ThymoquinoneCAS# 490-91-5 |
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 490-91-5 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 10281.0 | Appearance | Powder |
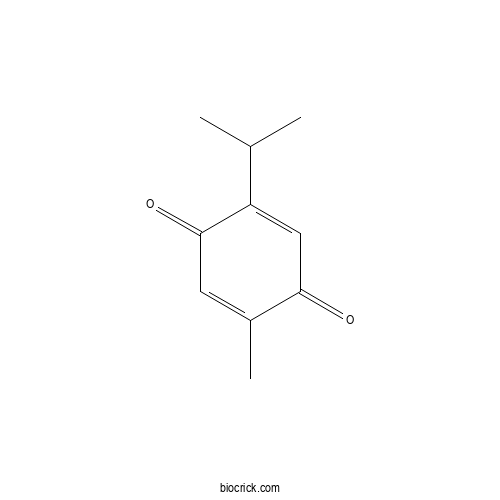
| Formula | C10H12O2 | M.Wt | 164.2 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | Soluble in Chloroform,Dichloromethane,Ethyl Acetate,DMSO,Acetone,etc. | ||
| Chemical Name | 2-methyl-5-propan-2-ylcyclohexa-2,5-diene-1,4-dione | ||
| SMILES | CC1=CC(=O)C(=CC1=O)C(C)C | ||
| Standard InChIKey | KEQHJBNSCLWCAE-UHFFFAOYSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C10H12O2/c1-6(2)8-5-9(11)7(3)4-10(8)12/h4-6H,1-3H3 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||

Thymoquinone Dilution Calculator

Thymoquinone Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 6.0901 mL | 30.4507 mL | 60.9013 mL | 121.8027 mL | 152.2533 mL |
| 5 mM | 1.218 mL | 6.0901 mL | 12.1803 mL | 24.3605 mL | 30.4507 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.609 mL | 3.0451 mL | 6.0901 mL | 12.1803 mL | 15.2253 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.1218 mL | 0.609 mL | 1.218 mL | 2.4361 mL | 3.0451 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0609 mL | 0.3045 mL | 0.609 mL | 1.218 mL | 1.5225 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
- Neoeuonymine
Catalog No.:BCX0806
CAS No.:33510-25-7
- Cortodoxone
Catalog No.:BCX0805
CAS No.:152-58-9
- Cortisone
Catalog No.:BCX0804
CAS No.:53-06-5
- Quercetin 7-O-glucuronide
Catalog No.:BCX0803
CAS No.:38934-20-2
- Coreopsin
Catalog No.:BCX0802
CAS No.:499-29-6
- Harmalan
Catalog No.:BCX0801
CAS No.:525-41-7
- Prosaikogenin G
Catalog No.:BCX0800
CAS No.:99365-23-8
- Pterin-6-carboxylic acid
Catalog No.:BCX0799
CAS No.:948-60-7
- 17-Hydroxygracillin
Catalog No.:BCX0798
CAS No.:90308-85-3
- Kanzonol D
Catalog No.:BCX0797
CAS No.:155233-20-8
- (-)-Epipodophyllotoxin
Catalog No.:BCX0796
CAS No.:4375-07-9
- Magnoloside B
Catalog No.:BCX0795
CAS No.:116872-05-0
- Monascin
Catalog No.:BCX0808
CAS No.:21516-68-7
- guan-fu base I
Catalog No.:BCX0809
CAS No.:110225-59-7
- Acetyl Dopamine Dimer I
Catalog No.:BCX0810
CAS No.:315188-82-0
- Monascorubrin
Catalog No.:BCX0811
CAS No.:13283-90-4
- 16-Hydroxyhexadecanoic acid
Catalog No.:BCX0812
CAS No.:506-13-8
- Xylotetraose
Catalog No.:BCX0813
CAS No.:22416-58-6
- Nepetalacton
Catalog No.:BCX0814
CAS No.:21651-62-7
- Kuwanon U
Catalog No.:BCX0815
CAS No.:123702-95-4
- Xylopentaose
Catalog No.:BCX0816
CAS No.:49694-20-4
- Hirudonucleodisulfide A
Catalog No.:BCX0817
CAS No.:1072789-37-7
- Xylohexaose
Catalog No.:BCX0818
CAS No.:49694-21-5
- Coreoside B
Catalog No.:BCX0819
CAS No.:1580464-83-0
Phytochemical investigation of Nigella sativa seed extract by HPTLC, HPLC and GC-MS: a comparative geographical study.[Pubmed:38684035]
Nat Prod Res. 2024 Apr 29:1-7.
This study aimed to ensure the quality of the seed as well as determine the phytochemical composition of Nigella sativa seed extract (NSSE) obtained from three different geographical locations. Pharmacognostic evaluation of the seed includes preliminary phytochemical screening, physicochemical evaluation, and study of heavy metal content, in addition to HPTLC, HPLC, and GC-MS studies of the extract obtained from the seed of the Nigella sativa (NS). HPTLC fingerprinting studies revealed the presence of various bioactive compounds. HPLC analysis confirms the quantitative variation of Thymoquinone (TQ) in the extracts, i.e. the maximum quantity of TQ was found in Vizag NSSE, followed by Punjab and Madhya Pradesh. GC-MS analysis reveals the presence of 33, 35, and 32 constituents in the extract obtained from Vizag, Madhya Pradesh, and Punjab, respectively. This study confirms the variation in the phytochemical composition as well as in the biomarker (Thymoquinone) content present in the collected samples.
Thymoquinone ameliorates symptoms of Parkinson's disease in a 6-OHDA rat model by downregulation of miR-204-3p.[Pubmed:38660812]
Behav Pharmacol. 2024 Apr 25.
microRNAs (miRNAs) play a significant role in the pathophysiology of Parkinson's disease. In this study, we evaluated the neuroprotective effect of Thymoquinone on the expression profiles of miRNA and cognitive functions in the 6-hydroxydopamine (6-OHDA)-induced Parkinson's model. Male adult Wistar albino rats (200-230 g, n = 36) were randomly assigned to six groups: Sham, Thymoquinone (10 mg/kg, p.o.), 6-OHDA, 6-OHDA + Thymoquinone (10 mg/kg), 6-OHDA + Thymoquinone (20 mg/kg), and 6-OHDA + Thymoquinone (50 mg/kg). Behavioral changes were detected using the open field and the elevated plus maze tests. The mature 728 miRNA expressions were evaluated by miRNA microarray (GeneChip miRNA 4.0). Ten miRNAs were selected (rno-miR-212-5p, rno-miR-146b-5p, rno-miR-150-5p, rno-miR-29b-2-5p, rno-miR-126a-3p, rno-miR-187-3p, rno-miR-34a-5p, rno-miR-181d-5p, rno-miR-204-3p, and rno-miR-30c-2-3p) and confirmed by real-time PCR. Striatum samples were stained with hematoxylin-eosin to determine the effect of dopaminergic lesions. One-way ANOVA test and independent sample t-test were used for statistical analyses. rno-miR-204-3p was upregulated at 6-OHDA and downregulated at the 50 mg/kg dose of Thymoquinone. In conclusion, Thymoquinone at a dose of 50 mg/kg ameliorates symptoms of Parkinson's disease in a 6-OHDA rat model by downregulation of miR-204-3p. Also, the results showed that Thymoquinone can improve locomotor activity and willing exploration and decreased anxiety. Therefore, Thymoquinone can be used as a therapeutic agent.
The Effect of Thymoquinone on the TNF-alpha/OTULIN/NF-kappaB Axis Against Cisplatin-Induced Testicular Tissue Damage.[Pubmed:38658488]
Reprod Sci. 2024 Apr 24.
One of the adverse effects of the antineoplastic drug cisplatin (CS) is damage to testicular tissue. This study aimed to examine the potential therapeutic effect of Thymoquinone (TQ), a strong antioxidant, against testicular damage caused by CS. In the experiment, 28 rats were used, and the rats were randomly divided into four groups: control (n = 7), CS (n = 7), CS + TQ (n = 7), and TQ (n = 7). The experiment was called off after all treatments were finished on day 15. Blood serum and testicular tissues were utilized for biochemical, histological, immunohistochemical, mRNA expression, and gene protein investigations. The testosterone level decreased and oxidative stress, histopathological damage, dysregulation in mitochondrial dynamics, inflammation and apoptotic cells increased in testicular tissue due to CS administration. TQ supplementation showed anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and anti-apoptotic effects in response to CS-induced testicular damage. In addition, TQ contributed to the reduction of CS-induced toxic effects by regulating the TNF-alpha/OTULIN/NF-kappaB pathway. TQ supplementation may be a potential therapeutic strategy against CS-induced testicular damage by regulating the TNF-alpha/OTULIN/NF-kappaB axis, inhibiting inflammation, oxidative stress, and apoptosis.
N-methyl-D-aspartate receptors and thymoquinone induce apoptosis and alteration in mitochondria in colorectal cancer cells.[Pubmed:38652404]
Med Oncol. 2024 Apr 23;41(5):123.
Colon cancer is on the rise in both men and women. In addition to traditional treatment methods, herbal treatments from complementary and alternative medicine are actively followed. Naturally derived from plants, Thymoquinone (TQ) has drawn a lot of attention in the field of cancer treatment. MK-801, an N-methyl-D-aspartate agonist, is used to improve memory and plasticity, but it has also lately been explored as a potential cancer treatment. This study aimed to determine the roles of N-Methyl-D-Aspartate agonists and Thymoquinone on mitochondria and apoptosis. HT-29 cells were treated with different TQ and MK-801 concentrations. We analyzed cell viability, apoptosis, and alteration of mitochondria. Cell viability significantly decreased depending on doses of TQ and MK-801. Apoptosis and mitochondrial dysfunctions induced by low and high doses of TQ and MK-801. Our study emphasizes the need for further safety evaluation of MK-801 due to the potential toxicity risk of TQ and MK-801. Optimal and toxic doses of TQ and MK-801 were determined for the treatment of colon cancer. It should be considered as a possibility that colon cancer can be treated with TQ and MK-801.
UHRF1 poly-auto-ubiquitination induced by the anti-cancer drug, thymoquinone, is involved in the DNA repair machinery recruitment.[Pubmed:38649007]
Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2024 Apr 20:106582.
DNA methylation is one of the most important epigenetic mark involved in many physiologic cellular processes and pathologies. During mitosis, the transmission of DNA methylation patterns from a mother to the daughter cells is ensured through the action of the Ubiquitin-like, containing PHD and RING domains, 1/DNA methyltransferase 1 (UHRF1/DNMT1) tandem. UHRF1 is involved in the silencing of many tumor suppressor genes (TSGs) via mechanisms that remain largely to be deciphered. The present study investigated the role and the regulation of UHRF1 poly-ubiquitination induced by Thymoquinone, a natural anti-cancer drug, known to enhance or re-activate the expression of TSGs. We found that the auto-ubiquitination of UHRF1, induced by TQ, is mediated by reactive oxygen species, and occurs following DNA damage. We demonstrated that the poly-ubiquitinated form of UHRF1 is K63-linked and can still silence the tumor suppressor gene p16(INK4A)/CDKN2A(.) We further showed that TQ-induced auto-ubiquitination is mediated via the activity of Tip60. Since this latter is known as a nuclear receptor co-factor, we investigated if the glucocorticoid receptor (GR) might be involved in the regulation of UHRF1 ubiquitination. Activation of the GR, with dexamethasone, did not influence auto-ubiquitination of UHRF1. However, we could observe that TQ induced a K48-linked poly-ubiquitination of GR, probably involved in the proteosomal degradation pathway. Mass-spectrometry analysis of FLAG-HA-tagged UHRF1 identified UHRF1 partners involved in DNA repair and showed that TQ increased their association with UHRF1, suggesting that poly-ubiquitination of UHRF1 is involved in the DNA repair process. We propose that poly-ubiquitination of UHRF1 serves as a scaffold to recruit the DNA repair machinery at DNA damage sites.
Thymoquinone is a natural antibiofilm and pathogenicity attenuating agent in Pseudomonas aeruginosa.[Pubmed:38638827]
Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2024 Apr 4;14:1382289.
Pseudomonas aeruginosa belongs to the critical pathogens that represent a global public health problem due to their high rate of resistance as listed by WHO. P. aeruginosa can result in many nosocomial infections especially in individuals with compromised immune systems. Attenuating virulence factors by interference with quorum sensing (QS) systems is a promising approach to treat P. aeruginosa-resistant infections. Thymoquinone is a natural compound isolated from Nigella sativa (black seed) essential oil. In this study, the minimum inhibitory concentration of Thymoquinone was detected followed by investigating the antibiofilm and antivirulence activities of the subinhibitory concentration of Thymoquinone against P. aeruginosa PAO1. The effect of Thymoquinone on the expression of QS genes was assessed by quantitative real-time PCR, and the protective effect of Thymoquinone against the pathogenesis of PAO1 in mice was detected by the mouse survival test. Thymoquinone significantly inhibited biofilm, pyocyanin, protease activity, and swarming motility. At the molecular level, Thymoquinone markedly downregulated QS genes lasI, lasR, rhlI, and rhlR. Moreover, Thymoquinone could protect mice from the pathologic effects of P. aeruginosa increasing mouse survival from 20% to 100%. In conclusion, Thymoquinone is a promising natural agent that can be used as an adjunct therapeutic agent with antibiotics to attenuate the pathogenicity of P. aeruginosa.
Phytochemical Composition, Antioxidant and Antimicrobial Activity of Three Monarda Species: M. bradburiana L. C. Beck, M. x media Willd., and M. punctata L.[Pubmed:38634813]
Chem Biodivers. 2024 Apr 18:e202301910.
Plants of the genus Monarda receive growing interest as the sources of herbal raw materials with wide range of potential applications in food, cosmetics, and phytopharmaceutical industry. This study aimed to evaluate the differences in chemical characteristics and biological activity among different organs of plants representing three underinvestigated species of this genus: Monarda bradburiana L. C. Beck, Monarda x media Willd., and Monarda punctata L. The content of phenolic compounds and the antioxidant activity of leaves, stems, and inflorescences were determined. Essential oil (EO) content, composition, and antimicrobial activity were also examined. M. punctata leaves and inflorescences had the highest EO content (4.43% and 5.59%, respectively), with carvacrol as a dominant constituent. Leaf EO was also rich in Thymoquinone (17.48%). In EOs of M. bradburiana and M. x media, thymol dominated. EOs inhibited the growth of all tested strains of microorganisms at a concentration of 0.625 microL x mL-1. The studied plant organs were rich in phenolic compounds, especially rosmarinic acid. M. bradburiana inflorescences were distinguished by high linarin content. Differences in flavonoid distribution seem to have special chemotaxonomic importance. Further research is needed to facilitate standardisation of the investigated plant organs as potential new herbal raw materials.
Effects of 5-fluorouracil, thymoquinone, and mammary stem cells' exosomes on in vitro cultured breast cancer cells.[Pubmed:38633189]
Open Vet J. 2024 Jan;14(1):525-533.
BACKGROUND: 5-fluorouracil (5-FU) is an antimetabolic agent used for treating slowly growing solid tumors like breast and ovarian carcinoma. Thymoquinone (TQ) is the main biologically active constituent of Nigella sativa, it has been found to demonstrate anticancerous effects in several preclinical studies, and this is because TQ possesses multitarget nature. Stem cells-derived exosomes are in the spotlight of research and are promising tissue regenerative and anticancer cell-derived nanovesicles. AIM: Herein, we studied the antineoplastic effects of Exosomes derived from mammary stem cells (MaSCs-Exo) on breast cancer cells, alone or combined with TQ when compared to a breast cancer chemotherapeutic agent; 5-FU. METHODS: Our approach included performing viability test and measuring the expression of pro-apoptotic gene (Bax), anti-apoptotic gene (BCL-2) and angiogenic gene (VEGF) on Human MCF-7 cells (breast adenocarcinoma cells), the MCF-7 cells were cultured and incubated with medium containing 5-FU (25 mug/ml), TQ (200 mug/ml), MaSCs-Exo (100 mug protein equivalent), a combination of TQ (200 mug/ml) and MaSCs-Exo (100 mug). RESULTS: Our obtained results show that TQ and MaSCs-Exo each can effectively inhibit breast cancer cell line (MCF-7) proliferation and growth. Also, the results show that the combination of TQ and MaSCs-Exo had higher cytotoxic effects on MCF-7 breast cancer cells than TQ or 5-FU, alone. CONCLUSION: The present study shows a promising anticancer potential of exosomes isolated from mammary stem cells; this effect was potentiated by adding TQ with MaSCs-derived exosomes.
Renoprotective effect of thymoquinone against rhabdomyolysis-induced acute kidney injury in the rat model.[Pubmed:38629092]
Iran J Basic Med Sci. 2024;27(5):552-559.
OBJECTIVES: Rhabdomyolysis leads to the release of myoglobin, sarcoplasmic proteins, and electrolytes into the blood circulation causing acute kidney injury (AKI). Thymoquinone, a natural compound found in Nigella sativa seeds, has antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects. This investigation assessed the renoprotective effect of Thymoquinone on rhabdomyolysis-induced AKI in rats. MATERIALS AND METHODS: Male Wistar rats were categorized into six groups (n = 6): 1. Control: (normal saline), 2. Glycerol (50 ml/kg, single dose, IM), 3-5: Glycerol + Thymoquinone (1, 2.5 and 5 mg/kg, 4 days, IP), 6. Thymoquinone (5 mg/kg). On day 5, serum and kidney tissue were isolated and the amounts of serum creatinine and blood urea nitrogen (BUN), renal malondialdehyde (MDA), glutathione (GSH.), tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-alpha), neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin (NGAL), and pathological changes were evaluated. RESULTS: Glycerol increased creatinine, BUN, MDA, TNF-alpha, and NGAL levels. It decreased GSH amounts and caused renal tubular necrosis, glomerular atrophy, and myoglobin cast in kidney tissue. Co-administration of glycerol and Thymoquinone reduced creatinine, BUN, histopathological alterations, and MDA levels, and enhanced GSH amounts. Administration of glycerol and Thymoquinone (5 mg/kg) had no significant effect on TNF-alpha amount but decreased NGAL protein levels. The administration of Thymoquinone (5 mg/kg) alone did not display a significant difference from the control group. CONCLUSION: Rhabdomyolysis from glycerol injection in rats can cause kidney damage. Thymoquinone may attenuate renal dysfunction and oxidative stress. However, the TNF-alpha level was not significantly affected. Further studies are needed to explore the potential therapeutic effects of Thymoquinone in managing AKI.
Self-micellizing solid dispersion of thymoquinone with enhanced biopharmaceutical and nephroprotective effects.[Pubmed:38590120]
Drug Deliv. 2024 Dec;31(1):2337423.
The present study was designed to develop a self-micellizing solid dispersion (SMSD) containing Thymoquinone (TQM), a phytonutrient obtained from Nigella sativa seeds, aiming to improve its biopharmaceutical and nephroprotective functions. The apparent solubility of TQM in polymer solutions was used to choose an appropriate amphiphilic polymer that could be used to make an SMSD system. Based on the apparent solubility, Soluplus(R) was selected as an appropriate carrier, and mixing with TQM, SMSD-TQM with different loadings of TQM (5-15%) was made by solvent evaporation and freeze-drying techniques, respectively, and the formulations were optimized. The optimized SMSD-TQM was evaluated in terms of particle size distribution, morphology, release characteristics, pharmacokinetic behavior, and nephroprotective effects in a rat model of acute kidney injury. SMSD-TQM significantly improved the dissolution characteristics (97.8%) of TQM in water within 60 min. Oral administration of SMSD-TQM in rats exhibited a 4.9-fold higher systemic exposure than crystalline TQM. In a cisplatin-induced (6 mg/kg, i.p.) acute kidney-damaged rat model, oral SMSD-TQM (10 mg/kg) improved the nephroprotective effects of TQM based on the results of kidney biomarkers and histological abnormalities. These findings suggest that SMSD-TQM might be efficacious in enhancing the nephroprotective effect of TQM by overcoming biopharmaceutical limitations.
Revolutionizing the Treatment of Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis: From Conventional Therapies to Advanced Drug Delivery Systems.[Pubmed:38589751]
AAPS PharmSciTech. 2024 Apr 8;25(4):78.
Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF) is a chronic and progressive interstitial lung disease that has been well-reported in the medical literature. Its incidence has risen, particularly in light of the recent COVID-19 pandemic. Conventionally, IPF is treated with antifibrotic drugs-pirfenidone and nintedanib-along with other drugs for symptomatic treatments, including corticosteroids, immunosuppressants, and bronchodilators based on individual requirements. Several drugs and biologicals such as fluorofenidone, Thymoquinone, amikacin, paclitaxel nifuroxazide, STAT3, and siRNA have recently been evaluated for IPF treatment that reduces collagen formation and cell proliferation in the lung. There has been a great deal of research into various treatment options for pulmonary fibrosis using advanced delivery systems such as liposomal-based nanocarriers, chitosan nanoparticles, PLGA nanoparticles, solid lipid nanocarriers, and other nanoformulations such as metal nanoparticles, nanocrystals, cubosomes, magnetic nanospheres, and polymeric micelles. Several clinical trials are also ongoing for advanced IPF treatments. This article elaborates on the pathophysiology of IPF, its risk factors, and different advanced drug delivery systems for treating IPF. Although extensive preclinical data is available for these delivery systems, the clinical performance and scale-up studies would decide their commercial translation.
Epigenetic Impact of Curcumin and Thymoquinone on Cancer Therapeutics.[Pubmed:38584537]
Curr Med Chem. 2024 Apr 4.
Today, one of the most prevalent reasons for death among people is carcinoma. Because it is still on the increase throughout the world, there is a critical need for in- -depth research on the pathogenic mechanisms behind the disease as well as for efficient treatment. In the field of epigenetics, gene expression alterations that are inherited but not DNA sequence changes are investigated. Three key epigenetic changes, histone modifications, DNA methylation and non-coding RNA (ncRNA) expression, are principally responsible for the initiation and progression of different tumors. These changes are interconnected and constitute many epigenetic changes. A form of polyphenolic chemical obtained from plants called curcumin has great bioactivity against several diseases, specifically cancer. A naturally occurring substance called Thymoquinone is well-known for its anticancer properties. Thymoquinone affects cancer cells through a variety of methods, according to preclinical studies. We retrieved information from popular databases, including PubMed, Google Scholar, and CNKI, to summarize current advancements in the efficiency of curcumin against cancer and its epigenetic regulation in terms of DNA methylation, histone modifications, and miRNA expression. The present investigation offers thorough insights into the molecular processes, based on epigenetic control, that underlie the clinical use of curcumin and Thymoquinone in cancerous cells.
Thymoquinone effects on autophagy, apoptosis, and oxidative stress in cisplatin-induced testicular damage in mice.[Pubmed:38568464]
J Assist Reprod Genet. 2024 Apr 3.
PURPOSE: In this study, the effect of Thymoquinone (TQ) on CP-induced spermatogenesis defects in mice has been investigated. METHODS: Sperm parameters, serum testosterone concentration, histology, Bax/Bcl-2 ratio, and expression of autophagy-related biomarkers have been assessed. Total antioxidant capacity (TAC), total oxidant status (TOS), and oxidative stress index (OSI) in testicular tissue were examined for the evaluation of oxidative stress levels. RESULTS: CP has induced histological changes and significantly increased the Bax/Bcl-2 ratio, decreased testosterone concentration, testicular weight, and sperm quality. CP induced oxidative stress by elevating OSI in the testicular tissue (p < 0.05). Expression of the autophagy-inducer genes (ATG7, ATG5, and Beclin-1) and ratio of LC3B/LC3A proteins were significantly decreased, while mTOR expression was increased in the CP group. TQ pretreatment dose-dependently decreased the Bax/Bcl-2 ratio and mTOR gene expression while increasing the expression of ATG5 and ATG7 genes, LC3B/LC3A ratio, and Beclin-1 proteins. TQ could also dose-dependently reverse the histology, testosterone level, and sperm quality of the CP-intoxicated mice. CONCLUSIONS: These findings show that TQ pretreatment can enhance sperm production by inducing autophagy and reducing apoptosis and oxidative stress in the CP-intoxicated mouse testicles.
Identification, validation and quantification of thymoquinone in conjunction with assessment of bioactive possessions and GC-MS profiling of pharmaceutically valuable crop Nigella (Nigella sativa L.) varieties.[Pubmed:38563005]
PeerJ. 2024 Mar 29;12:e17177.
BACKGROUND: Plants have been pivotal in traditional and modern medicine globally, with historical evidence supporting their therapeutic applications. Nigella (Nigella sativa L.) is an annual herbaceous plant of the Ranunculaceae family and is cultivated in the Middle East, Eastern Europe, and Western and Central Asia. The medicinal use of plants dates back thousands of years, documented in ancient writings from various civilizations. Alkaloids, phenolics, saponins, flavonoids, terpenoids, anthraquinones, and tannins found in plants exhibit antioxidant, immunomodulatory, anti-inflammatory, anticancer, antibacterial, and antidiabetic activities. METHODOLOGY: This study specifically examines the pharmacological potential of Nigella sativa L., emphasizing Thymoquinone-a compound with diverse nutraceutical benefits. The extraction, characterization, and quantification of Thymoquinone, alongside other physicochemical parameters, were carried out using ethanol through Soxhlet extraction procedures on five nigella varieties. HPLC analysis was performed to determine the maximum accumulation of Thymoquinone in the released variety of the plant and the chemical composition of the seed oil isolated from Nigella sativa L., varieties utilized in the study was determined through GC-MS analysis. RESULTS: The research revealed that the Ajmer nigella-20 variety stands out, exhibiting elevated levels of Thymoquinone (0.20 +/- 0.07%), antioxidants (76.18 +/- 1.78%), and substantial quantities of total phenols (31.85 +/- 0.97 mg GAEg(-1) seed) and flavonoids (8.150 +/- 0.360 mg QE 100 g(-1) seed) compared to other varieties. The GC-MS profiling showed the presence of 11 major compounds in the studied varieties, with p-cymene, longifolene, and myristic acid identified as the major chemical compounds present in the oil. CONCLUSION: The observed variations among Nigella varieties indicate the Ajmer nigella-20 variety as particularly promising for Thymoquinone and bioactive compound extraction. This study underscores Nigella's potential as a source of pharmacologically active compounds, highlighting the need for further exploration in therapeutic applications.
Use of Ozone Therapy and Thymoquinone in the Prevention of Formaldehyde Toxicity by Inhalation: An Experimental Study.[Pubmed:38544644]
Cureus. 2024 Feb 26;16(2):e54914.
INTRODUCTION: The study determined the damage caused by formaldehyde (FA) exposure in blood and liver samples using biochemical markers. Histopathological analysis was performed using the terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase dUTP nick end labeling (TUNEL) method and measurement of CD68 cell density. To what extent the antioxidant molecules Thymoquinone (TQ) and ozone (O(3)) reversed the damage caused by FA exposure was investigated, both when used alone and combined. METHODS: Fifty-six Sprague-Dawley male rats of eight to ten weeks of age were used in the experiment. The rats were divided into eight groups, with seven rats in each group: the untreated control group, the group treated with TQ (10 mg/kg/day), the group treated with O(3) (150 mug/kg/day), the group treated with TQ+O(3), the group exposed to FA (10 ppm 8 h/day), the group receiving FA+TQ, the group receiving FA+O(3), and the group receiving FA+TQ+O(3). Serum aspartate transaminase (AST), alanine transaminase (ALT), total antioxidant (TAS, U/mL), and total oxidant (TOS, nmol/mL) levels were analyzed. TAS and TOS levels, CD68 cell density, and apoptotic cells were determined in liver tissues. RESULTS: FA exposure caused an increase in serum AST and ALT levels of (p<0.05) experimental animals, a decrease in TAS levels in serum (p=0.03) and liver (p>0.05) and an increase in TOS levels (p>0.05), TUNEL positivity (p<0.001), and CD68 cell density (p=0.004). Administration of TQ and O(3) as antioxidants significantly reversed biochemical and histopathological alterations in the serum and liver. CONCLUSION: TQ and ozone therapy suppressed oxidative stress caused by FA exposure and reversed the emerging histopathological deteriorations. Ozone therapy did not suppress the effects of TQ. Therefore, ozone therapy can be given as a supportive therapy along with the main therapeutic agents. We think TQ and ozone therapy may be useful to protect individuals exposed to FA.


