AZ3146Mps1 inhibitor,potent and selective CAS# 1124329-14-1 |
- Mps1-IN-2
Catalog No.:BCC4153
CAS No.:1228817-38-6
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 1124329-14-1 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 56973724 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C24H32N6O3 | M.Wt | 452.55 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | DMSO : 100 mg/mL (220.97 mM; Need ultrasonic) | ||
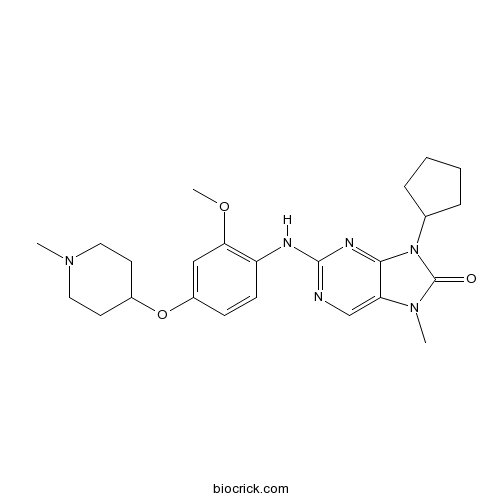
| Chemical Name | 9-cyclopentyl-2-[2-methoxy-4-(1-methylpiperidin-4-yl)oxyanilino]-7-methylpurin-8-one | ||
| SMILES | CN1CCC(CC1)OC2=CC(=C(C=C2)NC3=NC=C4C(=N3)N(C(=O)N4C)C5CCCC5)OC | ||
| Standard InChIKey | YUKWVHPTFRQHMF-UHFFFAOYSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C24H32N6O3/c1-28-12-10-17(11-13-28)33-18-8-9-19(21(14-18)32-3)26-23-25-15-20-22(27-23)30(24(31)29(20)2)16-6-4-5-7-16/h8-9,14-17H,4-7,10-13H2,1-3H3,(H,25,26,27) | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Potent and selective monopolar spindle 1 (Mps1) kinase inhibitor (IC50 = 35 nM). Displays selectivity over 46 other kinases including Cdk1 and aurora kinase B. Interferes with chromosome alignment and overrides spindle assembly checkpoint. Inhibits the recruitment of Mad1, Mad2 and centromere protein E (CENP-E) to kinetochores. |

AZ3146 Dilution Calculator

AZ3146 Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.2097 mL | 11.0485 mL | 22.097 mL | 44.194 mL | 55.2425 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.4419 mL | 2.2097 mL | 4.4194 mL | 8.8388 mL | 11.0485 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.221 mL | 1.1049 mL | 2.2097 mL | 4.4194 mL | 5.5243 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0442 mL | 0.221 mL | 0.4419 mL | 0.8839 mL | 1.1049 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0221 mL | 0.1105 mL | 0.221 mL | 0.4419 mL | 0.5524 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
AZ3146 is a potent and selective Monopolar Spindle 1 (Mps1) kinase inhibitor with IC50 value of 35 nM. AZ3146 acts by interfering with chromosome alignment and overriding the spindle assembly checkpoint.
MPS1 protein kinases play important roles in different steps in mitosis including chromosome attachment and functions at the centrosomes. Additionally, they are also involved in regulation of development and in multiple signaling pathways after mitosis.
In cellular culture, if Mps1 is inhibited by AZ3146 before mitotic entry, this inhibition abloshed the subsequent recruitment of Mad1 and Mad2 to kinetochores. However, if cells were treated with AZ3146 after mitotic entry, the Mad1-C-Mad2 core complex remains kinetochore bound, but O-Mad2 is not recruited to the core. , AZ3146 interferes with chromosome alignment and overrides spindle assembly checkpoint1.
Regarding the effect of AZ3146 administration in vivo, the evidence should be provided by performing the study in human or mice or other animal models.
Reference:
1. Hewitt L, Tighe A, Santaguida S, et al. Sustained Mps1 activity is required in mitosis to recruit O-Mad2 to the Mad1-C-Mad2 core complex. The Journal of cell biology.2010;190(1):25-34.
- Ganoderic acid Jb
Catalog No.:BCN7972
CAS No.:112430-68-9
- Ganoderic acid T-Q
Catalog No.:BCN3209
CAS No.:112430-66-7
- Ganoderic acid TN
Catalog No.:BCN2443
CAS No.:112430-64-5
- 2',5,7-Trihydroxy-8-methoxyflavanone
Catalog No.:BCN6004
CAS No.:112408-71-6
- 3'-Deoxy-4-O-methylsappanol
Catalog No.:BCN3675
CAS No.:112408-68-1
- 3-Deoxysappanchalcone
Catalog No.:BCN3736
CAS No.:112408-67-0
- Tetramethylpyrazine
Catalog No.:BCN1008
CAS No.:1124-11-4
- XL765
Catalog No.:BCC2060
CAS No.:1123889-87-1
- DMPQ dihydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC6977
CAS No.:1123491-15-5
- WAY-262611
Catalog No.:BCC5507
CAS No.:1123231-07-1
- BRL 52537 hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC6751
CAS No.:112282-24-3
- H-Asp(OcHex)-OH
Catalog No.:BCC2887
CAS No.:112259-66-2
- 3-Phenyl-1-(pyrrol-1-yl)propan-1-one
Catalog No.:BCN4005
CAS No.:112448-69-8
- U-54494A hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC6668
CAS No.:112465-94-8
- H-Glu(OcHex)-OH
Catalog No.:BCC2929
CAS No.:112471-82-6
- 4,4-Pentamethylenepiperidine hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC6059
CAS No.:1125-01-5
- 5-Aminoisoquinoline
Catalog No.:BCC8736
CAS No.:1125-60-6
- 6-Aldehydo-isoophiopogonone A
Catalog No.:BCN6629
CAS No.:112500-90-0
- Aristolactam FI
Catalog No.:BCN6005
CAS No.:112501-42-5
- Picrasidine S
Catalog No.:BCN6006
CAS No.:112503-87-4
- Absouline
Catalog No.:BCN1954
CAS No.:112513-33-4
- Isoabsouline
Catalog No.:BCN1955
CAS No.:112513-34-5
- Neolinine
Catalog No.:BCN6564
CAS No.:112515-37-4
- Tubuloside A
Catalog No.:BCN2806
CAS No.:112516-05-9
Effect of MPS1 Inhibition on Genotoxic Stress Responses in Murine Tumour Cells.[Pubmed:27272789]
Anticancer Res. 2016 Jun;36(6):2783-92.
BACKGROUND/AIM: The monopolar spindle 1 (MPS1) is a serine/threonine kinase that plays an important role in spindle assembly checkpoint signaling. To determine the possible relationship between MPS1 inhibition and genotoxic stress responses, herein we examined whether MPS1 inhibition influences cellular susceptibility towards two genotoxic treatments, etoposide and ionizing radiation (IR). MATERIALS AND METHODS: Two murine tumour cell lines, SCCVII and EMT6, were used. The effect of genotoxic treatments with or without two novel MPS1 inhibitors, NMS-P715 and AZ3146, on cellular survival, cell-cycle distribution, centrosome status and mitotic catastrophe (MC) was evaluated. RESULTS: MPS1 inhibition sensitized murine tumour cells to etoposide but not to IR. In addition, MPS1 inhibition altered cell-cycle progression and exacerbated centrosome abnormalities, resulting in enhanced MC induced by etoposide but not by IR. CONCLUSION: MPS1 inhibition promotes the etoposide-induced aberrant mitosis and, consequently, the induction of tumour cell death.
Naturally Occurring Mutations in the MPS1 Gene Predispose Cells to Kinase Inhibitor Drug Resistance.[Pubmed:26202014]
Cancer Res. 2015 Aug 15;75(16):3340-54.
Acquired resistance to therapy is perhaps the greatest challenge to effective clinical management of cancer. With several inhibitors of the mitotic checkpoint kinase MPS1 in preclinical development, we sought to investigate how resistance against these inhibitors may arise so that mitigation or bypass strategies could be addressed as early as possible. Toward this end, we modeled acquired resistance to the MPS1 inhibitors AZ3146, NMS-P715, and CCT251455, identifying five point mutations in the kinase domain of MPS1 that confer resistance against multiple inhibitors. Structural studies showed how the MPS1 mutants conferred resistance by causing steric hindrance to inhibitor binding. Notably, we show that these mutations occur in nontreated cancer cell lines and primary tumor specimens, and that they also preexist in normal lymphoblast and breast tissues. In a parallel piece of work, we also show that the EGFR p.T790M mutation, the most common mutation conferring resistance to the EGFR inhibitor gefitinib, also preexists in cancer cells and normal tissue. Our results therefore suggest that mutations conferring resistance to targeted therapy occur naturally in normal and malignant cells and these mutations do not arise as a result of the increased mutagenic plasticity of cancer cells.
Cenp-E inhibitor GSK923295: Novel synthetic route and use as a tool to generate aneuploidy.[Pubmed:26320186]
Oncotarget. 2015 Aug 28;6(25):20921-32.
Aneuploidy is a common feature of cancer, with human solid tumour cells typically harbouring abnormal chromosome complements. The aneuploidy observed in cancer is often caused by a chromosome instability phenotype, resulting in genomic heterogeneity. However, the role aneuploidy and chromosome instability play in tumour evolution and chemotherapy response remains poorly understood. In some contexts, aneuploidy has oncogenic effects, whereas in others it is anti-proliferative and tumour-suppressive. Dissecting fully the role aneuploidy plays in tumourigenesis requires tools and facile assays that allow chromosome missegregation to be induced experimentally in cells that are otherwise diploid and chromosomally stable. Here, we describe a chemical biology approach that induces low-level aneuploidy across a large population of cells. Specifically, cells are first exposed to GSK923295, an inhibitor targeting the mitotic kinesin Cenp-E; while the majority of chromosomes align at the cell's equator, a small number cluster near the spindle poles. By then driving these cells into anaphase using AZ3146, an inhibitor targeting the spindle checkpoint kinase Mps1, the polar chromosomes are missegregated. This results in, on average, two chromosome missegregation events per division, and avoids trapping chromosomes in the spindle midzone, which could otherwise lead to DNA damage. We also describe an efficient route for the synthesis of GSK923295 that employs a novel enzymatic resolution. Together, the approaches described here open up new opportunities for studying cellular responses to aneuploidy.
Sustained Mps1 activity is required in mitosis to recruit O-Mad2 to the Mad1-C-Mad2 core complex.[Pubmed:20624899]
J Cell Biol. 2010 Jul 12;190(1):25-34.
Mps1 is an essential component of the spindle assembly checkpoint. In this study, we describe a novel Mps1 inhibitor, AZ3146, and use it to probe the role of Mps1's catalytic activity during mitosis. When Mps1 is inhibited before mitotic entry, subsequent recruitment of Mad1 and Mad2 to kinetochores is abolished. However, if Mps1 is inhibited after mitotic entry, the Mad1-C-Mad2 core complex remains kinetochore bound, but O-Mad2 is not recruited to the core. Although inhibiting Mps1 also interferes with chromosome alignment, we see no obvious effect on aurora B activity. In contrast, kinetochore recruitment of centromere protein E (CENP-E), a kinesin-related motor protein, is severely impaired. Strikingly, inhibition of Mps1 significantly increases its own abundance at kinetochores. Furthermore, we show that Mps1 can dimerize and transphosphorylate in cells. We propose a model whereby Mps1 transphosphorylation results in its release from kinetochores, thus facilitating recruitment of O-Mad2 and CENP-E and thereby simultaneously promoting checkpoint signaling and chromosome congression.
TTK activates Akt and promotes proliferation and migration of hepatocellular carcinoma cells.[Pubmed:26418879]
Oncotarget. 2015 Oct 27;6(33):34309-20.
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is one of the most malignant cancers with poor clinical outcome. The protein kinase human monopolar spindle 1 (hMps1/TTK) gene expression is significantly increased in HCCs. However, its contributions to hepatocarcinogenesis remain unclear. In this study, we found that TTK was overexpressed in 77.63% (118/152) HCC specimens. Elevated TTK expression positively correlated with large tumor size and presence of the portal vein tumor thrombus (PVTT). Demethylation in its promoter increased TTK expression in HCC. In vitro assays revealed that TTK not only promoted cell proliferation and anchorage-independent growth, but also cell migration. Subsequent investigations revealed that TTK activated Akt/mTOR pathway in a p53 dependent manner. We also found that TTK specific kinase inhibitor AZ3146 could decrease HCC cell growth. In conclusion, TTK contributes to HCC tumorigenesis via promoting cell proliferation and migration. It may serve as a novel biomarker and a potential target in HCC cancer therapy.
A chemical tool box defines mitotic and interphase roles for Mps1 kinase.[Pubmed:20624898]
J Cell Biol. 2010 Jul 12;190(1):21-4.
In this issue, three groups (Hewitt et al. 2010. J. Cell Biol. doi:10.1083/jcb.201002133; Maciejowski et al. 2010. J. Cell Biol. doi:10.1083/jcb.201001050; Santaguida et al. 2010. J. Cell Biol. doi:10.1083/jcb.201001036) use chemical inhibitors to analyze the function of the mitotic checkpoint kinase Mps1. These studies demonstrate that Mps1 kinase activity ensures accurate chromosome segregation through its recruitment to kinetochores of mitotic checkpoint proteins, formation of interphase and mitotic inhibitors of Cdc20, and correction of faulty microtubule attachments.
Mps1 directs the assembly of Cdc20 inhibitory complexes during interphase and mitosis to control M phase timing and spindle checkpoint signaling.[Pubmed:20624902]
J Cell Biol. 2010 Jul 12;190(1):89-100.
The spindle assembly checkpoint (SAC) in mammals uses cytosolic and kinetochore-based signaling pathways to inhibit anaphase. In this study, we use chemical genetics to show that the protein kinase Mps1 regulates both aspects of the SAC. Human MPS1-null cells were generated via gene targeting and reconstituted with either the wild-type kinase (Mps1(wt)) or a mutant version (Mps1(as)) sensitized to bulky purine analogues. Mps1 inhibition sharply accelerated anaphase onset, such that cells completed mitosis in 12 min, and prevented Cdc20's association with either Mad2 or BubR1 during interphase, i.e., before the appearance of functional kinetochores. Furthermore, intramitotic Mps1 inhibition evicted Bub1 and all other known SAC transducers from the outer kinetochore, but contrary to a recent study, did not perturb aurora B-dependent phosphorylation. We conclude that Mps1 has two complementary roles in SAC regulation: (1) initial cytoplasmic activation of Cdc20 inhibitors and (2) recruitment of factors that promote sustained anaphase inhibition and chromosome biorientation to unattached kinetochores.


