FFN 511Fluorescent substrate for VMAT2 CAS# 1004548-96-2 |
- Erastin
Catalog No.:BCC4497
CAS No.:571203-78-6
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 1004548-96-2 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 91885442 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C17H20N2O2 | M.Wt | 284.35 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | Soluble to 25 mM in 1eq. HCl and to 5 mM in DMSO | ||
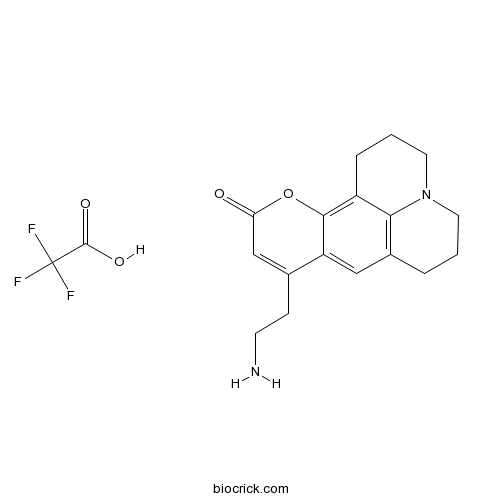
| SMILES | C1CC2=C3C(=C4C(=C2)C(=CC(=O)O4)CCN)CCCN3C1.C(=O)(C(F)(F)F)O | ||
| Standard InChIKey | XHUSAIWAUAMZRG-UHFFFAOYSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C17H20N2O2.C2HF3O2/c18-6-5-11-10-15(20)21-17-13-4-2-8-19-7-1-3-12(16(13)19)9-14(11)17;3-2(4,5)1(6)7/h9-10H,1-8,18H2;(H,6,7) | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Fluorescent false neurotransmitter (FFN). Targets neuronal vesicular monoamine transporter (VMAT) 2; inhibits serotonin binding to VMAT2 (IC50 = 1 μM). |

FFN 511 Dilution Calculator

FFN 511 Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 3.5168 mL | 17.584 mL | 35.1679 mL | 70.3359 mL | 87.9198 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.7034 mL | 3.5168 mL | 7.0336 mL | 14.0672 mL | 17.584 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.3517 mL | 1.7584 mL | 3.5168 mL | 7.0336 mL | 8.792 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0703 mL | 0.3517 mL | 0.7034 mL | 1.4067 mL | 1.7584 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0352 mL | 0.1758 mL | 0.3517 mL | 0.7034 mL | 0.8792 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
- 1-EBIO
Catalog No.:BCC6904
CAS No.:10045-45-1
- Dihydroresveratrol 3-O-glucoside
Catalog No.:BCN5821
CAS No.:100432-87-9
- Cobicistat (GS-9350)
Catalog No.:BCC2271
CAS No.:1004316-88-4
- Boric acid
Catalog No.:BCC7592
CAS No.:10043-35-3
- Lercanidipine
Catalog No.:BCC5239
CAS No.:100427-26-7
- Danshinspiroketallactone
Catalog No.:BCN3754
CAS No.:100414-80-0
- Sodium Picosulfate
Catalog No.:BCC4845
CAS No.:10040-45-6
- GSK 1562590 hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC8010
CAS No.:1003878-07-6
- Calcium chloride dihydrate
Catalog No.:BCC7582
CAS No.:10035-04-8
- Curcumenone
Catalog No.:BCN3008
CAS No.:100347-96-4
- L(+)-Rhamnose monohydrate
Catalog No.:BCN8368
CAS No.:10030-85-0
- Pemirolast potassium
Catalog No.:BCC4532
CAS No.:100299-08-9
- Rosiridin
Catalog No.:BCN5970
CAS No.:100462-37-1
- Gastrin I (human)
Catalog No.:BCC5958
CAS No.:10047-33-3
- Sterigmatocystin
Catalog No.:BCN6885
CAS No.:10048-13-2
- Blasticidin A
Catalog No.:BCN1830
CAS No.:100513-53-9
- TCS 2002
Catalog No.:BCC6074
CAS No.:1005201-24-0
- Aeruginolactone
Catalog No.:BCN3695
CAS No.:1005208-88-7
- Gelomulide N
Catalog No.:BCN6641
CAS No.:1005212-02-1
- CVT 10216
Catalog No.:BCC5606
CAS No.:1005334-57-5
- LCL161
Catalog No.:BCC1691
CAS No.:1005342-46-0
- Tirasemtiv
Catalog No.:BCC5183
CAS No.:1005491-05-3
- Monomethylsulochrin
Catalog No.:BCN7255
CAS No.:10056-14-1
- TC ASK 10
Catalog No.:BCC6301
CAS No.:1005775-56-3
Fluorescent false neurotransmitters visualize dopamine release from individual presynaptic terminals.[Pubmed:19423778]
Science. 2009 Jun 12;324(5933):1441-4.
The nervous system transmits signals between neurons via neurotransmitter release during synaptic vesicle fusion. In order to observe neurotransmitter uptake and release from individual presynaptic terminals directly, we designed fluorescent false neurotransmitters as substrates for the synaptic vesicle monoamine transporter. Using these probes to image dopamine release in the striatum, we made several observations pertinent to synaptic plasticity. We found that the fraction of synaptic vesicles releasing neurotransmitter per stimulus was dependent on the stimulus frequency. A kinetically distinct "reserve" synaptic vesicle population was not observed under these experimental conditions. A frequency-dependent heterogeneity of presynaptic terminals was revealed that was dependent in part on D2 dopamine receptors, indicating a mechanism for frequency-dependent coding of presynaptic selection.
Dopamine release at individual presynaptic terminals visualized with FFNs.[Pubmed:19721412]
J Vis Exp. 2009 Aug 31;(30). pii: 1562.
The nervous system transmits signals between neurons via neurotransmitter release during synaptic vesicle fusion. To observe neurotransmitter uptake and release from individual presynaptic terminals directly, we designed fluorescent false neurotransmitters as substrates for the synaptic vesicle monoamine transporter. Using these probes to image dopamine release in the striatum, we made several observations pertinent to synaptic plasticity. We found that the fraction of synaptic vesicles releasing neurotransmitter per stimulus was dependent on the stimulus frequency. A kinetically distinct "reserve" synaptic vesicle population was not observed under these experimental conditions. A frequency-dependent heterogeneity of presynaptic terminals was revealed that was dependent in part on D2 dopamine receptors, indicating a mechanism for frequency-dependent coding of presynaptic selection.


