the p53 activator Nutlin-3.[Pubmed:24962518]
Oncotarget. 2014 Jun 30;5(12):4347-60.
The anti-leukemic activity of the mitochondria-targeting small molecule Sodium Dichloroacetate (DCA), used alone and in association with the small molecule inhibitor of the p53/MDM2 interaction Nutlin-3, was analyzed in primary B-chronic lymphocytic leukemia (B-CLL) samples (n=22), normal peripheral blood cells (n=10) and in p53wild-type EHEB, JVM-2, JVM-3 B lymphoblastoid cell lines. DCA exhibited a dose-dependent anti-leukemic activity in both primary B-CLL and B leukemic cell lines with a functional p53 status and showed a synergistic cytotoxic activity when used in combination with Nutlin-3. At the molecular level, DCA positively regulated p53 activity, as documented by post-transcriptional modifications of p53 protein and synergized with Nutlin-3 in increasing the expression of the p53-target genes MDM2, PUMA, TIGAR and in particular p21. The potential role of p21 in mediating the DCA+Nutlin-3 anti-leukemic activity was underscored in knocking-down experiments. Indeed, transfection of leukemic cells with p21 siRNAs significantly decreased the DCA+Nutlin-3-induced cytotoxicity. Taken together, our data emphasize that DCA is a molecule that merits to be further evaluated as a chemotherapeutic agent for B-CLL, likely in combination with other therapeutic compounds.
A mitochondria-K+ channel axis is suppressed in cancer and its normalization promotes apoptosis and inhibits cancer growth.[Pubmed:17222789]
Cancer Cell. 2007 Jan;11(1):37-51.
The unique metabolic profile of cancer (aerobic glycolysis) might confer apoptosis resistance and be therapeutically targeted. Compared to normal cells, several human cancers have high mitochondrial membrane potential (DeltaPsim) and low expression of the K+ channel Kv1.5, both contributing to apoptosis resistance. Dichloroacetate (DCA) inhibits mitochondrial pyruvate dehydrogenase kinase (PDK), shifts metabolism from glycolysis to glucose oxidation, decreases DeltaPsim, increases mitochondrial H2O2, and activates Kv channels in all cancer, but not normal, cells; DCA upregulates Kv1.5 by an NFAT1-dependent mechanism. DCA induces apoptosis, decreases proliferation, and inhibits tumor growth, without apparent toxicity. Molecular inhibition of PDK2 by siRNA mimics DCA. The mitochondria-NFAT-Kv axis and PDK are important therapeutic targets in cancer; the orally available DCA is a promising selective anticancer agent.
Evidence for existence of tissue-specific regulation of the mammalian pyruvate dehydrogenase complex.[Pubmed:9405293]
Biochem J. 1998 Jan 1;329 ( Pt 1):191-6.
Tissue distribution and kinetic parameters for the four isoenzymes of pyruvate dehydrogenase kinase (PDK1, PDK2, PDK3 and PDK4) identified thus far in mammals were analysed. It appeared that expression of these isoenzymes occurs in a tissue-specific manner. The mRNA for isoenzyme PDK1 was found almost exclusively in rat heart. The mRNA for PDK3 was most abundantly expressed in rat testis. The message for PDK2 was present in all tissues tested but the level was low in spleen and lung. The mRNA for PDK4 was predominantly expressed in skeletal muscle and heart. The specific activities of the isoenzymes varied 25-fold, from 50nmol/min per mg for PDK2 to 1250nmol/min per mg for PDK3. Apparent Ki values of the isoenzymes for the synthetic analogue of pyruvate, dichloroacetate, varied 40-fold, from 0.2 mM for PDK2 to 8 mM for PDK3. The isoenzymes were also different with respect to their ability to respond to NADH and NADH plus acetyl-CoA. NADH alone stimulated the activities of PDK1 and PDK2 by 20 and 30% respectively. NADH plus acetyl-CoA activated these isoenzymes nearly 200 and 300%. Under comparable conditions, isoenzyme PDK3 was almost completely unresponsive to NADH, and NADH plus acetyl-CoA caused inhibition rather than activation. Isoenzyme PDK4 was activated almost 2-fold by NADH, but NADH plus acetyl-CoA did not activate above the level seen with NADH alone. These results provide the first evidence that the unique tissue distribution and kinetic characteristics of the isoenzymes of PDK are among the major factors responsible for tissue-specific regulation of the pyruvate dehydrogenase complex activity.


