4,5-Di-O-caffeoylquinic acid methyl esterCAS# 188742-80-5 |
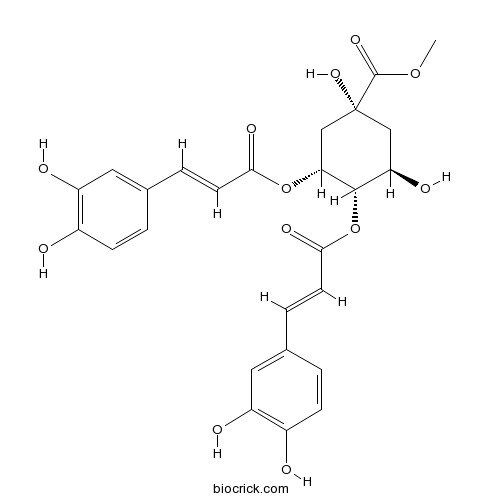
- 3,4-Di-O-caffeoylquinic acid methyl ester
Catalog No.:BCN6490
CAS No.:114637-83-1
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 188742-80-5 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 10052718 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C26H26O12 | M.Wt | 530.5 |
| Type of Compound | Phenylpropanoids | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | Soluble in Chloroform,Dichloromethane,Ethyl Acetate,DMSO,Acetone,etc. | ||
| Chemical Name | methyl (1R,3R,4S,5R)-3,4-bis[[(E)-3-(3,4-dihydroxyphenyl)prop-2-enoyl]oxy]-1,5-dihydroxycyclohexane-1-carboxylate | ||
| SMILES | COC(=O)C1(CC(C(C(C1)OC(=O)C=CC2=CC(=C(C=C2)O)O)OC(=O)C=CC3=CC(=C(C=C3)O)O)O)O | ||
| Standard InChIKey | PKJBSZTYNDRXEQ-GMGOHGFSSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C26H26O12/c1-36-25(34)26(35)12-20(31)24(38-23(33)9-5-15-3-7-17(28)19(30)11-15)21(13-26)37-22(32)8-4-14-2-6-16(27)18(29)10-14/h2-11,20-21,24,27-31,35H,12-13H2,1H3/b8-4+,9-5+/t20-,21-,24+,26-/m1/s1 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | 4,5-Di-O-caffeoylquinic acid methyl ester shows high efficiency and low toxicity with antivirus activity against RSV. |
| Targets | HSV |
| In vitro | Study on chemical constituents from Re-Du-Ning Injection (II).[Reference: WebLink]Chinese Traditional & Herbal Drugs, 2015 , 46 (11) :1597-602.To investigate the chemical constituents from Re-Du-Ning Injection (RDN). |

4,5-Di-O-caffeoylquinic acid methyl ester Dilution Calculator

4,5-Di-O-caffeoylquinic acid methyl ester Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 1.885 mL | 9.4251 mL | 18.8501 mL | 37.7003 mL | 47.1254 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.377 mL | 1.885 mL | 3.77 mL | 7.5401 mL | 9.4251 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.1885 mL | 0.9425 mL | 1.885 mL | 3.77 mL | 4.7125 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0377 mL | 0.1885 mL | 0.377 mL | 0.754 mL | 0.9425 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0189 mL | 0.0943 mL | 0.1885 mL | 0.377 mL | 0.4713 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
- 3-hydroxymorindone
Catalog No.:BCN3126
CAS No.:80368-74-7
- GSK3787
Catalog No.:BCC2263
CAS No.:188591-46-0
- Cl-4AS-1
Catalog No.:BCC7780
CAS No.:188589-66-4
- TFM-4AS-1
Catalog No.:BCC6069
CAS No.:188589-61-9
- SBI-0206965
Catalog No.:BCC3984
CAS No.:1884220-36-3
- Scandoside
Catalog No.:BCN3449
CAS No.:18842-99-4
- Paederosidic acid
Catalog No.:BCN3438
CAS No.:18842-98-3
- MAFP
Catalog No.:BCC7059
CAS No.:188404-10-6
- Pellitorine
Catalog No.:BCN4043
CAS No.:18836-52-7
- Isodomoic acid G
Catalog No.:BCN1839
CAS No.:188346-81-8
- Massonianoside B
Catalog No.:BCN1164
CAS No.:188300-19-8
- Californidine
Catalog No.:BCC8137
CAS No.:18830-99-4
- N-Acetylcaprolactam
Catalog No.:BCC9081
CAS No.:1888-91-1
- SC 560
Catalog No.:BCC7111
CAS No.:188817-13-2
- 8-Glucosyl-5,7-dihydroxy-2-(1-methylpropyl)chromone
Catalog No.:BCN7505
CAS No.:188818-27-1
- Streptozotocin
Catalog No.:BCN3834
CAS No.:18883-66-4
- HX 531
Catalog No.:BCC6082
CAS No.:188844-34-0
- HX 630
Catalog No.:BCC6083
CAS No.:188844-52-2
- DMA
Catalog No.:BCC1532
CAS No.:188860-26-6
- Hydroxytanshinone IIA
Catalog No.:BCN2497
CAS No.:18887-18-8
- Methyl tanshinonate
Catalog No.:BCN2553
CAS No.:18887-19-9
- Junipediol B 8-O-glucoside
Catalog No.:BCN4022
CAS No.:188894-19-1
- L 760735
Catalog No.:BCC7840
CAS No.:188923-01-5
- Cilengitide
Catalog No.:BCC3942
CAS No.:188968-51-6
Identification of alpha-glucosidase inhibitors from the leaves of Pluchea indica (L.) Less., a traditional Indonesian herb: promotion of natural product use.[Pubmed:24697406]
Nat Prod Res. 2014;28(17):1350-3.
A promising approach for treating diabetes mellitus (DM) is to decrease postprandial hyperglycaemia by suppressing carbohydrate digestion using alpha-glucosidase inhibitors. Pluchea indica leaf extracts possess inhibitory activity against intestinal maltase. Enzyme assay-guided fractionation by chromatography yielded five active caffeoylquinic acid derivatives (1-5). Their structures were elucidated by mass spectrometry and NMR analysis and completed by comparison with reference data. 3,5-Di-O-caffeoylquinic acid (1), 4,5-Di-O-caffeoylquinic acid methyl ester (2), 3,4,5-tri-O-caffeoylquinic acid methyl ester (3), 3,4,5-tri-O-caffeoylquinic acid (4) and 1,3,4,5-tetra-O-caffeoylquinic acid (5) were isolated. Comparison of the activities of each isolate suggested that both methyl esterification of quinic acid and the number of caffeate groups in the molecule were important for the inhibitory activity. This study provides basic information for further examination of the suitability of P. indica as a functional food and medicinal supplement for the treatment and prevention of diabetes.
[Aromatic constituents of Heteroplexis micocephal and their bioactivities].[Pubmed:21473152]
Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2011 Jan;36(1):48-56.
OBJECTIVE: To investigate the chemical constituents of Heteroplexis micocephal and their bioactivities. METHOD: The constituents were isolated by using a combination of various chromatographic techniques including column chromatography over macroporous adsorbent resin, silica gel, Pharmadex LH-20, and C-18, as well as reversed-phase HPLC. Structures of the isolates were identified by spectroscopic data analysis. In vitro cytotoxic, HIV-1 replication, neuroprotective, and anti-inflammatory activities were screened by using cell-based models. RESULT: Thirty-one compounds were obtained. Twelve of them are phenylpropanols, and the structures were elucidated as (+)-(7S,8R)-guaiacylglycerol (1), ferulic acid (2), cinnamate methyl ester (3), 1-eicosanyl 3,4-dihydroxycinnamate (4), morinin B (5), sinapyl diangelate (6), chlorogenic acid (7), 4-O-caffeoylquinic acid (8), 5-O-caffeoylquinic acid (9), 5-O-caffeoylquinic acid methyl ester (10), 1,5-di-O-caffeoylquinic acid (11) and 4,5-Di-O-caffeoylquinic acid methyl ester (12). Three lignans, (+)-pinoresinol (13), prinsepiol (14) and (+)-pinoresinol-O-beta-D-glucopyranoside (15). Four acetophenones, 2,4-diacetylanisole (16), espeleton (17), viscidone (18) and 12-hydroxytremetone-12-O-beta-D-glucopyranoside (19). Nine flavones, isosakuranetin (20), hesperetin (21), 3-methoxy-5,7,3',4'-tetrahydroxyflavone (22), acacetin (23), 5-hydroxy-7,4'- dimethoxyflavone (24), 7-methoxy-4',5, 6-trihydroxyflavone (25), 3,3'-dimethylquercetin (26), kaempferol 3-O-rutinoside (27), rutin (28). And three coumarins scopoletin (29), umbelliferone (30) and ayapin (31). Compound 6 and 22 showed selective cytotoxicities against a human stomach cancer cell line(BGC-823) and a human lung cancer cell line (A549) with IC50 values of 3.74 x 10(-5) and 7.17 x 10(-5) mol L(-1), respectively. In addition, Compound 6 showed a potent activity inhibiting HIV-1 replication with an IC50 value of 4.04 x 10(-6) mol L(-1), while 22 showed neuroprotective activity Against the MPP+ induced PC12-syn cell damage, with a relative protection ratio of 105.2% (P < 0.01) at a concentration of 10(-5) mol L(-1). Compound 26 and 31 showed inhibitory activities against the release of beta-glucuronidase of the polymorphous nuclear leukocytes induced by platelet activating factor (PAF), with inhibitory rates of 75.6% (P < 0.001) and 53. 9% (P < 0.01), respectively. CONCLUSION: Compounds 1-31 were obtained from the genus Heteroplexis for the first time. Compound 6 and 22 possessed selective cytotoxicities against human cancer cell lines BGC-823 and A549, respectively. In addition, Compound 6 showed a potent activity inhibiting HIV-1 replication while 22 showed neuroprotective activity against the MPP+ induced PC12-syn cell damage. Compound 26 and 31 were potent anti-inflammatory agents.
Phagnalon rupestre as a source of compounds active on contact hypersensitivity.[Pubmed:12094308]
Planta Med. 2002 Jun;68(6):561-4.
The effect of Phagnalon rupestre MeOH extract on dinitrofluorobenzene- and sheep red blood cells-induced hypersensitivity was investigated. Eight compounds were identified: three dimethylallyl-hydroquinone glucosides (1 - 3), 3,5- and 4,5-Di-O-caffeoylquinic acid methyl esters (4 and 5), their free carboxyl analogues (6 and 7), and luteolin 7-O-beta-glucoside (8). All were tested for dinitrofluorobenzene-induced contact hypersensitivity inhibitory activity. Flavonoid 8 was the most active (49 % and 79 % inhibition at 24 and 96 h, respectively). The hydroquinones 1, 2 and 3 were effective at 96 h after challenge (62 %, 73 % and 60 % inhibition, respectively), while some of the dicaffeoylquinic derivatives (4 and 7) produced slightly lower reduction of the inflammatory reaction.


