Notopterygium incisum
Notopterygium incisum
1. The products in our compound library are selected from thousands of unique natural products; 2. It has the characteristics of diverse structure, diverse sources and wide coverage of activities; 3. Provide information on the activity of products from major journals, patents and research reports around the world, providing theoretical direction and research basis for further research and screening; 4. Free combination according to the type, source, target and disease of natural product; 5. The compound powder is placed in a covered tube and then discharged into a 10 x 10 cryostat; 6. Transport in ice pack or dry ice pack. Please store it at -20 °C as soon as possible after receiving the product, and use it as soon as possible after opening.
Natural products/compounds from Notopterygium incisum
- Cat.No. Product Name CAS Number COA
-
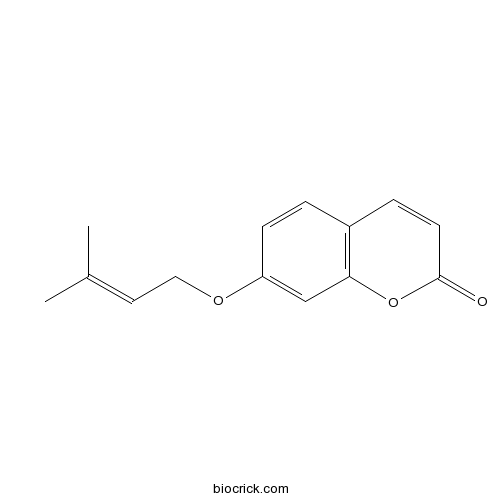
BCN2938
7-Prenylumbelliferone10387-50-5
Instructions
-
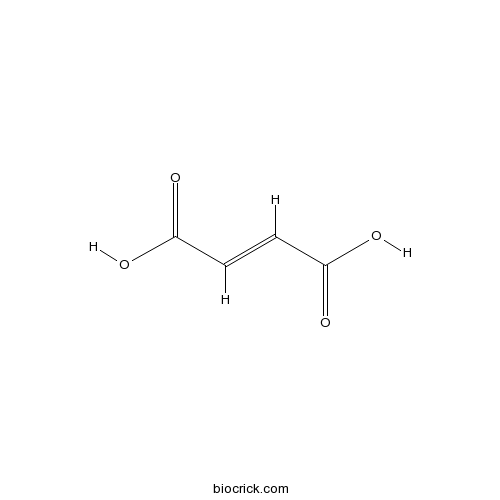
BCN5989
Fumaric acid110-17-8
Instructions
-
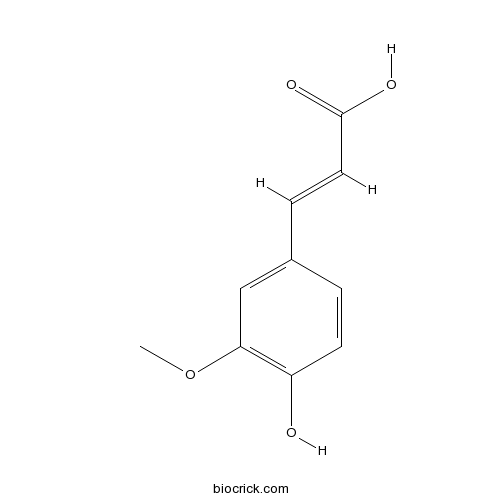
BCN5948
Ferulic acid1135-24-6
Instructions
-
BCN6168
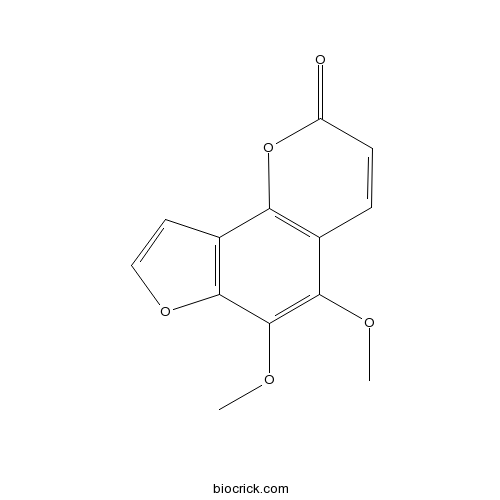
Pimpinellin131-12-4
Instructions
-
BCN8288
S-(+)-Marmesin13849-08-6
Instructions

-
BCN6255
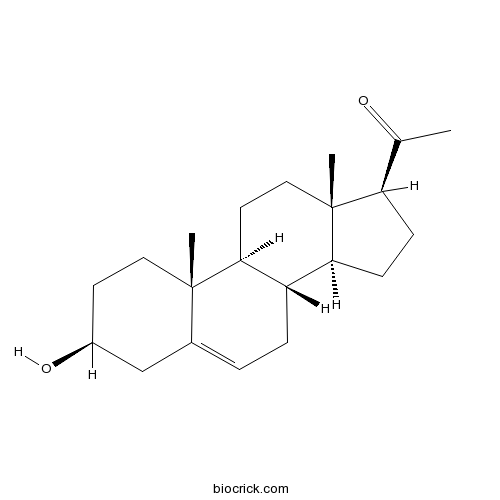
Pregnenolone145-13-1
Instructions
-
BCN3857
(-)-beta-Pinene18172-67-3
Instructions

-
BCN5065
Falcarindiol225110-25-8
Instructions

-
BCN5906
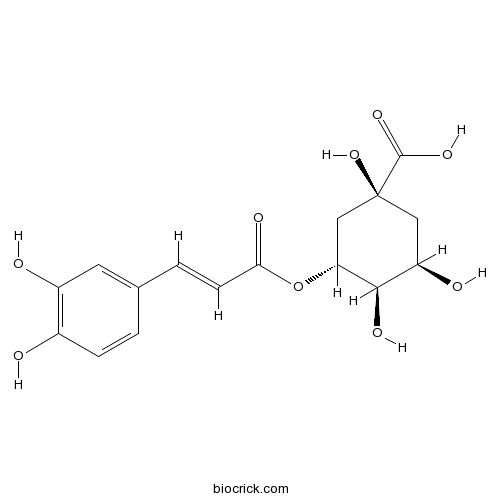
Chlorogenic acid327-97-9
Instructions
-
BCN9028
Byakangelicin482-25-7
Instructions

-
BCN5568
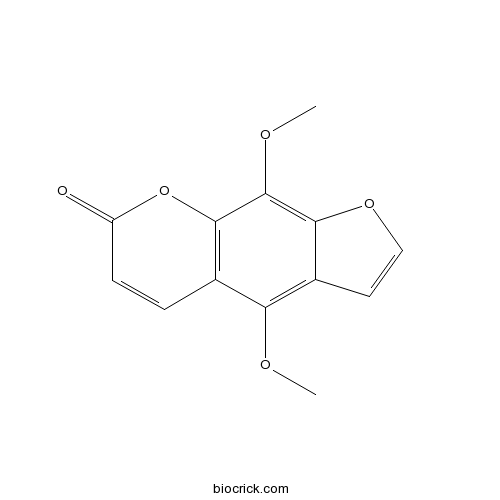
Isopimpinellin482-27-9
Instructions
-
BCN5897
Isoimperatorin482-45-1
Instructions
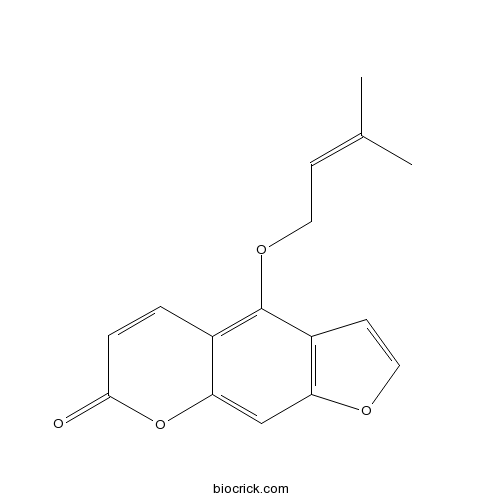
-
BCN2377
Isobergapten482-48-4
Instructions
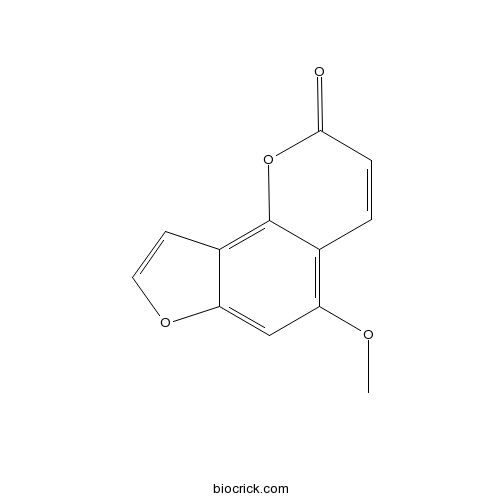
-
BCN5582
Bergapten484-20-8
Instructions
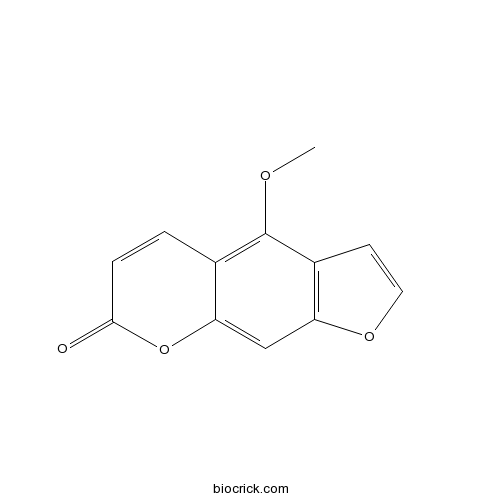
-
BCN5588
Bergaptol486-60-2
Instructions
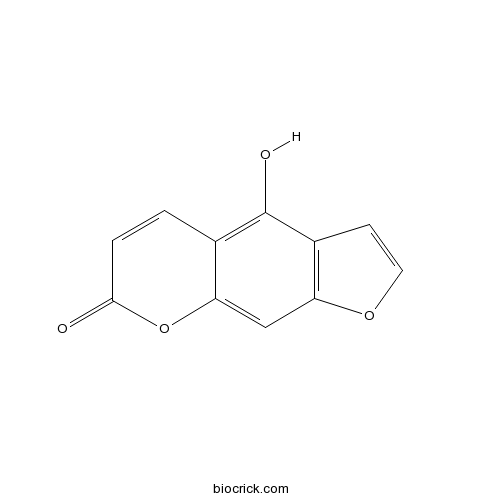
-
BCN2378
Nodakenin495-31-8
Instructions
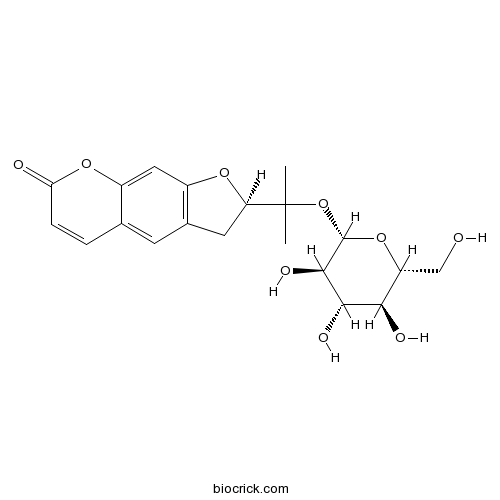
-
BCN5669
Angelicin523-50-2
Instructions
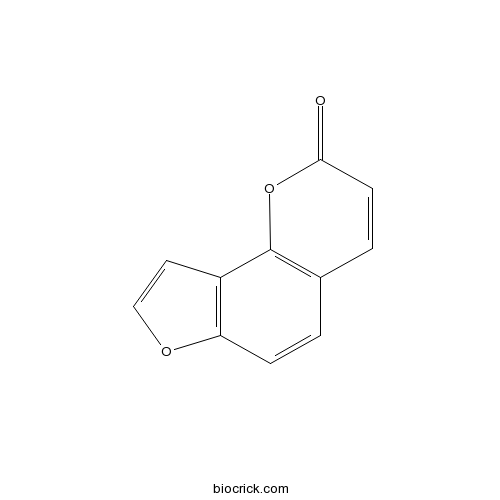
-
BCN1206
Palmitic acid57-10-3
Instructions

-
BCN4187
Shanzhiside methylester64421-28-9
Instructions
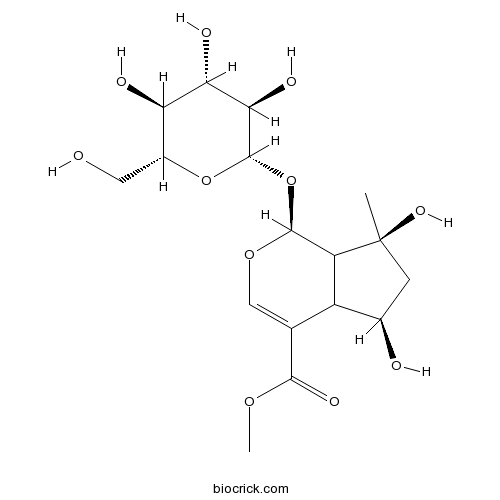
-
BCN2733
Bergamotine7380-40-7
Instructions

-
BCN4423
Smyrindioloside87592-77-6
Instructions
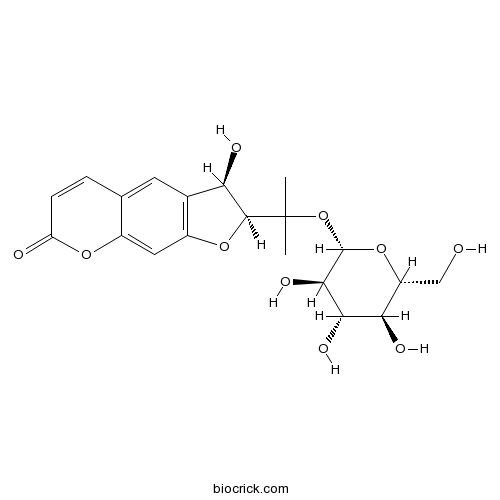
-
BCN6896
p-Hydroxyphenethyl anisate87932-34-1
Instructions

-
BCN5386
Notopterol88206-46-6
Instructions

Molecular mechanism of seed dormancy release induced by fluridone compared with cod stratification in Notopterygium incisum.[Pubmed: 29890940]
Notopterygium incisum is an important Chinese medicinal plant. Its mature seeds have underdeveloped embryos and are physiological dormant. We found the seeds with full developed embryos can germinate after treated by fluridone (FL), an inhibitor of abscisic acid (ABA). In order to understand the molecular mechanisms underlying seed dormancy release by FL, we compared the transcriptomic changes in dormancy release induced by two different methods, FL and cold stratification (CS) in N. incisum. We further analyzed the gene expression patterns involved in seed germination and dormancy using quantitative reverse-transcription PCR.
[Ecological suitability assessment for Notopterygium plants transplanting along altitudinal gradients].[Pubmed: 29098817]
A comprehensive field research had been focused on growing status, underground biomass and active constituents of Notopterygium incisum and N. franchetii to evaluate the ecological suitability and appropriate cultivation zones by growing the two species seedlings along different elevation gradient. The results showed that compared to the survival rate and underground biomass, the beneficial altitude region to N. incisum was ranged from 2 600 m to 4 100 m, while N. franchetii required a lower altitude which ranges from 1 700 m to 3 600 m. For the active constituent contents, the values were higher in the range of 2 600 to 3 600 m for N. incisum, but for N. franchetii, the range was form 1 700 to 3 600 m. This result provides instructional guidance and scientific basis for artificial cultivation of N. incisum and N. franchetii.
[Dynamics of plant biomass and nutrients accumulation of Notopterygium incisum in artificial cultivation].[Pubmed: 29098816]
In this study,field cultivation experiments of Notopterygium incisum had been carried out for three years, and samples had been collected monthly during growth seasons, and biomass and nutrient elements of aerial and underground part of sampled plants had been determined to assess their seasonal and interannual dynamics respectively. The results showed that biomass of underground part (dry weight) increased mainly in the second year after seedling transplanting, i.e., biomass increased about 32 times in the second year whilst less than 6 times and 2 times in the first year and in the third year, respectively. Therefore, efforts for yield improvement should be focused on the first two year in artificial cultivation of N. incisum. Accumulation of nutrient elements increased steady in the underground part during the first and second year, then showed a sharp decline in the first phase of growth season in the third year, while its accumulation in July to August of third year was higher than the value of second year. Ca, Fe, B and Zn were larger demand nutrient elements to meet growth demands whether for the underground part or aerial part during the second year and third year for N. incisum cultivation. This result provided instructional guidance and scientific basis for artificial cultivation and specific fertilizer of N. incisum.
[Cultural regionalization for Notopterygium incisum based on 3S technology platform Ⅲ. Functional regionalization for cultivation based on suitability evaluation of growth and production quality].[Pubmed: 29098815]
Based on the research results of suitability evaluation of growth and production quality, a functional production cultivation regionalization with high feasibility and operability to solve the problem of the separation of high quality and high yield were formatted for protection, wild monitoring, and cultivation of this plant by weighted sum of spatial suitability data of ecology and quality, as well as integrated with land use and cover data. The results of the study revealed that good quality and high yield area were mainly distributed in the original production areas in Sichuan province and where could carry out monitoring and commercialization cultivation. This method is expected to overcome shortage of traditional regionalization methods difficult to distinguish the contribution of ecological factors and quality factors, which provide an innovative theory and methodology for regionalization, and is helpful to practical application of wild resource protection, nature research, monitoring, and commercialization cultivation for Chinese material medica.
[Cultural regionalization for Notopterygium incisum based on 3S technology platform Ⅱ. Evaluation for quality suitability for N. incisum based on collocated Cokriging].[Pubmed: 29098814]
Quality characteristics based on active substance are focused for in the cultivation of traditional Chinese medicine(TCM) plants due to their economic values. However, ecological and quality suitability are not always a coincidence, which makes traditional cultural regionalization for TCM cultivation based on ecological suitability have great limitations in practical applications. A regionalization method integrated GIS and medicinal plants quality have been analyzed by using field quality data of Notopterygii Rhizoma et Radix as a case study. Spatial interpolation based on medicine quality by Cokriging method is reasonable, and the predicted values of interpolation are correlated with measured values significantly, which shows that cultural regionalization for TCM cultivation based on spatial quality suitability is possible theoretically. The results indicate that the most suitable areas for quality suitability were mainly distributed in Sichuan province (29.42%), while the spatial distribution of quality suitability and ecological suitability was not coincidence. The cultivation regionalization of TCM plants based on quality suitability is helpful to high quality and quantity cultivation of those TCM plants which spatial distribution of geoherbalism and ecological suitability is separated.
[Industrialization condition and development strategy of Notopterygii Rhizoma et Radix].[Pubmed: 29098813]
Notopterygii Rhizoma et Radix, the underground part of Notopterygium incisum and N. franchetii, is used as a classical traditional Chinese medicine, and as raw materials for 262 Chinese patent drugs production in 694 pharmaceutical factories currently. It plays an important role in the whole Chinese medicine industry with irreplaceable important economic and social values. However, wild resource of was abruptly depleted, and large-scale artificial cultivation has been inapplicable. In this study, Utilization history and the industrialization status of Notopterygii Rhizoma et Radix were summarized. Resource distribution, ecological suitability of Notopterygii Rhizoma et Radix and core technologies for seeds production, seedling breeding, large-scale cultivation has been reported by current studies, and basic conditions are already available for industrialization production of Notopterygii Rhizoma et Radix. However, there still some key technical problems need to be solved in the further research, and some policy dimensions need to be focused on in the coming industrialization cultivation of Notopterygii Rhizoma et Radix.
Comparative Transcriptome Analysis Reveals Adaptive Evolution of Notopterygium incisum and Notopterygium franchetii, Two High-Alpine Herbal Species Endemic to China.[Pubmed: 28696392]
None


