AlbendazoleCAS# 54965-21-8 |
- CX-4945 (Silmitasertib)
Catalog No.:BCC3693
CAS No.:1009820-21-6
- PA-824
Catalog No.:BCC1106
CAS No.:187235-37-6
- Celastrol
Catalog No.:BCN5986
CAS No.:34157-83-0
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 54965-21-8 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 2082 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C12H15N3O2S | M.Wt | 265.33 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | DMSO : 20 mg/mL (75.38 mM; Need ultrasonic) H2O : < 0.1 mg/mL (insoluble) | ||
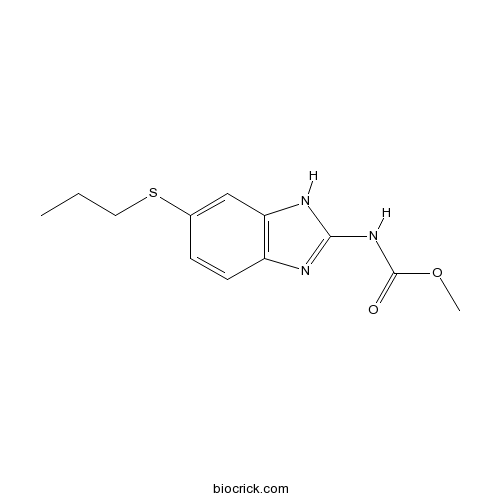
| Chemical Name | methyl N-(6-propylsulfanyl-1H-benzimidazol-2-yl)carbamate | ||
| SMILES | CCCSC1=CC2=C(C=C1)N=C(N2)NC(=O)OC | ||
| Standard InChIKey | HXHWSAZORRCQMX-UHFFFAOYSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C12H15N3O2S/c1-3-6-18-8-4-5-9-10(7-8)14-11(13-9)15-12(16)17-2/h4-5,7H,3,6H2,1-2H3,(H2,13,14,15,16) | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||

Albendazole Dilution Calculator

Albendazole Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 3.7689 mL | 18.8445 mL | 37.6889 mL | 75.3778 mL | 94.2223 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.7538 mL | 3.7689 mL | 7.5378 mL | 15.0756 mL | 18.8445 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.3769 mL | 1.8844 mL | 3.7689 mL | 7.5378 mL | 9.4222 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0754 mL | 0.3769 mL | 0.7538 mL | 1.5076 mL | 1.8844 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0377 mL | 0.1884 mL | 0.3769 mL | 0.7538 mL | 0.9422 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
Albendazole is an anthelmintic.
- Florilenalin
Catalog No.:BCN6422
CAS No.:54964-49-7
- 2-Oxopomolic acid
Catalog No.:BCN5732
CAS No.:54963-52-9
- Shikalkin
Catalog No.:BCC8359
CAS No.:54952-43-1
- Phytolaccagenic acid
Catalog No.:BCN8090
CAS No.:54928-05-1
- beta-Yohimbine
Catalog No.:BCN5733
CAS No.:549-84-8
- Quercetin 3-O-beta-D-xylopyranoside
Catalog No.:BCN2851
CAS No.:549-32-6
- 8-Oxyberberine
Catalog No.:BCN3135
CAS No.:549-21-3
- Amitriptyline HCl
Catalog No.:BCC5033
CAS No.:549-18-8
- Arborinine
Catalog No.:BCN7438
CAS No.:5489-57-6
- PD 334581
Catalog No.:BCC6300
CAS No.:548756-68-9
- Sanshodiol
Catalog No.:BCN6577
CAS No.:54854-91-0
- Protogracillin(P)
Catalog No.:BCC8352
CAS No.:54848-30-5
- Tamoxifen Citrate
Catalog No.:BCC4382
CAS No.:54965-24-1
- Physalin D
Catalog No.:BCN7919
CAS No.:54980-22-2
- Shikonin acetyl
Catalog No.:BCN2452
CAS No.:54984-93-9
- 3,3'',5-Triiodo-L-thyronine Sodium Salt
Catalog No.:BCN1419
CAS No.:55-06-1
- HYOSCINE HYDROCHLORIDE
Catalog No.:BCN8331
CAS No.:55-16-3
- Benzamide
Catalog No.:BCN5737
CAS No.:55-21-0
- Epinephrine HCl
Catalog No.:BCC4319
CAS No.:55-31-2
- McN-A 343
Catalog No.:BCC7042
CAS No.:55-45-8
- Atropine sulfate
Catalog No.:BCN2716
CAS No.:55-48-1
- 1-Phenylbiguanide hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC6870
CAS No.:55-57-2
- Hexamethonium Bromide
Catalog No.:BCC4561
CAS No.:55-97-0
- Busulfan
Catalog No.:BCC3742
CAS No.:55-98-1
Effect of 3 years of biannual mass drug administration with albendazole on lymphatic filariasis and soil-transmitted helminth infections: a community-based study in Republic of the Congo.[Pubmed:28372977]
Lancet Infect Dis. 2017 Jul;17(7):763-769.
BACKGROUND: The standard treatment strategy of mass drug administration with ivermectin plus Albendazole for lymphatic filariasis cannot be applied in central Africa, because of the risk of serious adverse events in people with high Loa loa microfilaraemia. Thus, alternative strategies are needed. We investigated one such alternative strategy for mass drug administration for elimination of lymphatic filariasis and soil-transmitted helminth infections in Republic of the Congo. METHODS: In 2012, we started a 3 year community trial of biannual mass administration of Albendazole in a village in Republic of the Congo. All volunteering inhabitants aged 2 years or older were offered Albendazole (400 mg) every 6 months. Infection with Wuchereria bancrofti was diagnosed with a rapid card immunochromatographic test for antigenaemia. People with antigenaemia were tested for microfilaraemia by night blood smears. Individuals were also tested for soil-transmitted helminth infections (ie, hookworm, Ascaris lumbricoides, Trichuris trichiura) with the Kato-Katz method. Assessment surveys were done at 12, 24, and 36 months. The main outcome measure was change in infection rates from baseline to year 3. FINDINGS: Therapeutic coverage was more than 80% in all six rounds of mass administration of Albendazole. Between 2012 and 2015, W bancrofti antigenaemia and microfilaraemia rates in the community fell significantly, from 17.3% (95% CI 14.7-20.0) to 4.7% (3.3-6.6; p<0.0001) and from 5.3% (3.9-7.1) to 0.3% (0.1-1.2; p<0.0001), respectively. The geometric mean microfilaria count in microfilaraemic people fell from 199.4 (120.4-330.5) per mL in 2012 to 39.1 (95% CIs not computed) per mL in 2015 (p=0.0095). Hookworm infection was undetectable after 1 year. Between 2012 and 2015, the number of A lumbricoides eggs expelled per g of faeces fell from 9844.6 (8209.0-11 480.0) to 724.4 (340.7-1114.2; p<0.0001), and of T trichiura eggs from 1107.4 (878.5-1336.3) to 366.0 (255.7-476.2; p<0.0001). INTERPRETATION: Our findings strongly support WHO's provisional strategy of biannual mass administration of Albendazole to eliminate lymphatic filariasis in areas where loiasis is co-endemic and ivermectin cannot be safely mass administered. FUNDING: Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation.
Exposure of Heligmosomoides polygyrus and Trichuris muris to albendazole, albendazole sulfoxide, mebendazole and oxantel pamoate in vitro and in vivo to elucidate the pathway of drug entry into these gastrointestinal nematodes.[Pubmed:28371660]
Int J Parasitol Drugs Drug Resist. 2017 Aug;7(2):159-173.
Millions of people are treated with anthelmintics to control soil-transmitted helminth infections; yet, drug distribution in the plasma and gastrointestinal tract compartments and the pathway of drug uptake into gastrointestinal nematodes responsible for the pharmacological effect are unknown. We assessed the distribution and uptake of Albendazole, Albendazole sulfoxide, Albendazole sulfone in the hookworm Heligmosomoides polygyrus in vitro and in vivo as well as the distribution and uptake of Albendazole, mebendazole, and oxantel pamoate in the whipworm Trichuris muris in vitro and in vivo. Oral and intraperitoneal treatments (100 mg/kg) were studied. Drug quantities in helminths and host compartments (stomach, the contents and mucosa of the small and large intestine, and the plasma) were determined using HPLC-UV/vis and anthelmintic activities were recorded using phenotypic readout. The influence of 1-aminobenzotriazole (ABT), an irreversible and unspecific cytochrome P450 inhibitor, on Albendazole disposition in mice harboring H. polygyrus was evaluated. In vivo, Albendazole was found in quantities up to 10 nmol per ten H. polygyrus and up to 31 nmol per ten T. muris. ABT did not change the levels of Albendazole or its metabolites in the plasma of mice harboring H. polygyrus or in H. polygyrus, whereas drug levels in the gastrointestinal tract of host mice doubled. Mebendazole and oxantel pamoate quantities per ten T. muris were as high as 21 nmol and 34 nmol, respectively. Albendazole revealed a very dynamic distribution and high rate of metabolism, hence, H. polygyrus and T. muris are exposed to Albendazole and both metabolites via multiple pathways. Diffusion through the cuticle seems to be the crucial pathway of oxantel pamoate uptake into T. muris, and likely also for mebendazole. No relationship between concentrations measured in helminths and concentrations in plasma, intestinal content and mucosa of mice, or drug efficacy was noted for any of the drugs studied.
Anthelmintic drug albendazole arrests human gastric cancer cells at the mitotic phase and induces apoptosis.[Pubmed:28352336]
Exp Ther Med. 2017 Feb;13(2):595-603.
As microtubules have a vital function in the cell cycle, oncologists have developed microtubule inhibitors capable of preventing uncontrolled cell division, as in the case of cancer. The anthelmintic drug Albendazole (ABZ) has been demonstrated to inhibit hepatocellular, ovarian and prostate cancer cells via microtubule targeting. However, its activity against human gastric cancer (GC) cells has remained to be determined. In the present study, ABZ was used to treat GC cells (MKN-45, SGC-7901 and MKN-28). A a CCK-8 cell proliferation assay was performed to assess the effects of ABZ on cell viability and cell cycle changes were assessed using flow cytometry. SGC-7901 cells were selected for further study, and flow cytometry was employed to determine the apoptotic rate, immunofluorescence analysis was employed to show changes of the microtubule structure as well as the subcellular localization and expression levels of cyclin B1, and western blot analysis was used to identify the dynamics of microtubule assembly. The expression levels of relevant proteins, including cyclin B1 and Cdc2, the two subunits of mitosis-promoting factor as well as apoptosis-asociated proteins were also assessed by western blot analysis. The results showed that ABZ exerted its anti-cancer activity in GC cell lines by disrupting microtubule formation and function to cause mitotic arrest, which is also associated with the accumulation of cyclin B1, and consequently induces apoptosis.
The effect of three-monthly albendazole treatment on Th2 responses: Differential effects on IgE and IL-5.[Pubmed:28370210]
Parasite Immunol. 2017 Jun;39(6).
Helminth parasites induce a strong Th2 response, characterized by high levels of IgE and elevated signature cytokines such as IL-5. As many global deworming programmes are underway, there is concern that this might lead to emergence of Th1-mediated pathologies when the counterbalancing helminth-induced Th2 response is absent. Therefore, we assessed the effect of deworming on Th2-mediated responses in a household-clustered randomized controlled trial in Indonesia. Total plasma IgE and whole-blood IL-5 responses to mitogen phytohaemagglutinin (PHA) were measured in 1494 and 682 subjects, respectively, at baseline, 9 and 21 months after three-monthly single-dose treatment with Albendazole or placebo. Anthelmintic treatment did not result in complete removal of helminth infections in the community. However, treatment significantly decreased IgE levels in Albendazole- compared to placebo-treated subjects. IL-5 responses to PHA were not significantly affected by anthelmintic treatment and tended to increase in Albendazole-treated subjects, indicating that intensive treatment of helminth parasites has different outcomes on B-cell (IgE levels) and T-cell (IL-5) responses. The data shows that 2 years of deworming can have differential effects on responses typified as Th2-mediated, which needs to be taken into account when examining the impact of helminths on noncommunicable diseases.


