HX 630RXR synergist CAS# 188844-52-2 |
- DAPT (GSI-IX)
Catalog No.:BCC3618
CAS No.:208255-80-5
- Semagacestat (LY450139)
Catalog No.:BCC3610
CAS No.:425386-60-3
- AR-A014418
Catalog No.:BCC1366
CAS No.:487021-52-3
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

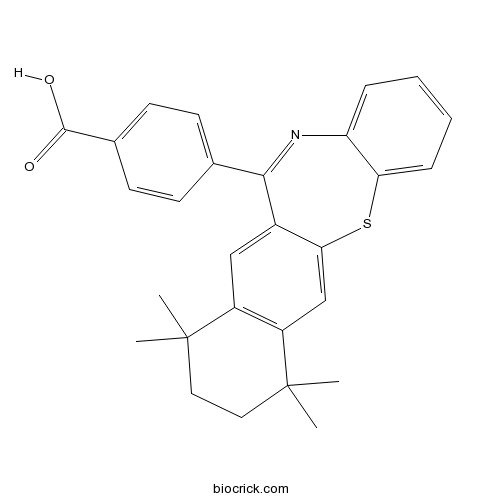
| Cas No. | 188844-52-2 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 9889522 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C28H27NO2S | M.Wt | 441.58 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | Soluble to 50 mM in DMSO | ||
| Chemical Name | 4-(7,7,10,10-tetramethyl-8,9-dihydronaphtho[2,3-b][1,5]benzothiazepin-12-yl)benzoic acid | ||
| SMILES | CC1(CCC(C2=C1C=C3C(=C2)SC4=CC=CC=C4N=C3C5=CC=C(C=C5)C(=O)O)(C)C)C | ||
| Standard InChIKey | PFGCWQPTOKPRRK-UHFFFAOYSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C28H27NO2S/c1-27(2)13-14-28(3,4)21-16-24-19(15-20(21)27)25(17-9-11-18(12-10-17)26(30)31)29-22-7-5-6-8-23(22)32-24/h5-12,15-16H,13-14H2,1-4H3,(H,30,31) | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | RXR agonist. Acts as a retinoid synergist; enhances the potency of AM 80 in a HL-60 cell differentiation assay. |

HX 630 Dilution Calculator

HX 630 Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.2646 mL | 11.323 mL | 22.646 mL | 45.2919 mL | 56.6149 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.4529 mL | 2.2646 mL | 4.5292 mL | 9.0584 mL | 11.323 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.2265 mL | 1.1323 mL | 2.2646 mL | 4.5292 mL | 5.6615 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0453 mL | 0.2265 mL | 0.4529 mL | 0.9058 mL | 1.1323 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0226 mL | 0.1132 mL | 0.2265 mL | 0.4529 mL | 0.5661 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
- HX 531
Catalog No.:BCC6082
CAS No.:188844-34-0
- Streptozotocin
Catalog No.:BCN3834
CAS No.:18883-66-4
- 8-Glucosyl-5,7-dihydroxy-2-(1-methylpropyl)chromone
Catalog No.:BCN7505
CAS No.:188818-27-1
- SC 560
Catalog No.:BCC7111
CAS No.:188817-13-2
- N-Acetylcaprolactam
Catalog No.:BCC9081
CAS No.:1888-91-1
- 4,5-Di-O-caffeoylquinic acid methyl ester
Catalog No.:BCN6492
CAS No.:188742-80-5
- 3-hydroxymorindone
Catalog No.:BCN3126
CAS No.:80368-74-7
- GSK3787
Catalog No.:BCC2263
CAS No.:188591-46-0
- Cl-4AS-1
Catalog No.:BCC7780
CAS No.:188589-66-4
- TFM-4AS-1
Catalog No.:BCC6069
CAS No.:188589-61-9
- SBI-0206965
Catalog No.:BCC3984
CAS No.:1884220-36-3
- Scandoside
Catalog No.:BCN3449
CAS No.:18842-99-4
- DMA
Catalog No.:BCC1532
CAS No.:188860-26-6
- Hydroxytanshinone IIA
Catalog No.:BCN2497
CAS No.:18887-18-8
- Methyl tanshinonate
Catalog No.:BCN2553
CAS No.:18887-19-9
- Junipediol B 8-O-glucoside
Catalog No.:BCN4022
CAS No.:188894-19-1
- L 760735
Catalog No.:BCC7840
CAS No.:188923-01-5
- Cilengitide
Catalog No.:BCC3942
CAS No.:188968-51-6
- Melilotigenin C
Catalog No.:BCN1165
CAS No.:188970-21-0
- 1-(4-Hydroxy-2,2-dimethylchroman-6-yl)ethanone
Catalog No.:BCN7710
CAS No.:1890153-71-5
- Corynantheine
Catalog No.:BCN3746
CAS No.:18904-54-6
- NGB 2904
Catalog No.:BCC7435
CAS No.:189061-11-8
- [Ala92]-p16 (84-103)
Catalog No.:BCC5837
CAS No.:189064-08-2
- Oroselol
Catalog No.:BCN3907
CAS No.:1891-25-4
Clinically potential subclasses of retinoid synergists revealed by gene expression profiling.[Pubmed:12533672]
Mol Cancer Ther. 2003 Jan;2(1):49-58.
Retinoids have chemopreventive and therapeutic potency in oncology and dermatology, although their application is restricted by many undesirable side effects. For the development of more effective and less toxic retinoids, gene expression analyses using DNA microarrays have the potential to supplement conventional screening methods, which are based on the changes in cell morphology and/or function. In this study, we applied the class prediction algorithm, which was used in the molecular phenotyping of tumors, for the classification of synthetic retinoids (Am80 and Tp80) and retinoid synergists (HX630, TZ335, and PA024) as all-trans retinoic acid-like, 9-cis retinoic acid-like, and control-like classes. By analyzing the effects of all-trans retinoic acid and 9-cis retinoic acid on the gene expressions in a human promyelocytic leukemia cell line, HL60, we successfully selected 50 marker genes whose expression pattern could distinguish these classes. Moreover, the classification revealed the existence of two subclasses among the retinoid synergists used with Am80. Close inspection of the DNA microarray analyses indicated that these two subclasses had different effects on the apoptosis of HL60 cells, and this was confirmed by in vivo experiments. These results indicate that the retinoidal activity of Am80, which has already been used in clinical trials, could be modulated differently by the two classes of retinoid synergists. Thus, these two subclasses of retinoid synergists have the potency to widen the usage of Am80. Our analyses demonstrated that the gene expression profiling could provide important information for developing useful retinoid synergists by compensating conventional screening methods.
Effect of natural and synthetic retinoids on the proliferation and differentiation of three canine melanoma cell lines.[Pubmed:11913557]
J Vet Med Sci. 2002 Feb;64(2):169-72.
The effect of two natural retinoids and synthetic retinoids with or without retinoid synergists on the proliferation and differentiation of 3 melanoma cell lines were investigated in vitro. No retinoids showed significant growth inhibitory effect on these cell lines when used alone, however, cell differentiation and significant growth inhibition were observed when treated with a combination of retinoids and a retinoid synergist. This study may suggest that, though the cells showed low susceptibilities when retinoids were treated alone, the combination of retinoids and a retinoid synergist may be effective to control the growth of canine melanoma cell lines.
Regulation of retinoidal actions by diazepinylbenzoic acids. Retinoid synergists which activate the RXR-RAR heterodimers.[Pubmed:9435893]
J Med Chem. 1997 Dec 19;40(26):4222-34.
In human HL-60 promyelocytic leukemia cells, diazepinylbenzoic acid derivatives can exhibit either antagonistic or synergistic effects on the differentiation-inducing activities of natural or synthetic retinoids, the activity depending largely on the nature of the substituents on the diazepine ring. Thus, a benzolog of the retinoid antagonist LE135 (6), 4-(13H-10,11,12,13-tetrahydro-10, 10,13,13,15-pentamethyldinaphtho[2,3-b][1,2-e]diazepin-7-yl) benzoic acid (LE540, 17), exhibits a 1 order of magnitude higher antagonistic potential than the parental LE135 (6). In contrast, 4-[5H-2,3-(2,5-dimethyl-2,5-hexano)-5-methyldibenzo[b,e] [1,4]diazepin-11-yl]-benzoic acid (HX600, 7), a structural isomer of the antagonistic LE135 (6), enhanced HL-60 cell differentiation induced by RAR agonists, such as Am80 (2). This synergistic effect was further increased for a thiazepine, HX630 (29), and an azepine derivative, HX640 (30); both synergized with Am80 (2) more potently than HX600 (7). Notably, the negative and positive effects of the azepine derivatives on retinoidal actions can be related to their RAR-antagonistic and RXR-agonistic properties, respectively, in the context of the RAR-RXR heterodimer.


