Calcium chloride dihydratetransformation of E.Coli and transfection of eukaryotic cells CAS# 10035-04-8 |
- 25,26-Dihydroxyvitamin D3
Catalog No.:BCC4201
CAS No.:29261-12-9
- Vitamin D4
Catalog No.:BCC2042
CAS No.:511-28-4
- Impurity B of Calcitriol
Catalog No.:BCC1645
CAS No.:66791-71-7
- Calcifediol-D6
Catalog No.:BCC4075
CAS No.:78782-98-6
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 10035-04-8 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 6093260 | Appearance | Powder |
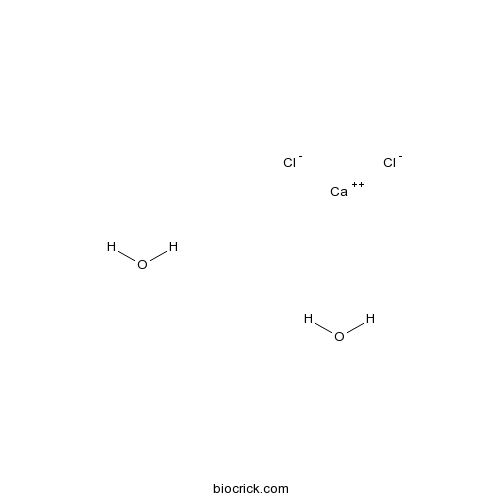
| Formula | CaCl2H4O2 | M.Wt | 147.01 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | Soluble to 1000 mM in water Soluble to 1000 mM in water | ||
| Chemical Name | calcium;dichloride;dihydrate | ||
| SMILES | O.O.[Cl-].[Cl-].[Ca++] | ||
| Standard InChIKey | LLSDKQJKOVVTOJ-UHFFFAOYSA-L | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/Ca.2ClH.2H2O/h;2*1H;2*1H2/q+2;;;;/p-2 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Commonly used laboratory reagent |

Calcium chloride dihydrate Dilution Calculator

Calcium chloride dihydrate Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 6.8023 mL | 34.0113 mL | 68.0226 mL | 136.0452 mL | 170.0565 mL |
| 5 mM | 1.3605 mL | 6.8023 mL | 13.6045 mL | 27.209 mL | 34.0113 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.6802 mL | 3.4011 mL | 6.8023 mL | 13.6045 mL | 17.0056 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.136 mL | 0.6802 mL | 1.3605 mL | 2.7209 mL | 3.4011 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.068 mL | 0.3401 mL | 0.6802 mL | 1.3605 mL | 1.7006 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
Calcium Chloride is a widely used reagent in the research of biochemistry.
Calcium play roles of great importance in physiological function, including signal transmitting, muscle contraction, and maintenance of cell morphology and stability. Chloride ions are essential in body fluids which maintain the acid/base balance and transduce nerve impulses.
Calcium Chloride is used in the preparation and transformation of competent Escherichia. Coli and in the transfection of eukaryotic cells with either plasmid DNA or high molecular weight genomic DNA. CaCl2 has been used in the stabilization and two-dimensional crystallization of the NADH-ubiquinone oxidoreductase from E. coli. The crystallization of procine pancreatic elastase in the presence of CaCl2 in the presence of sodium citrate reveals binding of calcium in the metal binding site of the protein. [1]
Calcium chloride was also assessed for its ability to bind dietary phosphorus both in vivo and in vitro. The outcome revealed that inhibition of phosphorus absorption by calcium chloride involves a complex interplay between chemical reactions and ion transport processes in the stomach and small intestine. Moreover, calcium chloride was assessed for the rapidity of reaction at pH 7 which showed 99% binding at 10 min. Calcium chloride is also a convenient and reliable reagent for creating aneurysm model. Doses of 13.6 mEq/10 ml calcium chloride solution were administrated to the abdominal aorta of nine mice daily. The diameters of vessel were measured in 7-day intervals and had significant increasing, which could be results of inflammatory infiltrates in the intima and media layers underlying mechanisms for this model include disrupting the elastic network within the media by calcium precipitations and activating the inflammatory response. [2, 3]
References:
[1] Dagert, M., and S. D. Ehrlich. "Prolonged incubation in calcium chloride improves the competence of Escherichia coli cells." Gene 6.1 (1979): 23-28.
[2] Sheikh, Mudassir S., et al. "Reduction of dietary phosphorus absorption by phosphorus binders. A theoretical, in vitro, and in vivo study." Journal of Clinical Investigation 83.1 (1989): 66.
[3] Chiou, Andy C., Bill Chiu, and William H. Pearce. "Murine aortic aneurysm produced by periarterial application of calcium chloride." Journal of Surgical Research 99.2 (2001): 371-376.
- Curcumenone
Catalog No.:BCN3008
CAS No.:100347-96-4
- L(+)-Rhamnose monohydrate
Catalog No.:BCN8368
CAS No.:10030-85-0
- Pemirolast potassium
Catalog No.:BCC4532
CAS No.:100299-08-9
- Apiopaeonoside
Catalog No.:BCN2801
CAS No.:100291-86-9
- Irinotecan hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCN2949
CAS No.:100286-90-6
- TZ9
Catalog No.:BCC5547
CAS No.:1002789-86-7
- Picrasidine J
Catalog No.:BCN5820
CAS No.:100234-62-6
- Picrasidine I
Catalog No.:BCN5819
CAS No.:100234-59-1
- AMG-208
Catalog No.:BCC1054
CAS No.:1002304-34-8
- Camstatin
Catalog No.:BCC5690
CAS No.:1002295-95-5
- 5,5'-Dimethoxysecoisolariciresinol
Catalog No.:BCN7941
CAS No.:1002106-91-3
- 2,3-dihydroxy-3-(4-hydroxyphenyl)propanoic acid
Catalog No.:BCN1641
CAS No.:100201-57-8
- GSK 1562590 hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC8010
CAS No.:1003878-07-6
- Sodium Picosulfate
Catalog No.:BCC4845
CAS No.:10040-45-6
- Danshinspiroketallactone
Catalog No.:BCN3754
CAS No.:100414-80-0
- Lercanidipine
Catalog No.:BCC5239
CAS No.:100427-26-7
- Boric acid
Catalog No.:BCC7592
CAS No.:10043-35-3
- Cobicistat (GS-9350)
Catalog No.:BCC2271
CAS No.:1004316-88-4
- Dihydroresveratrol 3-O-glucoside
Catalog No.:BCN5821
CAS No.:100432-87-9
- 1-EBIO
Catalog No.:BCC6904
CAS No.:10045-45-1
- FFN 511
Catalog No.:BCC7799
CAS No.:1004548-96-2
- Rosiridin
Catalog No.:BCN5970
CAS No.:100462-37-1
- Gastrin I (human)
Catalog No.:BCC5958
CAS No.:10047-33-3
- Sterigmatocystin
Catalog No.:BCN6885
CAS No.:10048-13-2
Calcium chloride rhenate(VII) dihydrate.[Pubmed:17762100]
Acta Crystallogr C. 2007 Sep;63(Pt 9):i77-9.
The crystal structure of calcium chloride rhenate(VII) dihydrate, CaCl(ReO4).2H2O, investigated at 85 K, consists of calcium cations, chloride anions, rhenate(VII) anions and water molecules. In the nearly tetrahedral rhenate(VII) anion, all constituent atoms lie on special positions of m2m (Re) and m (O) site symmetries. The Cl- anion and water O atom lie on special positions of m2m and 2 site symmetries, respectively. The Ca2+ ion, also on a special position (m2m), is eight-coordinated in a distorted square-antiprismatic coordination mode. The crystal has a layered structure stabilized by Ca-O coordination bonds and O-H...Cl hydrogen bonds.
Structure of the X-phase of 38% brominated betaine calcium chloride dihydrate.[Pubmed:11373387]
Acta Crystallogr B. 2001 Jun;57(Pt 3):296-302. Epub 2001 Jun 1.
The structures of the high- and low-temperature phases of 38% brominated BCCD [betaine (trimethylammonioacetate) Calcium chloride dihydrate], the latter being known as the X-phase, have been determined by single-crystal neutron diffraction at 295 and 20 K, respectively. The symmetry of the X-phase is described by the P2(1)2(1)2(1) space group. The distortion with respect to the high-temperature Pnma phase is characterized by anti-symmetric displacements of the betaine molecules as well as of the Ca octahedra. On the basis of a symmetry-mode analysis, we propose an interpretation of the direct phase transition that occurs around 80 K between these two phases.


