dl-AloesolCAS# 104871-04-7 |
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 104871-04-7 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 5318230 | Appearance | Powder |
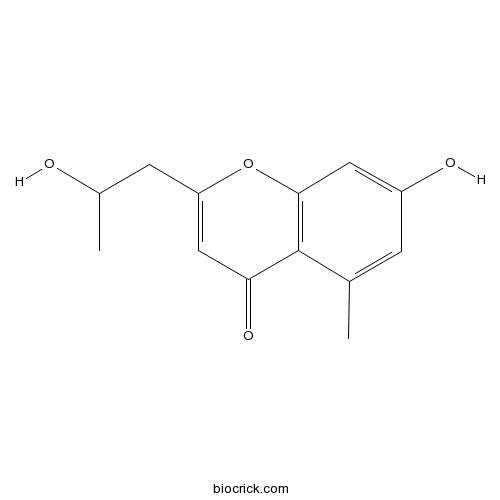
| Formula | C13H14O4 | M.Wt | 234.25 |
| Type of Compound | Phenols | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | Soluble in Chloroform,Dichloromethane,Ethyl Acetate,DMSO,Acetone,etc. | ||
| Chemical Name | 7-hydroxy-2-(2-hydroxypropyl)-5-methylchromen-4-one | ||
| SMILES | CC1=CC(=CC2=C1C(=O)C=C(O2)CC(C)O)O | ||
| Standard InChIKey | ZYCNQWOKCMJKEZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C13H14O4/c1-7-3-9(15)5-12-13(7)11(16)6-10(17-12)4-8(2)14/h3,5-6,8,14-15H,4H2,1-2H3 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | dl-Aloesol is a natural product from the secondary metabolites of endophytic fungus HCCB06030. |
| Structure Identification | Chem Pharm Bull (Tokyo). 1991 Mar;39(3):704-8.Metabolism of aloesin and related compounds by human intestinal bacteria: a bacterial cleavage of the C-glucosyl bond and the subsequent reduction of the acetonyl side chain.[Pubmed: 2070451]
|

dl-Aloesol Dilution Calculator

dl-Aloesol Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 4.2689 mL | 21.3447 mL | 42.6894 mL | 85.3789 mL | 106.7236 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.8538 mL | 4.2689 mL | 8.5379 mL | 17.0758 mL | 21.3447 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.4269 mL | 2.1345 mL | 4.2689 mL | 8.5379 mL | 10.6724 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0854 mL | 0.4269 mL | 0.8538 mL | 1.7076 mL | 2.1345 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0427 mL | 0.2134 mL | 0.4269 mL | 0.8538 mL | 1.0672 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
- (+)-Isopulegol
Catalog No.:BCN4975
CAS No.:104870-56-6
- NF 023
Catalog No.:BCC6985
CAS No.:104869-31-0
- NF 157
Catalog No.:BCC7367
CAS No.:104869-26-3
- UPF 1069
Catalog No.:BCC2213
CAS No.:1048371-03-4
- Germanicol acetate
Catalog No.:BCN7264
CAS No.:10483-91-7
- Alpha-Terpineol
Catalog No.:BCN8136
CAS No.:10482-56-1
- COR 170
Catalog No.:BCC6282
CAS No.:1048039-15-1
- Masitinib mesylate
Catalog No.:BCC1729
CAS No.:1048007-93-7
- MRS 2768 tetrasodium salt
Catalog No.:BCC7800
CAS No.:1047980-83-5
- 4-O-Methylsappanol
Catalog No.:BCN5863
CAS No.:104778-16-7
- Sappanone B
Catalog No.:BCN7942
CAS No.:104778-15-6
- Plantamajoside
Catalog No.:BCN6279
CAS No.:104777-68-6
- Borapetoside B
Catalog No.:BCN6593
CAS No.:104901-05-5
- Tranilast Sodium
Catalog No.:BCC4091
CAS No.:104931-56-8
- H-D-Val-OtBu.HCl
Catalog No.:BCC3146
CAS No.:104944-18-5
- Ethyl β-D-ribo-hex-3-ulopyranoside
Catalog No.:BCC8977
CAS No.:104953-08-4
- 8-Hydroxydigitoxigenin
Catalog No.:BCN5864
CAS No.:1049674-06-7
- Naspm trihydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC7476
CAS No.:1049731-36-3
- A 331440 dihydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC7963
CAS No.:1049740-32-0
- Cardiogenol C hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC7790
CAS No.:1049741-55-0
- PS 1145 dihydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC7949
CAS No.:1049743-58-9
- 3-Acetoxy-4,7(11)-cadinadien-8-one
Catalog No.:BCN5865
CAS No.:104975-02-2
- Tacrolimus (FK506)
Catalog No.:BCC4952
CAS No.:104987-11-3
- Ascomycin(FK 520)
Catalog No.:BCC1370
CAS No.:104987-12-4
Metabolism of aloesin and related compounds by human intestinal bacteria: a bacterial cleavage of the C-glucosyl bond and the subsequent reduction of the acetonyl side chain.[Pubmed:2070451]
Chem Pharm Bull (Tokyo). 1991 Mar;39(3):704-8.
By anaerobic incubation with a bacterial mixture from human feces, aloesin (aloeresin B; 1) was converted to 2-acetonyl-7-hydroxy-5-methylchromone (aloesone; 3) and dl-7-hydroxy-2-(2'-hydroxypropyl)-5-methylchromone (aloesol; 4a + 4b) through a cleavage of the C-glucosyl bond, followed by reduction of the acetonyl side chain. An analogous compound, aloeresin A (2), was converted to p-coumaric acid and aloesin (1), the latter being subsequently transformed to aloesone (3) and dl-Aloesol (4a + 4b). On the other hand, 7-O-methylated derivatives (7, 5a and 5b) of aloesin and of 8-C-glucosylaloesol were not cleaved to the corresponding aglycones, suggesting the importance of a free hydroxy group adjacent to the C-glucosyl group in the molecule for the bacterial cleavage of aloesin derivatives. This is the first report on the cleavage of the C-glycosyl bond of chromone C-glucosides by intestinal bacteria.


