4,4-Pentamethylenepiperidine hydrochlorideM2 proton channel blocker CAS# 1125-01-5 |
- BCX 1470
Catalog No.:BCC1413
CAS No.:217099-43-9
- BCX 1470 methanesulfonate
Catalog No.:BCC1414
CAS No.:217099-44-0
- PMSF
Catalog No.:BCC1229
CAS No.:329-98-6
- Nafamostat Mesylate(FUT-175)
Catalog No.:BCC1228
CAS No.:82956-11-4
- Aprotinin
Catalog No.:BCC1220
CAS No.:9087-70-1
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 1125-01-5 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 22252831 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C10H20ClN | M.Wt | 189.73 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | Soluble to 100 mM in water and to 100 mM in DMSO | ||
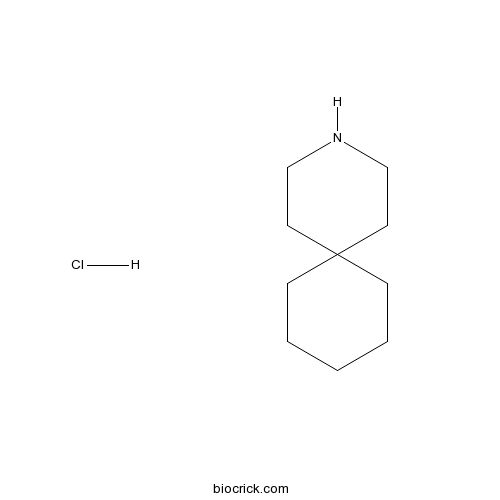
| Chemical Name | 3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane;hydrochloride | ||
| SMILES | C1CCC2(CC1)CCNCC2.Cl | ||
| Standard InChIKey | XDRWSBJRLMRJKA-UHFFFAOYSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C10H19N.ClH/c1-2-4-10(5-3-1)6-8-11-9-7-10;/h11H,1-9H2;1H | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | M2 proton channel blocker (IC50 = 0.92 μM). Inhibits influenza virus M2 protein (AM2). |

4,4-Pentamethylenepiperidine hydrochloride Dilution Calculator

4,4-Pentamethylenepiperidine hydrochloride Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 5.2706 mL | 26.3532 mL | 52.7065 mL | 105.413 mL | 131.7662 mL |
| 5 mM | 1.0541 mL | 5.2706 mL | 10.5413 mL | 21.0826 mL | 26.3532 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.5271 mL | 2.6353 mL | 5.2706 mL | 10.5413 mL | 13.1766 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.1054 mL | 0.5271 mL | 1.0541 mL | 2.1083 mL | 2.6353 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0527 mL | 0.2635 mL | 0.5271 mL | 1.0541 mL | 1.3177 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
- H-Glu(OcHex)-OH
Catalog No.:BCC2929
CAS No.:112471-82-6
- U-54494A hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC6668
CAS No.:112465-94-8
- 3-Phenyl-1-(pyrrol-1-yl)propan-1-one
Catalog No.:BCN4005
CAS No.:112448-69-8
- AZ3146
Catalog No.:BCC3731
CAS No.:1124329-14-1
- Ganoderic acid Jb
Catalog No.:BCN7972
CAS No.:112430-68-9
- Ganoderic acid T-Q
Catalog No.:BCN3209
CAS No.:112430-66-7
- Ganoderic acid TN
Catalog No.:BCN2443
CAS No.:112430-64-5
- 2',5,7-Trihydroxy-8-methoxyflavanone
Catalog No.:BCN6004
CAS No.:112408-71-6
- 3'-Deoxy-4-O-methylsappanol
Catalog No.:BCN3675
CAS No.:112408-68-1
- 3-Deoxysappanchalcone
Catalog No.:BCN3736
CAS No.:112408-67-0
- Tetramethylpyrazine
Catalog No.:BCN1008
CAS No.:1124-11-4
- XL765
Catalog No.:BCC2060
CAS No.:1123889-87-1
- 5-Aminoisoquinoline
Catalog No.:BCC8736
CAS No.:1125-60-6
- 6-Aldehydo-isoophiopogonone A
Catalog No.:BCN6629
CAS No.:112500-90-0
- Aristolactam FI
Catalog No.:BCN6005
CAS No.:112501-42-5
- Picrasidine S
Catalog No.:BCN6006
CAS No.:112503-87-4
- Absouline
Catalog No.:BCN1954
CAS No.:112513-33-4
- Isoabsouline
Catalog No.:BCN1955
CAS No.:112513-34-5
- Neolinine
Catalog No.:BCN6564
CAS No.:112515-37-4
- Tubuloside A
Catalog No.:BCN2806
CAS No.:112516-05-9
- Citrusinol
Catalog No.:BCN8083
CAS No.:112516-43-5
- CI994 (Tacedinaline)
Catalog No.:BCC2159
CAS No.:112522-64-2
- ent-16alpha,17-Dihydroxyatisan-3-one
Catalog No.:BCN6607
CAS No.:112523-91-8
- Pioglitazone HCl
Catalog No.:BCC2278
CAS No.:112529-15-4
The hallucinogen 2,5-dimethoxy-4-iodoamphetamine hydrochloride activates neurotrophin receptors in a neuronal cell line and promotes neurites extension.[Pubmed:28315978]
J Neural Transm (Vienna). 2017 Jun;124(6):749-759.
Decreased neurotrophic factors expression and neurotrophin receptors signalling have repeatedly been reported in association with stress, depression, and neurodegenerative disorders. We have previously identified the hallucinogen 2,5-dimethoxy-4-iodoamphetamine hydrochloride (DOI) as protective against trophic deprivation-induced cytotoxicity in human neuroblastoma SK-N-SH cells and established the dependence of this effect on the 5-HT2A receptor, tyrosine kinases activity, and the extracellular signal-regulated kinase pathway. In the current study, we investigated the effect of DOI on tropomyosin-related kinase receptor A (TrkA) phosphorylation. Treatment with DOI increased TrkA tyrosine phosphorylation in SK-N-SH cells, determined by immunoprecipitation with TrkA antibody and immunoblotting with anti-phosphotyrosine- and TrkA-antibodies. Analysis of DOI's effect on individual TrkA residues in SK-N-SH cells showed that it increases TrkA Tyr490 phosphorylation (177 +/- 23% after 5 muM DOI for 30 min compared to vehicle). Furthermore, DOI treatment increased the percentage of SK-N-SH cells extending neurites in a TrkA-dependent manner (17.2 +/- 2.2% after 5 muM DOI treatment for 6 days compared to 5.6 +/- 1.7% after vehicle). In a different cell model-lymphoblastoid cell lines-DOI treatment increased tropomyosin-related kinase receptor B (TrkB) phosphorylation, determined by immunoprecipitation with TrkB antibody and immunoblotting with anti-phosphotyrosine antibody and total Trk antibody. Our results identify the Trk receptors as a downstream target of the hallucinogen DOI. In light of the known involvement of Trk receptors in mental diseases, their participation in DOI-mediated effects warrants further investigation.
Unusual 4-arsonoanilinium cationic species in the hydrochloride salt of (4-aminophenyl)arsonic acid and formed in the reaction of the acid with copper(II) sulfate, copper(II) chloride and cadmium chloride.[Pubmed:28378716]
Acta Crystallogr C Struct Chem. 2017 Apr 1;73(Pt 4):325-330.
Structures having the unusual protonated 4-arsonoanilinium species, namely in the hydrochloride salt, C6H9AsNO3(+).Cl(-), (I), and the complex salts formed from the reaction of (4-aminophenyl)arsonic acid (p-arsanilic acid) with copper(II) sulfate, i.e. hexaaquacopper(II) bis(4-arsonoanilinium) disulfate dihydrate, (C6H9AsNO3)2[Cu(H2O)6](SO4)2.2H2O, (II), with copper(II) chloride, i.e. poly[bis(4-arsonoanilinium) [tetra-mu-chlorido-cuprate(II)]], {(C6H9AsNO3)2[CuCl4]}n, (III), and with cadmium chloride, i.e. poly[bis(4-arsonoanilinium) [tetra-mu-chlorido-cadmate(II)]], {(C6H9AsNO3)2[CdCl4]}n, (IV), have been determined. In (II), the two 4-arsonoanilinium cations are accompanied by [Cu(H2O)6](2+) cations with sulfate anions. In the isotypic complex salts (III) and (IV), they act as counter-cations to the {[CuCl4](2-)}n or {[CdCl4](2-)}n anionic polymer sheets, respectively. In (II), the [Cu(H2O)6](2+) ion sits on a crystallographic centre of symmetry and displays a slightly distorted octahedral coordination geometry. The asymmetric unit for (II) contains, in addition to half the [Cu(H2O)6](2+) ion, one 4-arsonoanilinium cation, a sulfate dianion and a solvent water molecule. Extensive O-H...O and N-H...O hydrogen bonds link all the species, giving an overall three-dimensional structure. In (III), four of the chloride ligands are related by inversion [Cu-Cl = 2.2826 (8) and 2.2990 (9) A], with the other two sites of the tetragonally distorted octahedral CuCl6 unit occupied by symmetry-generated Cl-atom donors [Cu-Cl = 2.9833 (9) A], forming a two-dimensional coordination polymer network substructure lying parallel to (001). In the crystal, the polymer layers are linked across [001] by a number of bridging hydrogen bonds involving N-H...Cl interactions from head-to-head-linked As-O-H...O 4-arsonoanilinium cations. A three-dimensional network structure is formed. Cd(II) compound (IV) is isotypic with Cu(II) complex (III), but with the central CdCl6 complex repeat unit having a more regular M-Cl bond-length range [2.5232 (12)-2.6931 (10) A] compared to that in (III). This series of compounds represents the first reported crystal structures having the protonated 4-arsonoanilinium species.
Study on the interaction of 6-(2-morpholin-4-yl-ethyl)-6H-indolo [2,3-b]quinoxaline hydrochloride with human serum albumin by fluorescence spectroscopy.[Pubmed:28355158]
Methods Appl Fluoresc. 2016 Sep 14;4(3):034012.
Under physiological conditions, in vitro interaction between the bio-active substance 6-(2-morpholin-4-yl-ethyl)-6H-indolo[2,3-b]quinoxaline hydrochloride (MIQ) and human serum albumin (HSA) was investigated at an excitation wavelength 260 nm and at different temperatures (298 K, 308 K and 313 K) by fluorescence emission spectroscopy. From spectral analysis, MIQ showed a strong ability to quench the intrinsic fluorescence of HSA through a static quenching procedure. The binding constant is estimated asK A = 2.55 x 10(-4) l . mol(-1) at 298 K. Based on the thermodynamic parameters evaluated from the van 't Hoff equation, the enthalpy change (DeltaH degrees ) and entropy change (DeltaS degrees ) were derived to be negative values. A value of 2.37 nm for the average distance r between MIQ (acceptor) and tryptophan residues of HSA (donor) was derived from the fluorescence resonance energy transfer. UV/vis absorption spectra were used to confirm the quenching mechanism.
Identification of pyrolysis products of the new psychoactive substance 2-amino-1-(4-bromo-2,5-dimethoxyphenyl)ethanone hydrochloride (bk-2C-B) and its iodo analogue bk-2C-I.[Pubmed:28371351]
Drug Test Anal. 2018 Jan;10(1):229-236.
2-Amino-1-(4-bromo-2,5-dimethoxyphenyl)ethanone hydrochloride (bk-2C-B) has recently emerged as a new psychoactive substance (NPS). It is most commonly consumed orally, although there are indications that it might also be ingested by inhalation or 'smoking'. Information about the stability of bk-2C-B when exposed to heat is unavailable and the potential for pyrolytic degradation and formation of unknown substances available for inhalation prompted an investigation using a simulated 'meth pipe' scenario. Twelve products following pyrolysis of bk-2C-B were detected and verified by organic synthesis of the corresponding standards. In addition, 2-amino-1-(4-iodo-2,5-dimethoxyphenyl)ethanone hydrochloride (bk-2C-I) was characterized for the first time and subjected to pyrolysis as well. Similar products were formed, which indicated that the replacement of the bromo with the iodo substituent did not affect the pyrolysis pattern under the conditions used. Two additional products were detected in the bk-2C-I pyrolates, namely 1-(2,5-dimethoxyphenyl)-ethanone and 1-iodo-4-ethenyl-5-methoxyphenol. The potential ingestion of pyrolysis products with unknown toxicity adds an element of concern. Copyright (c) 2017 John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.
Discovery of spiro-piperidine inhibitors and their modulation of the dynamics of the M2 proton channel from influenza A virus.[Pubmed:19469531]
J Am Chem Soc. 2009 Jun 17;131(23):8066-76.
Amantadine has been used for decades as an inhibitor of the influenza A virus M2 protein (AM2) in the prophylaxis and treatment of influenza A infections, but its clinical use has been limited by its central nervous system (CNS) side effects as well as emerging drug-resistant strains of the virus. With the goal of searching for new classes of M2 inhibitors, a structure-activity relation study based on 2-[3-azaspiro(5,5)undecanol]-2-imidazoline (BL-1743) was initiated. The first generation BL-1743 series of compounds has been synthesized and tested by two-electrode voltage-clamp (TEV) assays. The most active compound from this library, 3-azaspiro[5,5]undecane hydrochloride (9), showed an IC(50) as low as 0.92 +/- 0.11 microM against AM2, more than an order of magnitude more potent than amantadine (IC(50) = 16 microM). (15)N and (13)C solid-state NMR was employed to determine the effect of compound 9 on the structure and dynamics of the transmembrane domain of AM2 (AM2-TM) in phospholipid bilayers. Compared to amantadine, spiro-piperidine 9 (1) induces a more homogeneous conformation of the peptide, (2) reduces the dynamic disorder of the G34-I35 backbone near the water-filled central cavity of the helical bundle, and (3) influences the dynamics and magnetic environment of more residues within the transmembrane helices. These data suggest that spiro-piperidine 9 binds more extensively with the AM2 channel, thus leading to stronger inhibitory potency.


