NF 157Selective P2Y11/P2X1 antagonist CAS# 104869-26-3 |
- Tubastatin A HCl
Catalog No.:BCC3877
CAS No.:1310693-92-5
- Entinostat (MS-275,SNDX-275)
Catalog No.:BCC3595
CAS No.:209783-80-2
- M344
Catalog No.:BCC2162
CAS No.:251456-60-7
- Panobinostat (LBH589)
Catalog No.:BCC3601
CAS No.:404950-80-7
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 104869-26-3 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 71433548 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C49H28F2N6Na6O23S6 | M.Wt | 1437.08 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | Soluble to 50 mM in water | ||
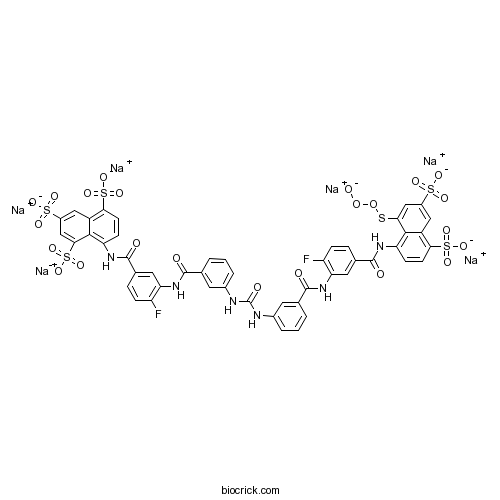
| Chemical Name | hexasodium;8-[[4-fluoro-3-[[3-[[3-[[2-fluoro-5-[(8-oxidoperoxysulfanyl-4,6-disulfonatonaphthalen-1-yl)carbamoyl]phenyl]carbamoyl]phenyl]carbamoylamino]benzoyl]amino]benzoyl]amino]naphthalene-1,3,5-trisulfonate | ||
| SMILES | C1=CC(=CC(=C1)NC(=O)NC2=CC=CC(=C2)C(=O)NC3=C(C=CC(=C3)C(=O)NC4=C5C(=CC(=CC5=C(C=C4)S(=O)(=O)[O-])S(=O)(=O)[O-])S(=O)(=O)[O-])F)C(=O)NC6=C(C=CC(=C6)C(=O)NC7=C8C(=CC(=CC8=C(C=C7)S(=O)(=O)[O-])S(=O)(=O)[O-])SOO[O-])F.[Na+].[Na+].[Na+].[Na+].[Na+].[Na+] | ||
| Standard InChIKey | QJFCMJZVZFAWGF-UHFFFAOYSA-H | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C49H34F2N6O23S6.6Na/c50-33-9-7-25(47(60)54-35-11-13-40(84(70,71)72)31-19-29(82(64,65)66)21-39(43(31)35)81-80-79-63)17-37(33)56-45(58)23-3-1-5-27(15-23)52-49(62)53-28-6-2-4-24(16-28)46(59)57-38-18-26(8-10-34(38)51)48(61)55-36-12-14-41(85(73,74)75)32-20-30(83(67,68)69)22-42(44(32)36)86(76,77)78;;;;;;/h1-22,63H,(H,54,60)(H,55,61)(H,56,58)(H,57,59)(H2,52,53,62)(H,64,65,66)(H,67,68,69)(H,70,71,72)(H,73,74,75)(H,76,77,78);;;;;;/q;6*+1/p-6 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Purinergic receptor antagonist that potently inhibits P2Y11 receptor activity (IC50 = 463 nM). Displays selectivity for P2Y11 and P2X1 receptors over P2Y1, P2Y2, P2X2, P2X3, P2X4 and P2X7 receptors. Inhibits NAD+-induced activation of human granulocytes. |

NF 157 Dilution Calculator

NF 157 Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 0.6959 mL | 3.4793 mL | 6.9586 mL | 13.9171 mL | 17.3964 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.1392 mL | 0.6959 mL | 1.3917 mL | 2.7834 mL | 3.4793 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.0696 mL | 0.3479 mL | 0.6959 mL | 1.3917 mL | 1.7396 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0139 mL | 0.0696 mL | 0.1392 mL | 0.2783 mL | 0.3479 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.007 mL | 0.0348 mL | 0.0696 mL | 0.1392 mL | 0.174 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
- UPF 1069
Catalog No.:BCC2213
CAS No.:1048371-03-4
- Germanicol acetate
Catalog No.:BCN7264
CAS No.:10483-91-7
- Alpha-Terpineol
Catalog No.:BCN8136
CAS No.:10482-56-1
- COR 170
Catalog No.:BCC6282
CAS No.:1048039-15-1
- Masitinib mesylate
Catalog No.:BCC1729
CAS No.:1048007-93-7
- MRS 2768 tetrasodium salt
Catalog No.:BCC7800
CAS No.:1047980-83-5
- 4-O-Methylsappanol
Catalog No.:BCN5863
CAS No.:104778-16-7
- Sappanone B
Catalog No.:BCN7942
CAS No.:104778-15-6
- Plantamajoside
Catalog No.:BCN6279
CAS No.:104777-68-6
- 3alpha-Akebonoic acid
Catalog No.:BCN5862
CAS No.:104777-61-9
- Entacapone sodium salt
Catalog No.:BCC4107
CAS No.:1047659-02-8
- Afuresertib
Catalog No.:BCC5502
CAS No.:1047644-62-1
- NF 023
Catalog No.:BCC6985
CAS No.:104869-31-0
- (+)-Isopulegol
Catalog No.:BCN4975
CAS No.:104870-56-6
- dl-Aloesol
Catalog No.:BCN7265
CAS No.:104871-04-7
- Borapetoside B
Catalog No.:BCN6593
CAS No.:104901-05-5
- Tranilast Sodium
Catalog No.:BCC4091
CAS No.:104931-56-8
- H-D-Val-OtBu.HCl
Catalog No.:BCC3146
CAS No.:104944-18-5
- Ethyl β-D-ribo-hex-3-ulopyranoside
Catalog No.:BCC8977
CAS No.:104953-08-4
- 8-Hydroxydigitoxigenin
Catalog No.:BCN5864
CAS No.:1049674-06-7
- Naspm trihydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC7476
CAS No.:1049731-36-3
- A 331440 dihydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC7963
CAS No.:1049740-32-0
- Cardiogenol C hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC7790
CAS No.:1049741-55-0
- PS 1145 dihydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC7949
CAS No.:1049743-58-9
Extracellular NAD+ is an agonist of the human P2Y11 purinergic receptor in human granulocytes.[Pubmed:16926152]
J Biol Chem. 2006 Oct 20;281(42):31419-29.
Micromolar concentrations of extracellular beta-NAD+ (NAD(e)+) activate human granulocytes (superoxide and NO generation and chemotaxis) by triggering: (i) overproduction of cAMP, (ii) activation of protein kinase A, (iii) stimulation of ADP-ribosyl cyclase and overproduction of cyclic ADP-ribose (cADPR), a universal Ca2+ mobilizer, and (iv) influx of extracellular Ca2+. Here we demonstrate that exposure of granulocytes to millimolar rather than to micromolar NAD(e)+ generates both inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate (IP3) and cAMP, with a two-step elevation of intracellular calcium levels ([Ca2+]i): a rapid, IP3-mediated Ca2+ release, followed by a sustained influx of extracellular Ca2+ mediated by cADPR. Suramin, an inhibitor of P2Y receptors, abrogated NAD(e)+-induced intracellular increases of IP3, cAMP, cADPR, and [Ca2+]i, suggesting a role for a P2Y receptor coupled to both phospholipase C and adenylyl cyclase. The P2Y(11) receptor is the only known member of the P2Y receptor subfamily coupled to both phospholipase C and adenylyl cyclase. Therefore, we performed experiments on hP2Y(11)-transfected 1321N1 astrocytoma cells: micromolar NAD(e)+ promoted a two-step elevation of the [Ca2+]i due to the enhanced intracellular production of IP3, cAMP, and cADPR in 1321N1-hP2Y(11) but not in untransfected 1321N1 cells. In human granulocytes NF157, a selective and potent inhibitor of P2Y(11), and the down-regulation of P2Y(11) expression by short interference RNA prevented NAD(e)+-induced intracellular increases of [Ca2+]i and chemotaxis. These results demonstrate that beta-NAD(e)+ is an agonist of the P2Y(11) purinoceptor and that P2Y(11) is the endogenous receptor in granulocytes mediating the sustained [Ca2+]i increase responsible for their functional activation.
Synthesis and structure-activity relationships of suramin-derived P2Y11 receptor antagonists with nanomolar potency.[Pubmed:16250663]
J Med Chem. 2005 Nov 3;48(22):7040-8.
Selective and potent P2Y(11) receptor antagonists have yet to be developed, thus impeding an evaluation of this G protein-coupled receptor mainly expressed on immune cells. Taking suramin with moderate inhibitory potency as a template, 18 ureas with variations of the methyl groups of suramin and their precursors were functionally tested at P2Y(11), P2Y(1), and P2Y(2) receptors. Fluorine substitution of the methyl groups of suramin led to the first nanomolar P2Y(11) antagonist (8f, NF157, pK(i): 7.35). For selectivity, 8f was also tested at various P2X receptors. 8f displayed selectivity for P2Y(11) over P2Y(1) (>650-fold), P2Y(2) (>650-fold), P2X(2) (3-fold), P2X(3) (8-fold), P2X(4) (>22-fold), and P2X(7) (>67-fold) but no selectivity over P2X(1). QSAR studies confirm that residues with favored resonance and size parameters in the aromatic linker region can indeed lead to an increased potency as is the case for 8f. A symmetric structure linking two anionic clusters seems to be required for bioactivity. 8f may be helpful for studies evaluating the physiological role of P2Y(11) receptors.


