(S)-(-)-Bay K 8644Ca2+-channel activator (L-type) CAS# 98625-26-4 |
- I-BET-762
Catalog No.:BCC4474
CAS No.:1260907-17-2
- Bromodomain Inhibitor, (+)-JQ1
Catalog No.:BCC1132
CAS No.:1268524-70-4
- I-BET151 (GSK1210151A)
Catalog No.:BCC4476
CAS No.:1300031-49-5
- GSK1324726A
Catalog No.:BCC4038
CAS No.:1300031-52-0
- PFI-1 (PF-6405761)
Catalog No.:BCC2225
CAS No.:1403764-72-6
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 98625-26-4 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 6603728 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C16H15F3N2O4 | M.Wt | 356.3 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Synonyms | (S)-(-)-Bay-K-8644; (-)-BAY-R-5417; (-)-BAY-K-8644 | ||
| Solubility | DMSO : 125 mg/mL (350.83 mM; Need ultrasonic) H2O : < 0.1 mg/mL (insoluble) | ||
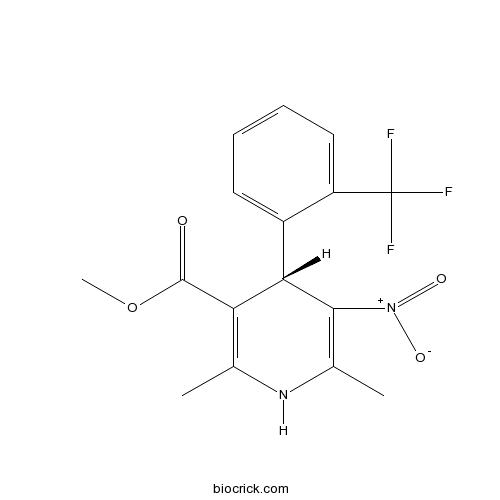
| Chemical Name | methyl (4S)-2,6-dimethyl-5-nitro-4-[2-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]-1,4-dihydropyridine-3-carboxylate | ||
| SMILES | CC1=C(C(C(=C(N1)C)[N+](=O)[O-])C2=CC=CC=C2C(F)(F)F)C(=O)OC | ||
| Standard InChIKey | ZFLWDHHVRRZMEI-ZDUSSCGKSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C16H15F3N2O4/c1-8-12(15(22)25-3)13(14(21(23)24)9(2)20-8)10-6-4-5-7-11(10)16(17,18)19/h4-7,13,20H,1-3H3/t13-/m0/s1 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | L-type Ca2+-channel activator with positive inotropic, vasoconstrictive and behavioral effects in vivo. Enantiomer of (±)-Bay K 8644. |

(S)-(-)-Bay K 8644 Dilution Calculator

(S)-(-)-Bay K 8644 Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.8066 mL | 14.0331 mL | 28.0662 mL | 56.1325 mL | 70.1656 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.5613 mL | 2.8066 mL | 5.6132 mL | 11.2265 mL | 14.0331 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.2807 mL | 1.4033 mL | 2.8066 mL | 5.6132 mL | 7.0166 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0561 mL | 0.2807 mL | 0.5613 mL | 1.1226 mL | 1.4033 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0281 mL | 0.1403 mL | 0.2807 mL | 0.5613 mL | 0.7017 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
Bay-K-8644 (S)-(-)- is an agonist of L-type Ca2+ channel. Bay-K-8644 (S)-(-)- activates Ba2+ currents (IBa) (EC50=32 nM).
In Vitro:(±)-Bay K 8644, a conventional racemic mixture of Bay K 8644, is widely used as an L-type Ca2+ channel agonist. Each optical isomer possesses opposite effects on IBa (R(+)-Bay K 8644 as an antagonist and Bay-K-8644 (S)-(-)- as an agonist. Bay-K-8644 (S)-(-)- can prevent the inhibitory actions of two distinct cyclic nucleotide pathways on IBa in gastric myocytes of the guinea pig antrum[1]. The Ca2+ channel activity is enhanced by 3–30 μM Bay-K-8644 (S)-(-)-, an agonist of L-type Ca2+ channels[2]. The interactions of two Ca2+ channel activators Bay-K-8644 (S)-(-)- and FPL 64176 is examined on smooth muscle L-type Ca2+ channels. FPL 64176 (300 nM) causes a sustained contraction of rat tail artery strips. This contractile response is inhibited by approximately 70% by Bay-K-8644 (S)-(-)- (EC50=14 nM). Bay-K-8644 (S)-(-)- (100 nM) increases whole-cell Ca2+ currents in A7r5 smooth muscle cells but effectively blocks further stimulation by 1 μM FPL 64176[3].
References:
[1]. Zhu HL, et al. Antagonistic actions of S(-)-Bay K 8644 on cyclic nucleotide-induced inhibition of voltage-dependent Ba(2+) currents in guinea pig gastric antrum. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2008 Dec;378(6):609-15.
[2]. Mironov SL, et al. L-type Ca2+ channels in inspiratory neurones of mice and their modulation by hypoxia. J Physiol. 1998 Oct 1;512 ( Pt 1):75-87.
[3]. Rampe D, et al. Functional interactions between two Ca2+ channel activators, (S)-Bay K 8644 and FPL 64176, in smooth muscle. Mol Pharmacol. 1992 Apr;41(4):599-602.
- Schisandrone
Catalog No.:BCN3316
CAS No.:98619-25-1
- Cryptanoside A
Catalog No.:BCN7481
CAS No.:98570-81-1
- Sominone
Catalog No.:BCN8006
CAS No.:98569-64-3
- 4-Chloro-6-iodoquinazoline
Catalog No.:BCC8703
CAS No.:98556-31-1
- Methyl 2-bromomethyl-3-nitrobenzoate
Catalog No.:BCC9035
CAS No.:98475-07-1
- Pseudoginsenoside RT5
Catalog No.:BCN1076
CAS No.:98474-78-3
- Pseudoginsenoside RT1
Catalog No.:BCN2794
CAS No.:98474-74-9
- Myelin Basic Protein (68-82), guinea pig
Catalog No.:BCC1020
CAS No.:98474-59-0
- Metoprolol Succinate
Catalog No.:BCC6519
CAS No.:98418-47-4
- Finasteride
Catalog No.:BCC2491
CAS No.:98319-26-7
- Nodulisporic acid C2
Catalog No.:BCC8326
CAS No.:
- Boc-D-3-Pal-OH
Catalog No.:BCC2652
CAS No.:98266-33-2
- Sarmentocymarin
Catalog No.:BCN7489
CAS No.:98633-61-5
- Nitrocaramiphen hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC6655
CAS No.:98636-73-8
- Zedoarondiol
Catalog No.:BCN3560
CAS No.:98644-24-7
- Methyl ganoderate H
Catalog No.:BCN3258
CAS No.:98665-11-3
- Ganoderic acid F
Catalog No.:BCN3037
CAS No.:98665-14-6
- Ganoderic Acid J
Catalog No.:BCN8436
CAS No.:100440-26-4
- Lucidenic acid D2
Catalog No.:BCN8202
CAS No.:98665-16-8
- Ganoderic acid H
Catalog No.:BCN3038
CAS No.:98665-19-1
- Ganoderic acid I
Catalog No.:BCN2865
CAS No.:98665-20-4
- Ganolucidic acid A
Catalog No.:BCN2444
CAS No.:98665-21-5
- Ganoderic acid G
Catalog No.:BCN2915
CAS No.:98665-22-6
- Dregeoside Da1
Catalog No.:BCN4764
CAS No.:98665-65-7
Influence of (-)-S-Bay K 8644, (+/-)-Bay W 5035 and (+/-)-Bay T 5006 on hemodynamics and FITC-dextran 3 elution kinetics in isolated rat hearts.[Pubmed:7689998]
Gen Pharmacol. 1993 May;24(3):631-6.
1. We investigated the effects of the new calcium-agonists (+/-)-Bay W 5035 and (+/-)-Bay T 5006 in comparison to (-)-S-Bay K 8644 on hemodynamics and epimyocardial perfusion in Langendorff rat hearts. 2. At equieffective inotropic concentration, vasoconstriction of coronary resistance vessels was significantly less after (+/-)-Bay W 5035 or (+/-)-Bay T 5006 than after (-)-S-Bay K 8644 application. 3. FITC-Dextran 3 elution kinetics indicated that the epimyocardial vascular volume was significantly reduced only by (-)-S-Bay K 8644. 4. Moreover, (-)-S-Bay K 8644 enhanced transcoronary exchange more markedly than (+/-)-Bay W 5035 or (+/-)-Bay T 5006, reflecting the differences in coronary constrictor activity. 5. We conclude that in comparison to (-)-S-Bay K 8644 the relation between inotropy and vasoconstriction is more favorable for (+/-)-Bay W 5035 or (+/-)-Bay T 5006.
Antagonistic actions of S(-)-Bay K 8644 on cyclic nucleotide-induced inhibition of voltage-dependent Ba(2+) currents in guinea pig gastric antrum.[Pubmed:18648774]
Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2008 Dec;378(6):609-15.
(+/-)-Bay K 8644, a conventional racemic mixture of Bay K 8644, is widely used as an L-type Ca(2+) channel agonist. Although interactions between Bay K 8644 and cyclic nucleotide have been described, they have not been properly characterized. We have investigated whether two optical isomers of Bay K 8644 (i.e., R(+)- and S(-)-Bay K 8644) modify cyclic nucleotide (cAMP and cGMP)-induced inhibitory effects on nifedipine-sensitive voltage-dependent Ba(2+) currents (I (Ba)) recorded from guinea pig gastric myocytes. Conventional whole-cell recordings were used to compare the effects of R(+)-Bay K 8644 and S(-)-Bay K 8644 on I (Ba). S(-)-Bay K 8644 enhanced the peak amplitude of I (Ba) evoked by depolarizing pulses to +10 mV from a holding potential of -70 mV in a concentration-dependent manner (EC(50) = 32 nM), while R(+)-Bay K 8644 inhibited I (Ba) (IC(50) = 975 nM). When R(+)-Bay K 8644 (0.5 microM) was applied, I (Ba) was suppressed to 71 +/- 10% of control. In the presence of R(+)-Bay K 8644 (0.5 microM), additional application of forskolin and sodium nitroprusside (SNP) further inhibited I (Ba). Conversely, in the presence of S(-)-Bay K 8644 (0.5 microM), subsequent application of forskolin and SNP did not affect I (Ba). Similarly, in the presence of 0.5 microM S(-)-Bay K 8644, db-cAMP and 8-Br-cGMP had no effect on I (Ba). These results indicate that S(-)-Bay K 8644, but not R(+)-Bay K 8644, can prevent the inhibitory actions of two distinct cyclic nucleotide pathways on I (Ba) in gastric myocytes of the guinea pig antrum.
The design of (-)-(S)-2-nitrooxyethyl 1,4-dihydro-2,6-dimethyl-3-nitro-4-(2-trifluoromethylphenyl) pyridine-5-carboxylate: a cardioselective positive inotropic derivative of Bay K 8644.[Pubmed:10498219]
Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 1999 Sep 6;9(17):2613-4.
The title compound, (-)-(S)-9, is a novel cardioselective calcium channel modulator that exhibits a calcium channel agonist effect on heart, a weak calcium channel antagonist effect on smooth muscle, and releases nitric oxide in vitro. (-)-(S)-9 is a useful lead-compound for the design of positive inotropic agents to treat congestive heart failure, and to study the structure-function relationship of calcium channel modulation.
Comparative effects of the dihydropyridine-type calcium-agonists (-)-S-Bay K 8644, (+/-)-Bay-W 5035 and (+/-)-Bay-T 5006 on human platelet aggregability.[Pubmed:7523235]
Gen Pharmacol. 1994 May;25(3):447-50.
1. Human platelet aggregation induced by collagen is concentration-dependently inhibited by dihydropyridine (DHP)-type calcium(Ca)-agonists. 2. There was no significant difference between the maximal anti-aggregatory effects or the anti-aggregatory potencies of (-)-S-Bay-K 8644 (EC50: 5.3 +/- 1.5 x 10(-5) M), (+/-)-Bay-W 5035 (EC50: 14.9 +/- 8.8 x 10(-5) M) or (+/-)-Bay-T 5006 (EC50: 2.7 +/- 1.9 x 10(-5) M) (P > 0.05). 3. Antiaggregatory effects of DHP-type Ca-agonists seem to be independent of Ca-channel activation.
Opposite cardiac actions of the enantiomers of Bay K 8644 at different membrane potentials in guinea-pig papillary muscles.[Pubmed:1692975]
Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1990 Mar;341(3):232-9.
The influence of membrane potential on the effects of the enantiomers and the racemate of Bay K 8644 [1,4-dihydro-2,6-dimethyl-3-nitro-4-(2-trifluor-methylphenyl)-p yri dine-5-carboxylate] on force of contraction and on action potentials were studied in guinea-pig papillary muscles in order to detect possible changes in the direction of drug action or in potency. Membrane potential was varied by changing the potassium concentration ([K+]o) in the bathing solution. At normal resting potential, (-)-Bay K 8644 enhanced force of contraction and prolonged the action potential duration measured at 50% of repolarization (APD) to the same extent as the racemate and with similar pD2 values. After membrane depolarization by raising [K+]o from 5.4 to 17.4 mmol/l, the (-)-enantiomer and the racemate prolonged the APD to a similar degree but enhanced force to a lesser extent. The maximum rate of depolarization of slow action potentials, Vmax, was increased at the highest concentrations (10(-5) mol/l). The effects of (+)-Bay K 8644 were more complicated. At high concentrations (10(-5) mol/l) it decreased force of contraction and APD, the pD2 values were one order of magnitude lower than for the (-)-enantiomer and the racemate. A high concentration (+)-Bay K 8644 (10(-5) mol/l) virtually abolished contractile activity at all membrane potentials, the extent of shortening in APD increased with membrane depolarization in elevated [K+]o. Vmax of slow action potentials was decreased.(ABSTRACT TRUNCATED AT 250 WORDS)
Enantiomer selectivity and the development of tolerance to the behavioral effects of the calcium channel activator BAY K 8644.[Pubmed:2465070]
Brain Res Bull. 1988 Dec;21(6):865-72.
The putative behavioral effects of the enantiomers of BAY K 8644 and the behavioral responses to (+/-)-BAY K 8644 following chronic injection were assessed on motor function in mice. The interaction of the enantiomers of BAY K 8644 with mouse brain dihydropyridine binding sites was also evaluated. The calcium channel activating enantiomer (-)-S-BAY K 8644 impaired rotarod and motor activity with an ED50 value of 0.5 mg/kg. The calcium channel blocker enantiomer (+)-R-BAY K 8644 neither affected rotarod nor motor activity. (+)-R-BAY K 8644, and the structurally related dihydropyridine calcium channel blockers nifedipine and (-)-202-791 inhibited the impairment of rotarod activity by (-)-S-BAY K 8644 in a dose-dependent manner. (+/-)-BAY K 8644 produced convulsions in mice with a CD50 of 5 mg/kg. Chronic injection of (+/-)-BAY K 8644 (8 mg/kg IP once each day for four days) resulted in a significant tolerance to, and increase in recovery from, the motor deficits produced by (+/-)-BAY K 8644. Furthermore, chronic treatment with (+/-)-BAY K 8644 increased the onset time, but did not reduce the number of mice having convulsions to (+/-)-BAY K 8644. Chronic injection of nifedipine did not affect the motor deficit and convulsive activity of (+/-)-BAY K 8644. The behavioral effects of (+/-)-BAY K 8644 were observed at significant brain levels of drug. [3H]Nitrendipine binding to mouse brain dihydropyridine binding sites was unchanged in mice chronically injected with either (+/-)-BAY K 8644 or nifedipine.(ABSTRACT TRUNCATED AT 250 WORDS)
The optical isomers of the 1,4-dihydropyridine BAY K 8644 show opposite effects on Ca channels.[Pubmed:2412855]
Eur J Pharmacol. 1985 Aug 15;114(2):223-6.
The optical isomers of the 1,4-dihydropyridine BAY K 8644 were studied in isolated rabbit aorta and heart preparations. The (-)-enantiomer has the known vasoconstricting and positive inotropic properties of the Ca agonistic compound. In contrast, its antipode shows at about 10-50 times higher concentrations the vasodilating and negative inotropic effects of Ca antagonistic drugs. It is concluded that neither simple chemical nor physical actions can be responsible for the opposite effects of Ca antagonistic and Ca agonistic dihydropyridines.


