ThiazovivinROCK inhibitor CAS# 1226056-71-8 |
- Lenalidomide hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC1697
CAS No.:1243329-97-6
- Celastrol
Catalog No.:BCN5986
CAS No.:34157-83-0
- Necrostatin 2 racemate
Catalog No.:BCC2077
CAS No.:852391-15-2
- Necrostatin 2
Catalog No.:BCC1793
CAS No.:852391-19-6
- Necrostatin 2 S enantiomer
Catalog No.:BCC2078
CAS No.:852391-20-9
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 1226056-71-8 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 46209426 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C15H13N5OS | M.Wt | 311.36 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | DMSO : ≥ 30 mg/mL (96.35 mM) *"≥" means soluble, but saturation unknown. | ||
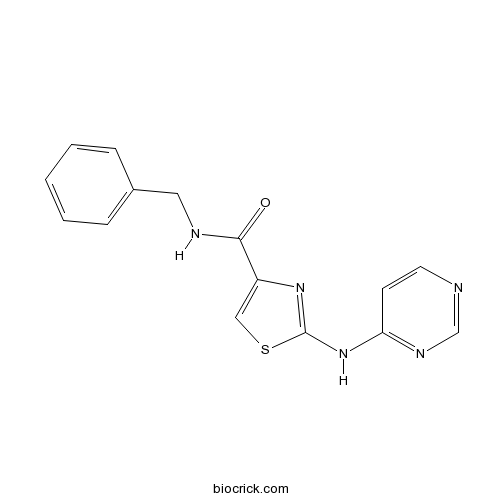
| Chemical Name | N-benzyl-2-(pyrimidin-4-ylamino)-1,3-thiazole-4-carboxamide | ||
| SMILES | C1=CC=C(C=C1)CNC(=O)C2=CSC(=N2)NC3=NC=NC=C3 | ||
| Standard InChIKey | DOBKQCZBPPCLEG-UHFFFAOYSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C15H13N5OS/c21-14(17-8-11-4-2-1-3-5-11)12-9-22-15(19-12)20-13-6-7-16-10-18-13/h1-7,9-10H,8H2,(H,17,21)(H,16,18,19,20) | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Thiazovivin is a novel ROCK inhibitor with IC50 of 0.5 μM in a cell-free assay, promotes hESC survival after single-cell dissociation.Although displaying little impact on cell proliferation, Thiazovivin treatment significantly enhances the survival of human embryonic stem cells (hESCs) after enzymatic dissociation more than 30-fold, while homogenously maintaining pluripotency with the characteristic colony morphology, expression of typical pluripotency markers such as alkaline phosphatase (ALP), and normal karyotype. Dissociated hESCs treated with Thiazovivin display dramatically increased adhesion to matrigel- or laminin-coated plates but not to gelatin-coated plates within a few hours. Thiazovivin treatment increases cell-ECM adhesion-mediated β1 integrin activity, which synergizes with growth factors to promote cell survival. In addition to activating integrin, Thiazovivin but not Tyrintegin (Ptn) protects hESCs from death in the absence of ECM in suspension through E-cadherin-mediated cell-cell interaction. Thiazovivin treatment potently inhibits endocytosis of E-cadherin, consequently stabilizing E-cadherin on the cell surface and leading to reestablishment of cell-cell interaction, which is essential for hESC survival in ECM-free conditions. Thiazovivin but not Tyrintegin (Ptn) at 2 μM inhibits Rho-associated kinase (ROCK) activity and protects hESCs at a similar level as the widely used selective ROCK inhibitor Y-27632 at 10 μM, suggesting that Rho-ROCK signaling regulates cell-ECM and cell-cell adhesion. Thiazovivin at 1 μM increases the reprogramming efficiency of CB mononuclear cells to induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs) by more than 10 times. |

Thiazovivin Dilution Calculator

Thiazovivin Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 3.2117 mL | 16.0586 mL | 32.1172 mL | 64.2343 mL | 80.2929 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.6423 mL | 3.2117 mL | 6.4234 mL | 12.8469 mL | 16.0586 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.3212 mL | 1.6059 mL | 3.2117 mL | 6.4234 mL | 8.0293 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0642 mL | 0.3212 mL | 0.6423 mL | 1.2847 mL | 1.6059 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0321 mL | 0.1606 mL | 0.3212 mL | 0.6423 mL | 0.8029 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
Greatly enhances the efficiency of fibroblast reprogramming to generate induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs) when used in combination with SB 431542 and PD 0325901. Improves the survival of human embryonic stem cells (hESCs) upon trypsinization.
- p-Anisil
Catalog No.:BCC9112
CAS No.:1226-42-2
- Garbanzol
Catalog No.:BCN6811
CAS No.:1226-22-8
- 11-Hydroxyhumantenine
Catalog No.:BCN4863
CAS No.:122590-04-9
- 11-Hydroxyrankinidine
Catalog No.:BCN4814
CAS No.:122590-03-8
- Ajugamarin F4
Catalog No.:BCN3656
CAS No.:122587-84-2
- Ajugamarin G1
Catalog No.:BCN3659
CAS No.:122587-83-1
- Esculentoside T
Catalog No.:BCC1077
CAS No.:
- SKLB1002
Catalog No.:BCC4312
CAS No.:1225451-84-2
- Gelomulide B
Catalog No.:BCN6588
CAS No.:122537-60-4
- Gelomulide A
Catalog No.:BCN6580
CAS No.:122537-59-1
- DCC-2618
Catalog No.:BCC1520
CAS No.:1225278-16-9
- AG 99
Catalog No.:BCC6667
CAS No.:122520-85-8
- PKC fragment (530-558)
Catalog No.:BCC5830
CAS No.:122613-29-0
- Ajugamarin H1
Catalog No.:BCN3658
CAS No.:122616-88-0
- Ibutilide Fumarate
Catalog No.:BCC5076
CAS No.:122647-32-9
- MK3102
Catalog No.:BCC6417
CAS No.:1226781-44-7
- Norpterosin B glucoside
Catalog No.:BCN7302
CAS No.:1226785-88-1
- Norpterosin B
Catalog No.:BCN7101
CAS No.:1226892-20-1
- FLLL32
Catalog No.:BCC6499
CAS No.:1226895-15-3
- ATB-346
Catalog No.:BCC5289
CAS No.:1226895-20-0
- SB 277011A dihydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC7887
CAS No.:1226917-67-4
- BAY 87-2243
Catalog No.:BCC4131
CAS No.:1227158-85-1
- 4-Fluoro-1-(3-(pyrimidin-5-yl)phenyl)-1-(2-(trifluoromethyl)pyridin-4-yl)-1H-isoindol-3-amine
Catalog No.:BCC5113
CAS No.:1227163-56-5
- AZD3839
Catalog No.:BCC6471
CAS No.:1227163-84-9
Thiazovivin, a Rho kinase inhibitor, improves stemness maintenance of embryo-derived stem-like cells under chemically defined culture conditions in cattle.[Pubmed:26307658]
Anim Reprod Sci. 2015 Oct;161:47-57.
Despite numerous reported attempts, successful isolation of genuine embryonic stem cells of cattle has been rare. Previous studies have shown that Thiazovivin, a Rho-associated kinase inhibitor, improves the survival and self-renewal of human embryonic stem cells. The present study demonstrates the effect of Thiazovivin on the derivation of embryo-derived stem-like cells. Attachment rates of blastocyst and embryonic cell clumps onto feeder cells in the Thiazovivin treatment group were greater than those of the control group. The pluripotency markers of the OCT4 and NANOG genes, and the adhesion molecule E-cadherin were increased by Thiazovivin treatment. This study suggests that Thiazovivin treatment improves the maintenance of stemness in a putative stem-like cell populations of cattle by promoting the expression of pluripotency marker genes, as well as enhancing the expression of the E-cadherin gene, resulting in an increase in cell adhesion.
[Effect of a new ROCK inhibitor thiazovivin on the morphology and function of human corneal endothelial cells].[Pubmed:27647250]
Zhonghua Yan Ke Za Zhi. 2016 Sep 11;52(9):686-92.
OBJECTIVE: To evaluate the effect of Thiazovivin, a novel ROCK inhibitor, on the morphology and function of human corneal endothelial cells(HCECs). METHODS: The primary HCECs were identified by light microscopy and immunofluorescence staining of neuron-specific enolase. To screen the optimal concentration and action time of Thiazovivin for maintaining the morphology and function of primary HCECs, Na (+)/K (+)-ATPase and N-cadherin were chosen as indicators, and the morphology and function of HCECs in various concentrations(0 mumol/L, 2 mumol/L, 4 mumol/L, and 6 mumol/L)for different durations(24 h and 48 h)were examined by immunofluorescence experiments. The effect of Thiazovivin on the expression of ROCK was investigated by immunofluorescence and Western blot. RESULTS: The primary HCECs cultured were hexagonal, closely packed, homogeneously and obviously stained by neuron-specific enolase. The immunofluorescence staining of Na(+)/K(+)-ATPase showed that when the primary HCECs cultured with various concentrations of Thiazovivin(0, 2, 4, 6 mumol/L)for 24 h, the fluorescence were obvious, and the average absorbance values(A)were 1.27+/-0.08, 3.72+/-0.17, 21.07+/-4.67, 3.69+/-0.34, respectively. And the immunofluorescence staining of N-cadherin revealed that when the primary HCECs treated with 4 mumol/L Thiazovivin for 24 h, the cell boundary was clear and the structure of the cells was intact. While the treating time of Thiazovivin(4 mumol/L)on HCECs extended to 48 h, the immunofluorescence staining of Na(+)/K(+)-ATPase and N-cadherin showed that compared to HCECs treated with Thiazovivin(4 mumol/L)for 24 h, the fluorescence intensity did not change significantly, but the cells arranged slightly untidy. In addition, the immunofluorescence staining of ROCK was weakened and the expression of ROCK was reduced by Thiazovivin. Thiazovivin was effective for protecting the morphology and function of HCECs. An optimal improvement in the morphology, connection and function of HCECs was found when the primary HCECs were cultured with 4 mumol/L Thiazovivin for 24 h. Moreover, the expression of ROCK protein could be significantly inhibited by Thiazovivin. (Chin J Ophthalmol, 2016, 52: 686-692).
Reprogramming of endometrial adult stromal cells in the presence of a ROCK inhibitor, thiazovivin, could obtain more efficient iPSCs.[Pubmed:25490878]
Cell Biol Int. 2015 May;39(5):515-8.
Today, there is a need for a platform to efficiently generate and maintain a feeder free culture of pluripotent stem cells by small molecules or pharmacological agents. Induced pluripotent stem cell (iPSC) is considered a promising resource for restorative cell therapy in clinical areas. While fully reprogrammed iPSCs are similar to embryonic stem cells, iPSCs could be derived from the patient's own cells (autologous), which avoids the immune rejection activities. Recent advances have demonstrated that iPSCs could be generated from human fibroblasts using only four transcription factors: OCT4, SOX2, CMYC, and KLF4. However, the limitations of reprogramming technologies include low efficiency, slow kinetics, transgene integration and residual expression. Surprisingly, adult stem cells from human endometrium (endometrial stem cells; EnSCs) express OCT4 and KLF4 pluripotency factors. On the other hand, small molecule inhibitors of specific signaling pathways such as Thiazovivin have been used in various aspects of iPSC generation and maintenance. Thiazovivin is a selective small molecule that directly targets Rho-associated kinase (ROCK) and increases expression of pluripotency factors. The process using Thiazovivin could be easier, faster and more cost effective than transgene integration into somatic cells. So reprogramming of OCT4 and KLF4 expressing EnSCs by a ROCK inhibitor, Thiazovivin, could result in producing more efficient iPSCs compared with fibroblasts or conventional somatic cells without integration any transgene and retroviral vector.
A chemical platform for improved induction of human iPSCs.[Pubmed:19838168]
Nat Methods. 2009 Nov;6(11):805-8.
The slow kinetics and low efficiency of reprogramming methods to generate human induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs) impose major limitations on their utility in biomedical applications. Here we describe a chemical approach that dramatically improves (200-fold) the efficiency of iPSC generation from human fibroblasts, within seven days of treatment. This will provide a basis for developing safer, more efficient, nonviral methods for reprogramming human somatic cells.


