Sodium Picosulfatelaxative CAS# 10040-45-6 |
- Resminostat hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC1888
CAS No.:1187075-34-8
- RG2833
Catalog No.:BCC1893
CAS No.:1215493-56-3
- Daminozide
Catalog No.:BCC1514
CAS No.:1596-84-5
- Tasquinimod
Catalog No.:BCC1987
CAS No.:254964-60-8
- CHAPS
Catalog No.:BCC1476
CAS No.:75621-03-3
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 10040-45-6 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 68654 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C18H13NNa2O8S2 | M.Wt | 481.41 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Synonyms | Sodium Picosulphate | ||
| Solubility | DMSO : 100 mg/mL (207.72 mM; Need ultrasonic) H2O : ≥ 100 mg/mL (207.72 mM) *"≥" means soluble, but saturation unknown. | ||
| Chemical Name | disodium;[4-[pyridin-2-yl-(4-sulfonatooxyphenyl)methyl]phenyl] sulfate | ||
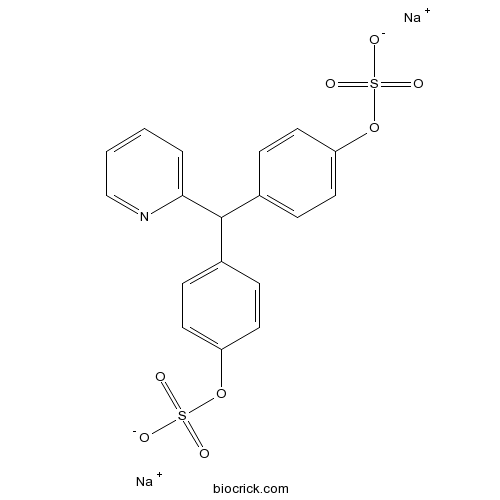
| SMILES | [Na+].[Na+].[O-][S](=O)(=O)Oc1ccc(cc1)C(c2ccc(O[S]([O-])(=O)=O)cc2)c3ccccn3 | ||
| Standard InChIKey | GOZDTZWAMGHLDY-UHFFFAOYSA-L | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C18H15NO8S2.2Na/c20-28(21,22)26-15-8-4-13(5-9-15)18(17-3-1-2-12-19-17)14-6-10-16(11-7-14)27-29(23,24)25;;/h1-12,18H,(H,20,21,22)(H,23,24,25);;/q;2*+1/p-2 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Sodium Picosulfate inhibits absorption of water and electrolytes, and increases their secretion.
Target: Others
Sodium Picosulfate displays cytotoxic effects on cultured liver cells. 800 and 1600 mg/mL induces dose-dependently vacuolic and fatty change as well as necrosis combined with a lowered mitotic activity and a slight increase in LDH values of the rapidly growing cultured liver cells of rabbit. Comparable but less severe effects are observed in 4-day old liver cell cultures of rat, while liver cells cultured for 6 to 11 days tolerate 1600 mg/mL Sodium Picosulfate. In human liver cultures the number of cells is slightly lowered at 800 and 1600 mg/mL and the number of nuclei in division is decreased dependent on dose [1]. Sodium Picosulphate has no major influence on ileal and colonic epithelial cell proliferation. In a 12 weeks study, 10 mg/kg Sodium Picosulphate continuously treatment does not influence the labeling index of Brdu (LI) in the ileum and induces no statistically significant increase of the LI when the treated groups are compared with the control group. The proliferative pattern along the crypts remains unchanged with sodium picosulphate treatment throughout the study [2]. Sodium Picosulphate does not induce chronic changes in colonic motility in rats under long-term treatment. 10mg/kg/day Sodium Picosulphate pretreated for 23 weeks does not induce any significant change in the duration of long spike bursts (LSB) which are associated with phasic contractions, or in LSB frequency in the fasted state or after a 3-gram meal [3]. References: | |||||

Sodium Picosulfate Dilution Calculator

Sodium Picosulfate Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.0772 mL | 10.3862 mL | 20.7723 mL | 41.5446 mL | 51.9308 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.4154 mL | 2.0772 mL | 4.1545 mL | 8.3089 mL | 10.3862 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.2077 mL | 1.0386 mL | 2.0772 mL | 4.1545 mL | 5.1931 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0415 mL | 0.2077 mL | 0.4154 mL | 0.8309 mL | 1.0386 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0208 mL | 0.1039 mL | 0.2077 mL | 0.4154 mL | 0.5193 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
Sodium Picosulfate is a laxative.
Sodium Picosulfate is a laxative that inhibits water and electrolytes absorption and increases their secretion. In cultured human, rat and rabbit liver cells, sodium picosulfate (1600 μg/ml) reduced the protein content in rabbit liver cells. Also, hepatocytes of rabbit were more sensitive to sodium picosulfate [1].
In patients underwent a barium enema, sodium picosulphate reduced the serum concentrations of sodium, potassium and urea by 1.299, 0.163 and 0.556, respectively [2]. In patients with morphine sulphate induced constipation, sodium picosulfate was well-tolerated and significantly improved constipation with normal stool consistency, not requiring suppositories, manual evacuation or enemas [3]. In patients with chronic constipation, sodium picosulphate (7 mg) improved stool frequency and straining in 82.8% patients and reduced bloating [4].
References:
[1]. Nishikawa J, Kast A. Effects of sodium picosulfate, bisacodyl and sennoside in cultured human, rat and rabbit liver cells. Arzneimittelforschung, 1981, 31(6): 1010-1013.
[2]. Ryan F, Anobile T, Scutt D, et al. Effects of oral sodium picosulphate Picolax on urea and electrolytes. Nurs Stand, 2005, 19(45): 41-45.
[3]. Twycross RG, McNamara P, Schuijt C, et al. Sodium picosulfate in opioid-induced constipation: results of an open-label, prospective, dose-ranging study. Palliat Med, 2006, 20(4): 419-423.
[4]. Wulkow R, Vix JM, Schuijt C, et al. Randomised, placebo-controlled, double-blind study to investigate the efficacy and safety of the acute use of sodium picosulphate in patients with chronic constipation. Int J Clin Pract, 2007, 61(6): 944-950.
- GSK 1562590 hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC8010
CAS No.:1003878-07-6
- Calcium chloride dihydrate
Catalog No.:BCC7582
CAS No.:10035-04-8
- Curcumenone
Catalog No.:BCN3008
CAS No.:100347-96-4
- L(+)-Rhamnose monohydrate
Catalog No.:BCN8368
CAS No.:10030-85-0
- Pemirolast potassium
Catalog No.:BCC4532
CAS No.:100299-08-9
- Apiopaeonoside
Catalog No.:BCN2801
CAS No.:100291-86-9
- Irinotecan hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCN2949
CAS No.:100286-90-6
- TZ9
Catalog No.:BCC5547
CAS No.:1002789-86-7
- Picrasidine J
Catalog No.:BCN5820
CAS No.:100234-62-6
- Picrasidine I
Catalog No.:BCN5819
CAS No.:100234-59-1
- AMG-208
Catalog No.:BCC1054
CAS No.:1002304-34-8
- Camstatin
Catalog No.:BCC5690
CAS No.:1002295-95-5
- Danshinspiroketallactone
Catalog No.:BCN3754
CAS No.:100414-80-0
- Lercanidipine
Catalog No.:BCC5239
CAS No.:100427-26-7
- Boric acid
Catalog No.:BCC7592
CAS No.:10043-35-3
- Cobicistat (GS-9350)
Catalog No.:BCC2271
CAS No.:1004316-88-4
- Dihydroresveratrol 3-O-glucoside
Catalog No.:BCN5821
CAS No.:100432-87-9
- 1-EBIO
Catalog No.:BCC6904
CAS No.:10045-45-1
- FFN 511
Catalog No.:BCC7799
CAS No.:1004548-96-2
- Rosiridin
Catalog No.:BCN5970
CAS No.:100462-37-1
- Gastrin I (human)
Catalog No.:BCC5958
CAS No.:10047-33-3
- Sterigmatocystin
Catalog No.:BCN6885
CAS No.:10048-13-2
- Blasticidin A
Catalog No.:BCN1830
CAS No.:100513-53-9
- TCS 2002
Catalog No.:BCC6074
CAS No.:1005201-24-0
Upper airway obstruction resulting from acute mucosal injury induced by direct ingestion of sodium picosulfate/magnesium citrate powder.[Pubmed:27752627]
Clin Exp Emerg Med. 2016 Jun 30;3(2):109-111.
A 59-year-old man presented to the emergency department with a chief complaint of sore throat after swallowing Sodium Picosulfate/magnesium citrate powder for bowel preparation, without first dissolving it in water. The initial evaluation showed significant mucosal injury involving the oral cavity, pharynx, and epiglottis. Endotracheal intubation was performed for airway protection in the emergency department, because the mucosal swelling resulted in upper airway compromise. After conservative treatment in the intensive care unit, he underwent tracheostomy because stenosis of the supraglottic and subglottic areas was not relieved. The tracheostomy tube was successfully removed after confirming recovery, and he was discharged 3 weeks after admission.
Acute Gastric Injury Caused by Undissolved Sodium Picosulfate/Magnesium Citrate Powder.[Pubmed:27732774]
Clin Endosc. 2017 Jan;50(1):87-90.
Sodium Picosulfate/magnesium citrate (SPMC) is a widely used oral bowel cleansing agent considered to be relatively safe. However, partially dissolved or undissolved SPMC powder may cause severe injuries of the esophagus and stomach. We report a very rare case of acute gastric injury without esophageal damage caused by the ingestion of undissolved SPMC powder. A 69-year-old man experienced epigastric pain after swallowing SPMC powder without dissolving it in water in preparation for a screening colonoscopy. He realized his mistake immediately and subsequently drank 2 L of water. The esophagogastroduodenoscopy conducted after 12 hours indicated an acute gastric ulceration without injury of the esophagus or duodenum. The endoscopy conducted after 6 weeks of oral proton pump inhibitor treatment showed healing of the gastric injury. This suggested that drinking large amounts of water after ingesting partially dissolved or undissolved SPMC powder can prevent serious esophageal injury, but offers no preventive benefit for acute gastric injury.
[Comparison of colon-cleansing methods in preparation for colonoscopy-comparative of solutions of mannitol and sodium picosulfate].[Pubmed:28062864]
Rev Gastroenterol Peru. 2016 Oct-Dec;36(4):293-297.
OBJECTIVES: The purpose of the present study is to compare intestinal preparation with mannitol and sodium picosulphate, assessing patient's acceptance, side effects and cleaning capacity. MATERIAL AND METHODS: This is a prospective, nom randomized, blind study, in which the evaluator had no information about the preparation applied. The sample obtained was divided into two groups according to the bowel preparation applied, with 153 patients prepared with 10% mannitol and 84 patients with Sodium Picosulfate. The evaluation of colon preparation was done using the Boston Scale (Boston Bowel Preparation Scale - BBP) through a three-point scoring system for each of the three regions of the colon: right, left and transverse colon. RESULTS: Of the 237 patients that were evaluated, 146 (61.60%) were female and 91 (38.4%) were male. Regarding the group that used mannitol, 98 were female (64.05%) and 55 were male (35.95%). Among the patients who used Sodium Picosulfate, 48 were female (57.14%) and 36 were male (42.86%), with no statistical differences between both groups (p> 0.32). Considering that an adequate preparation scores >/= 6 in the Boston Scale, the bowel cleansing preparation was satisfactory in both groups. 93% of the patients who used mannitol and 81% of the patients who used Sodium Picosulfate had adequate preparation (score of >/= 6). Moreover, we consider that the average score in the preparation with Mannitol was 9, while the Sodium Picosulfate score was 7. There were no significant differences between the two groups. CONCLUSION: There is consensus among authors who state that colonoscopy's safety and success are highly related to the cleansing outcome, regardless of the method used. The same can be observed in the present study, on which both preparations were proved safe and effective for bowel cleansing, according to the Boston scale, as well as accepted by patients and free of complications.


