Astragalus membranaceus
Astragalus membranaceus
1. The products in our compound library are selected from thousands of unique natural products; 2. It has the characteristics of diverse structure, diverse sources and wide coverage of activities; 3. Provide information on the activity of products from major journals, patents and research reports around the world, providing theoretical direction and research basis for further research and screening; 4. Free combination according to the type, source, target and disease of natural product; 5. The compound powder is placed in a covered tube and then discharged into a 10 x 10 cryostat; 6. Transport in ice pack or dry ice pack. Please store it at -20 °C as soon as possible after receiving the product, and use it as soon as possible after opening.

Natural products/compounds from Astragalus membranaceus
- Cat.No. Product Name CAS Number COA
-
BCN8240
Odoriflavene101153-41-7
Instructions
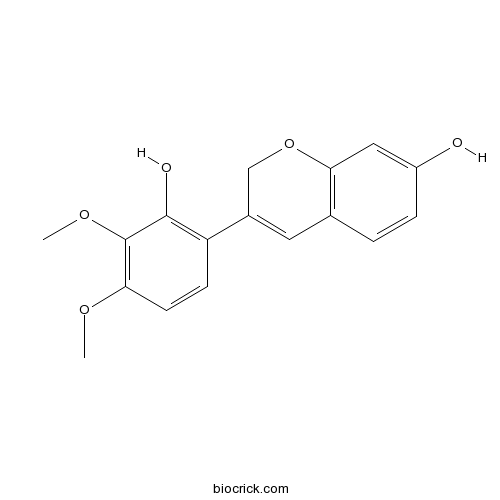
-
BCN8213
Complanatoside116183-66-5
Instructions
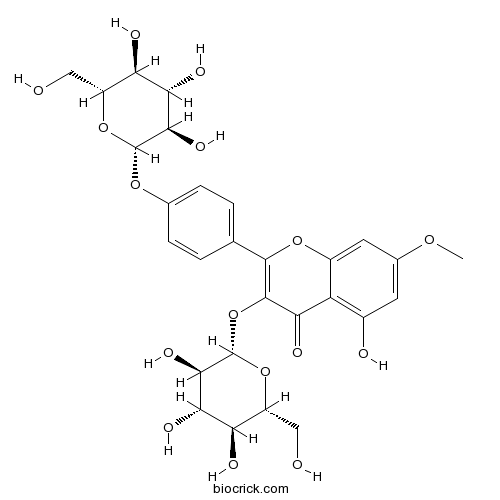
-
BCN6049
Quercetin117-39-5
Instructions
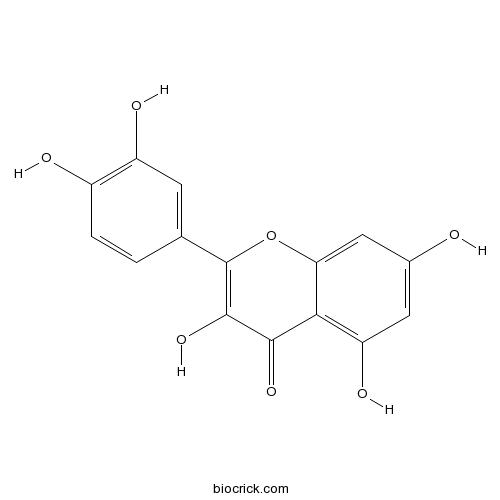
-
BCN8541
DL-Arabinose147-81-9
Instructions
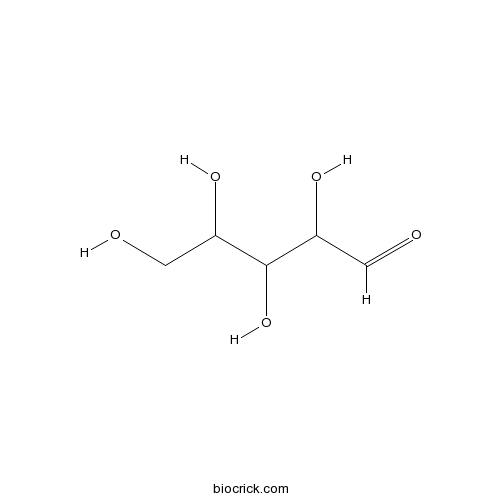
-
BCN8239
Colutehydroquinone181311-16-0
Instructions
-
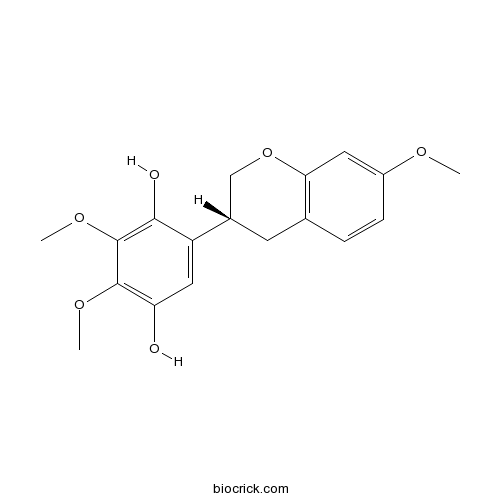
BCN5930
Calycosin20575-57-9
Instructions

-
BCN6277
Echinatin34221-41-5
Instructions
-
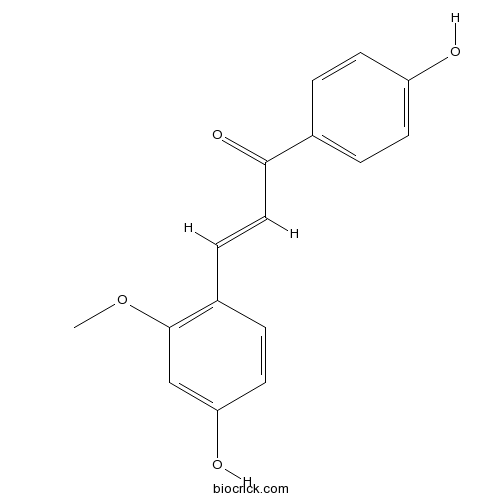
BCN5318
3'-O-Methylorobol36190-95-1
Instructions

-
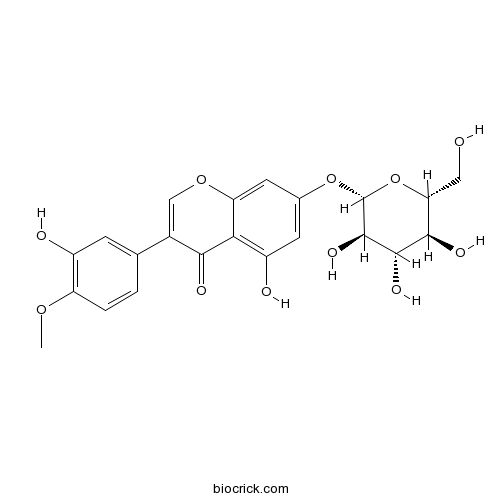
BCN8613
Pratensein 7-O-glucopyranoside36191-03-4
Instructions
-
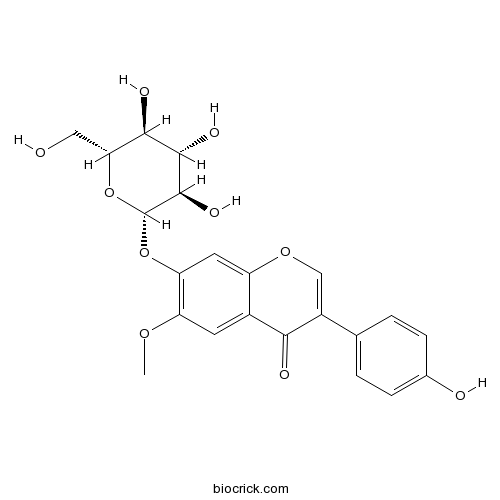
BCN5895
Glycitin40246-10-4
Instructions
-
BCN5896
Glycitein40957-83-3
Instructions
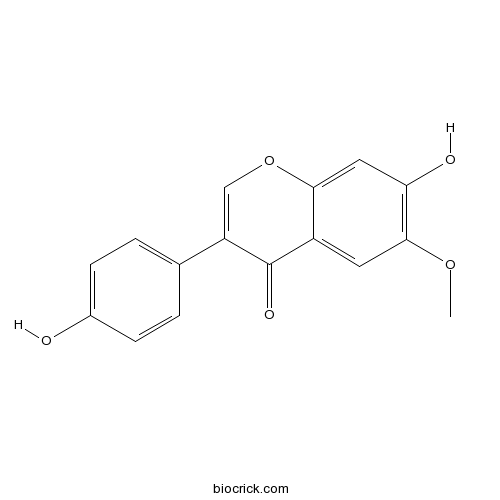
-
BCN5551
Isorhamnetin480-19-3
Instructions

-
BCN1061
Formononetin485-72-3
Instructions

-
BCN5926
Ononin486-62-4
Instructions

-
BCN5590
Daidzein486-66-8
Instructions

-
BCN1259
D-(+)-Glucose50-99-7
Instructions
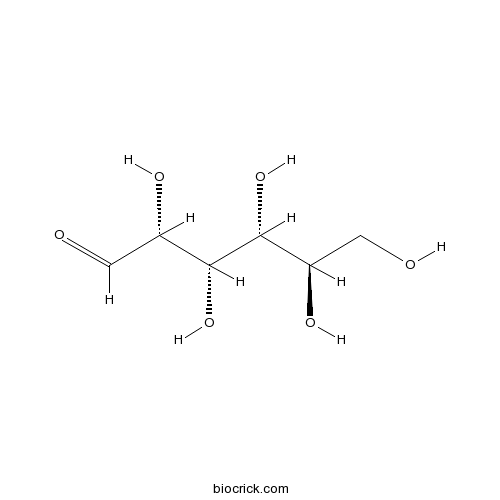
-
BCN2598
Soyasaponin Bb51330-27-9
Instructions

-
BCN5653
Kaempferol520-18-3
Instructions
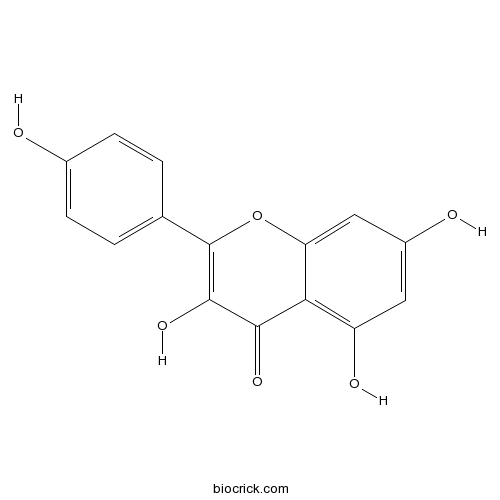
-
BCN5944
Liquiritin551-15-5
Instructions

-
BCN5946
Liquiritigenin578-86-9
Instructions

-
BCN6333
Licochalcone B58749-23-8
Instructions

-
BCN9085
(3r)-7,2'-Dihydroxy-3',4'-dimethoxyisoflavan64474-51-7
Instructions

-
BCN8248
Pendulone69359-09-7
Instructions

-
BCN8483
Cycloastragenol78574-94-4
Instructions
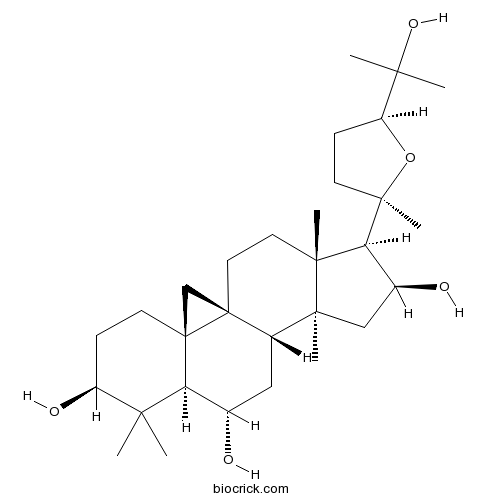
-
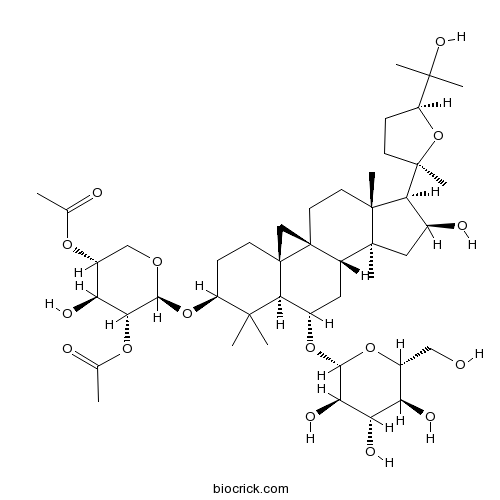
BCN2979
Isoastragaloside I84676-88-0
Instructions
-
BCN5962
Astragaloside II84676-89-1
Instructions

-
BCN5961
Astragaloside I84680-75-1
Instructions

-
BCN5963
Astragaloside III84687-42-3
Instructions
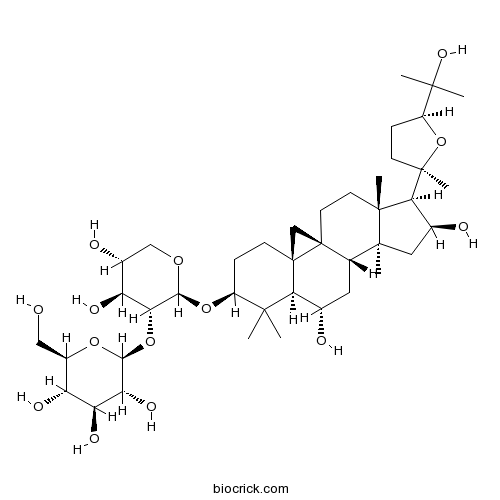
-
BCN5960
Astragaloside IV84687-43-4
Instructions
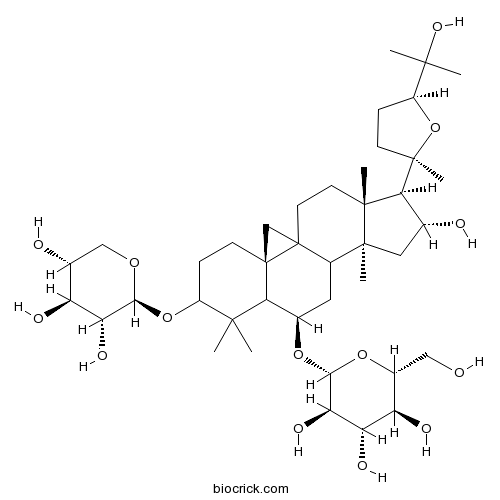
-
BCN2788
Astrasieversianin VII86764-11-6
Instructions
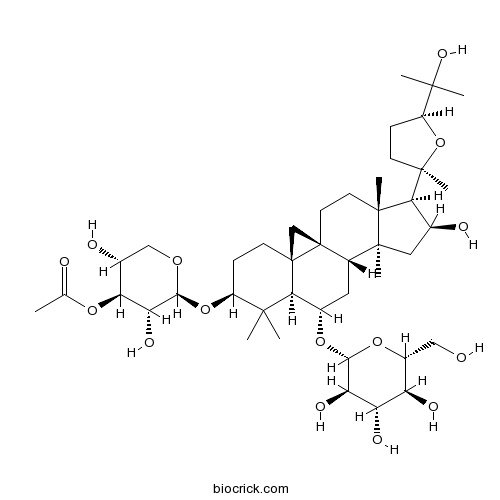
-
BCN4512
Isoliquiritigenin961-29-5
Instructions
Effects of Astragalus membranaceus fiber on growth performance, nutrient digestibility, microbial composition, VFA production, gut pH, and immunity of weaned pigs.[Pubmed: 30117299]
Astragalus membranaceus is an herbaceous perennial plant, growing to about 2 feet tall, with sprawling stems and alternate leaves about 12-24 leaflets. In total, 24 cross bred (Duroc × Landrace × Yorkshire) piglets weaned at 4 weeks with an average body weight of 10.84 ± 1.86 kg, were divided into four groups and randomly assigned to dietary treatments containing different AMSLF levels (0.00%, 2.50%, 5.00%, and 7.50%). The piglets in the control group (0.00% AMSLF) were fed basal diet and other treatment groups were fed basal diet in addition to 2.50%, 5.00%, and 7.50% pulverized AMSLF. The results indicated that supplementation with AMSLF significantly (p < 0.05) decreased diarrheal incidence in piglets. There was significant difference between treatment in terms of ADFI, ADG and FCR. Both 5.00% and 7.50% treatments significantly increased growth performance. The digestibility of gross energy and dry matter increased (p > 0.05) with increasing AMSLF level. The level of blood IL-2 and TNF-α were significantly affected by AMSLF supplementation with 7.50% AMSLF group having higher (p < 0.05) IL-2 and TNF-α levels than the other treatment groups. The 16SrDNA sequencing results from the four treatments showed that the potentially active bacterial microbial population and diversity in pig cecum were dominated by the phyla Bacteriodetes and Firmicutes regardless of the AMSLF supplementation. The Shannon diversity, PD whole tree diversity indices and Chao analyses exhibited significant variability in species richness across the treatments. The principal coordinates analysis (PCoA) showed significant (p < 0.1) differences between bacterial communities in all treatment groups. Results from the current study suggested that AMSLF supplementation increased composition of bacterial microbiota in pig gut. In conclusion, dietary supplements with AMSLF could potentially be used to prevent diarrheal incidence and improved pig production.
[Complex network analysis of law on Chinese herbal drugs intervention on radiation induced lung injury].[Pubmed: 30111064]
To mainly analyze the prescription rules of Chinese herbal drugs for radiation induced lung injury, optimize the prescriptions, and provide a reference for the clinical treatment of radiation induced lung injury. The major Chinese databases CNKI, CBM and Wanfang data were searched to obtain the literature on Chinese herbal drugs for radiation induced lung injury. BICOMS 2 software was used to extract and collect all Chinese herbal drugs information and generate the co-occurrence matrix; NetDraw and Gcluto software were then used to make network map and visualization matrix for analysis. A total of 552 articles (19 types and 304 Chinese herbal drugs) were included. Ophiopogon japonicus had the highest frequency (229 times), followed by Astragalus membranaceus(181 times), Glycyrrhiza uralensis (166 times), and Scutellaria baicalensis (150 times). After the classification of efficacy, deficiency-supplementing medicinal (69 kinds of Chinese herbs), heat-clearing medicine (51 kinds of Chinese herbs) and phlegm cough medicine (42 kinds of Chinese herbs) accounted for 53.29% of all the Chinese herbs, acting in the main position. After the prescription analysis for the top 25 herbal prescriptions, six main structures of common prescriptions were found for the treatment of radiation induced lung injury. There are many kinds of Chinese herbal drugs for the treatment of radiation induced lung injury in clinical application. In the future, researchers can mainly focus on Ophiopogon japonicus etc. as the main drugs, combine with other high-frequency Chinese herbal drugs found in this study, or directly refer to the main structures of commonly used prescriptions found in this analysis.
[Establishment of fingerprint of Astragali Radix polysaccharides based on endo-1,4-β-mannanase hydrolysis and identification of Astragali Radix of different germplasm resources].[Pubmed: 30111056]
The polysaccharides of different germplasm resources of Astragalus membranaceus var. mongholicus〓(cultured Astragalus Radix (RA) and natural RA) and A. membranaceus (MJ) (cultured RA and natural RA) were studied by using the optimal enzymatic conditions of endo-1,4-β-mannanase. Saccharide fingerprints were obtained for the identification and evaluation of the germplasm resources of RA by Fluorophore-assisted Carbohydrate Electrophoresis (FACE). The data were analyzed by principal component analysis to obtain the difference between RA of different germplasm resources. The results showed that trisaccharide, tetrasaccharide and pentasaccharide of endo-1,4-β-mannanase hydrolyzate could be used as the differential fragments to distinguish MG (cultured RA and natural RA); the pentasaccharide and hexasaccharide can be used as differentially expressed carbohydrate fragments that distinguish MJ (cultured RA and natural RA); the trisaccharide and tetrasaccharide can be used as the differential fragments to distinguish the cultured MG and cultured MJ. Studies have shown that polysaccharide products degraded by endo-1,4-β-mannanase can well distinguish RA species (MG and MJ), growth mode (cultured RA and natural RA). This study laid the foundation for the quality evaluation of Astragalus medicinal herbs and screening of active oligosaccharides.
Assessment of the physicochemical properties and bacterial composition of Lactobacillus plantarum and Enterococcus faecium-fermented Astragalus membranaceus using single molecule, real-time sequencing technology.[Pubmed: 30089930]
We investigated if fermentation with probiotic cultures could improve the production of health-promoting biological compounds in Astragalus membranaceus. We tested the probiotics Enterococcus faecium, Lactobacillus plantarum and Enterococcus faecium + Lactobacillus plantarum and applied PacBio single molecule, real-time sequencing technology (SMRT) to evaluate the quality of Astragalus fermentation. We found that the production rates of acetic acid, methylacetic acid, aethyl acetic acid and lactic acid using E. faecium + L. plantarum were 1866.24 mg/kg on day 15, 203.80 mg/kg on day 30, 996.04 mg/kg on day 15, and 3081.99 mg/kg on day 20, respectively. Other production rates were: polysaccharides, 9.43%, 8.51%, and 7.59% on day 10; saponins, 19.6912 mg/g, 21.6630 mg/g and 20.2084 mg/g on day 15; and flavonoids, 1.9032 mg/g, 2.0835 mg/g, and 1.7086 mg/g on day 20 using E. faecium, L. plantarum and E. faecium + L. plantarum, respectively. SMRT was used to analyze microbial composition, and we found that E. faecium and L. plantarum were the most prevalent species after fermentation for 3 days. E. faecium + L. plantarum gave more positive effects than single strains in the Astragalus solid state fermentation process. Our data demonstrated that the SMRT sequencing platform is applicable to quality assessment of Astragalus fermentation.
Astragaloside IV improves vascular endothelial dysfunction by inhibiting the TLR4/NF-κB signaling pathway.[Pubmed: 30081006]
Astragaloside IV (As-IV) is the major active ingredient of Astragalus membranaceus and has diverse pharmacological activities, including anti-inflammatory and antioxidant effects. However, the beneficial effect of As-IV on protecting vascular endothelial dysfunction is not completely understood. The aim of this study was to investigate the protective effect and mechanism of As-IV on vascular endothelial dysfunction.
Astragalus membranaceus (Fisch.) Bunge repairs intestinal mucosal injury induced by LPS in mice.[Pubmed: 30075775]
Astragalus membranaceus (Fisch.) Bunge is one of the most widely used traditional Chinese herbal medicines. It is used as immune stimulant, tonic, antioxidant, hepatoprotectant, diuretic, antidiabetic, anticancer, and expectorant. The purpose of the study was to investigate the curative effects of the decoction obtained from Astragalus membranaceus root in intestinal mucosal injury induced by LPS in mice. An LPS-induced intestinal mucosal injury mice model was applied in the study.


